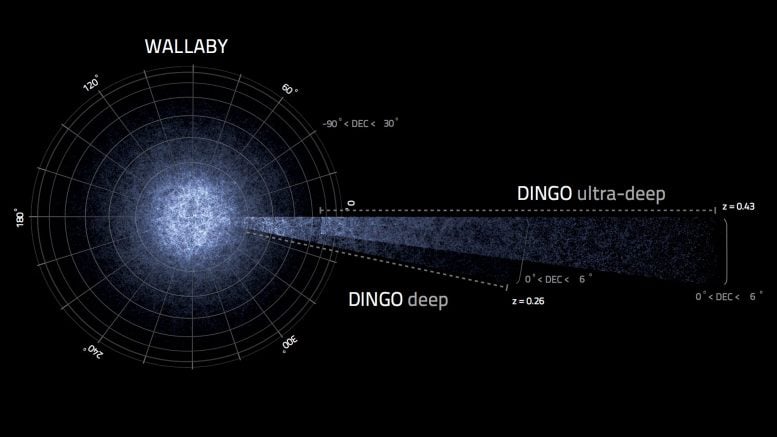
The simulated galaxies ASKAP surveys WALLABY and DINGO are predicted to find. WALLABY will survey a large portion of the sky and DINGO will survey a smaller section but in much greater detail. Credit: Derek K Gerstmann, ICRAR; Alan R. Duffy, ICRAR; Martin J. Meyer, ICRAR; Lister Staveley-Smith, ICRAR; Maksym Bernyk, Swinburne University of Technology; Darren J. Croton, Swinburne University of Technology; Barbel S. Koribalski, CSIRO; Stefan Westerlund, ICRAR and Andreas Wicenec, ICRAR
Scientists are predicting that the new ASKAP galaxy surveys, WALLABY and DINGO, will find an amazing 700,000 new galaxies, spread over trillions of cubic light years of space.
Australia’s newest radio telescope is predicted to find an unprecedented 700,000 new galaxies, say scientists planning for CSIRO’s next-generation Australian Square Kilometer Array Pathfinder (ASKAP).
In a paper to be published Sunday in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Australian researchers have combined computer simulations with ASKAP’s specifications to predict the new telescope’s extraordinary capabilities.
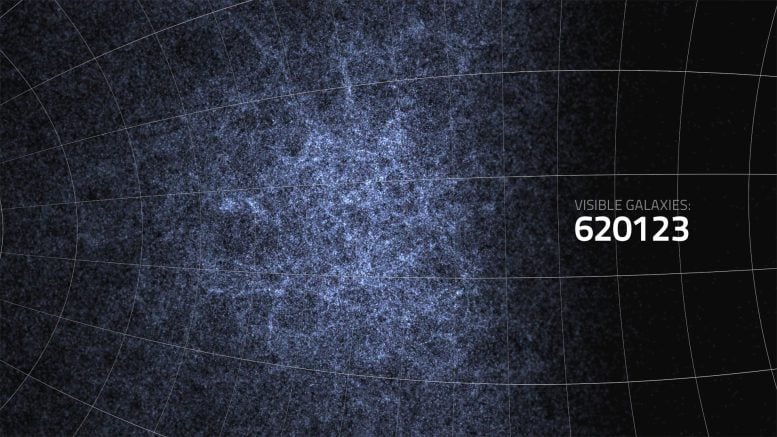

A still from the simulation fly-through video showing the galaxies WALLABY is predicted to find. Credit: Derek K Gerstmann, ICRAR; Alan R. Duffy, ICRAR; Martin J. Meyer, ICRAR; Lister Staveley-Smith, ICRAR; Maksym Bernyk, Swinburne University of Technology; Darren J. Croton, Swinburne University of Technology; Barbel S. Koribalski, CSIRO; Stefan Westerlund, ICRAR and Andreas Wicenec, ICRAR
“ASKAP is a highly capable telescope. Its surveys will find more galaxies, further away and be able to study them in more detail than any other radio telescope in the world until the SKA Is built,” said Dr. Alan Duffy from The University of Western Australia node of the International Center for Radio Astronomy Research.
“Our simulation is similar to testing a Formula 1 car in a wind tunnel before using it on the track.”
ASKAP will start scanning southern skies in 2013 as a forerunner to the massive Square Kilometer Array (SKA), which will be shared between Australia-New Zealand and Southern Africa.
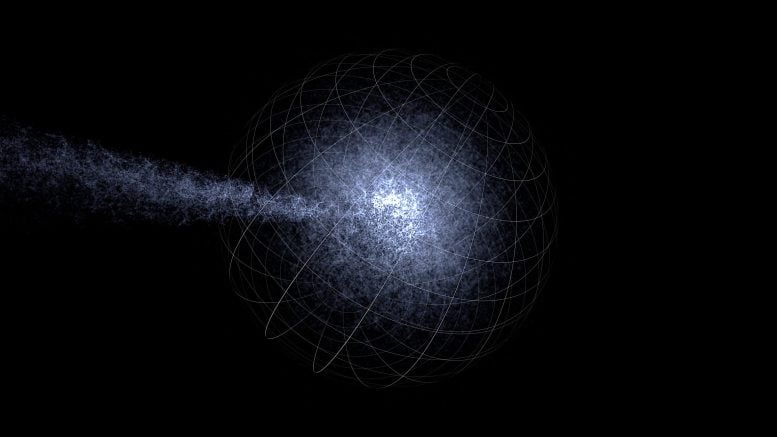

A 3 Dimensional view of the WALLABY and DINGO survey simulations. Credit: Derek K Gerstmann, ICRAR; Alan R. Duffy, ICRAR; Martin J. Meyer, ICRAR; Lister Staveley-Smith, ICRAR; Maksym Bernyk, Swinburne University of Technology; Darren J. Croton, Swinburne University of Technology; Barbel S. Koribalski, CSIRO; Stefan Westerlund, ICRAR and Andreas Wicenec, ICRAR
Dr. Duffy said two ASKAP surveys, WALLABY and DINGO, would examine galaxies to study hydrogen gas – the fuel that forms stars – and how those galaxies had changed in the last 4 billion years, allowing us to better understand how our own galaxy, the Milky Way, grew.
“We predict that WALLABY will find an amazing 600,000 new galaxies and DINGO 100,000, spread over trillions of cubic light years of space.”
Dr. Duffy said the new ASKAP galaxy surveys would also allow astronomers to probe the nature of one of astronomy’s greatest mysteries – Dark Energy.
A fly-through video of the galaxies ASKAP is expected to discover in the WALLABY and DINGO surveys.
Combining a large simulation of the Universe with new theories of galaxy formation − including the effects of supermassive black holes − had led scientists to accurately predict where as-yet undiscovered galaxies should be located, Dr. Duffy said.
“We calculated how much of the model Universe ASKAP could observe using details of the telescope’s capabilities,” said co-author Dr Baerbel Koribalski, who has recently been appointed as an Office of the Chief Executive Science Leader at the CSIRO.
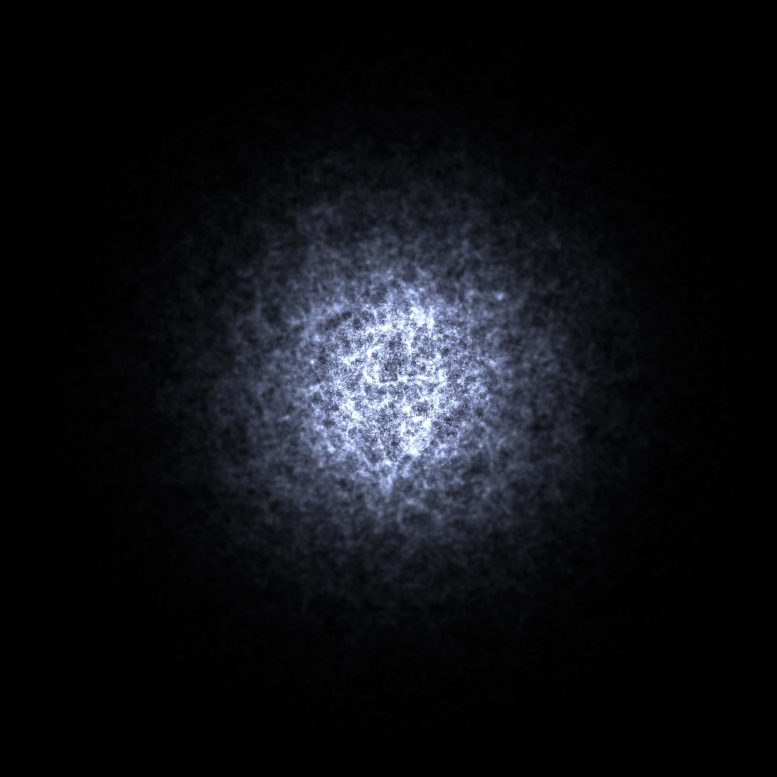

The galaxies WALLABY is predicted to discover. Credit: Derek K Gerstmann, ICRAR; Alan R. Duffy, ICRAR; Martin J. Meyer, ICRAR; Lister Staveley-Smith, ICRAR; Maksym Bernyk, Swinburne University of Technology; Darren J. Croton, Swinburne University of Technology; Barbel S. Koribalski, CSIRO; Stefan Westerlund, ICRAR and Andreas Wicenec, ICRAR
Co-author Associate Professor Darren Croton from Swinburne University of Technology also said the predictions would be used to help scientists refine how to handle the large quantity of data ASKAP will produce and test theories of galaxy formation.
“If we don’t see this many galaxies, then the Universe is strangely different to our simulations,” Associate Professor Croton said.
ASKAP will become part of the world’s largest telescope – the SKA.
Reference: “Predictions for ASKAP neutral hydrogen surveys” by Alan R. Duffy, Martin J. Meyer, Lister Staveley-Smith, Maksym Bernyk, Darren J. Croton, Bärbel S. Koribalski, Derek Gerstmann and Stefan Westerlund, 11 November 2012, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21987.x
ICRAR is a joint venture between Curtin University and The University of Western Australia providing research excellence in the field of radio astronomy.








Be the first to comment on "ASKAP Telescope Predicted to Find 700,000 New Galaxies"