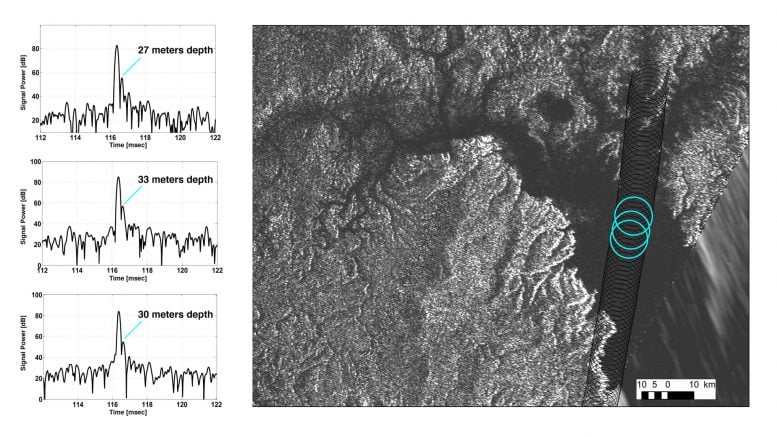
Cassini radar data reveal the depth of a liquid methane/ethane sea on Saturn’s moon Titan near the mouth of a large, flooded river valley. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASI/Cornell
During a recent flyby, the Cassini spacecraft observed new, bright features in the seas that might be related to the mysterious feature that researchers dubbed the “magic island.”
NASA’s Cassini mission continues its adventures in extraterrestrial oceanography with new findings about the hydrocarbon seas on Saturn’s moon Titan.
The findings are being presented this week at the Division for Planetary Sciences Meeting of the American Astronomical Society held in Tucson, Arizona.
To the delight of Cassini scientists, two new bright features appeared in Titan’s largest sea, Kraken Mare, during the August 21 flyby. In contrast to a previously reported bright, mystery feature in another of Titan’s large seas, Ligeia Mare, the new features in Kraken Mare were observed in both radar data and images from Cassini’s Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS). Having observations at two different wavelengths provides researchers with important clues to the nature of these enigmatic objects
The VIMS data suggest the new features might have similarities to places in and around the seas that the Cassini team has interpreted as waves or wet ground. The observations support two of the possible explanations the team thinks are most likely – that the features might be waves or floating debris.
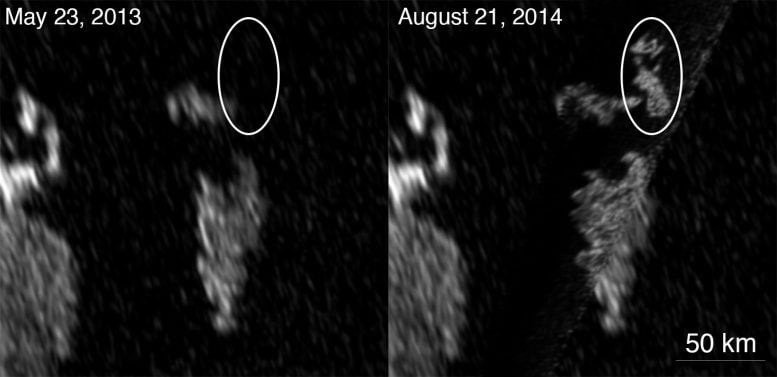
Cassini’s radar instrument images show that a bright feature appeared in Kraken Mare, Titan’s largest sea. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASI/Cornell
Unfortunately for mystery lovers, the August Titan flyby marked the final opportunity for Cassini’s radar to observe Kraken Mare. However, the spacecraft is scheduled to observe the original “magic island” feature in Ligeia Mare once more, in January 2015.
The August Titan flyby also included a segment designed to collect altimetry (or height) data, using the spacecraft’s radar instrument along a 120-mile (200-kilometer) shore-to-shore track of Kraken Mare. For a 25-mile (40-kilometer) segment of this data along the sea’s eastern shoreline, Cassini’s radar beam bounced off the sea bottom and back to the spacecraft, revealing the sea’s depth in that area. This region, which is near the mouth of a large, flooded river valley, showed depths of 66 to 115 feet (20 to 35 meters). Cassini will perform this experiment one last time in January 2015, to try to measure the depth of Punga Mare. Punga Mare is the smallest of three large seas in Titan’s far north, and the only sea whose depth has not been observed by Cassini.
Scientists think that, for the areas in which Cassini did not observe a radar echo from the seafloor, Kraken Mare might be too deep for the radar beam to penetrate. Alternatively, the signal over this region might simply have been absorbed by the liquid, which is mostly methane and ethane. The altimetry data for the area in and around Kraken Mare also showed relatively steep slopes leading down to the sea, which also suggests the Kraken Mare might indeed be quite deep.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Italian Space Agency. JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The VIMS team is based at the University of Arizona in Tucson. The radar instrument was built by JPL and the Italian Space Agency, working with team members from the US and several European countries.






Be the first to comment on "Cassini Spots a Bright Feature in Titan’s Largest Sea, Kraken Mare"