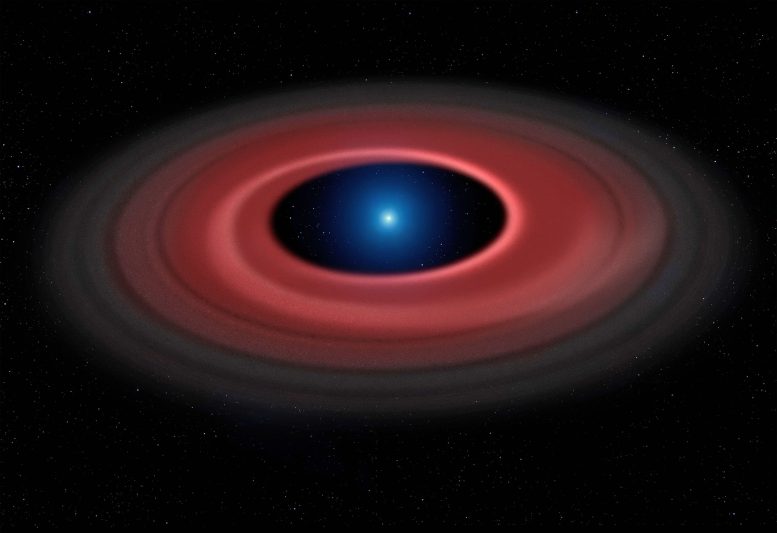

This artist’s impression shows how an asteroid torn apart by the strong gravity of a white dwarf has formed a ring of dust particles and debris orbiting the Earth-sized burnt out stellar core SDSS J1228+1040. Gas produced by collisions within the disc is detected in observations obtained over twelve years with ESO’s Very Large Telescope, and reveal a narrow glowing arc. Credit: Mark Garlick and University of Warwick/ESO
Using the Very Large Telescope, an international team of astronomers has studied in detail for the first time the remains of a fatal interaction between a dead star and an asteroid. This gives a glimpse of the far-future fate of the Solar System.
Led by Christopher Manser, a Ph.D. student at the University of Warwick in the United Kingdom, the team used data from ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and other observatories to study the shattered remains of an asteroid around a stellar remnant — a white dwarf called SDSS J1228+1040.
Using several instruments, including the Ultraviolet and Visual Echelle Spectrograph (UVES) and X-shooter, both attached to the VLT, the team obtained detailed observations of the light coming from the white dwarf and its surrounding material over an unprecedented period of twelve years between 2003 and 2015. Observations over periods of years were needed to probe the system from multiple viewpoints.
“The image we get from the processed data shows us that these systems are truly disc-like, and reveals many structures that we cannot detect in a single snapshot,” explained lead author Christopher Manser.
The team used a technique called Doppler tomography — similar in principle to medical tomographic scans of the human body — which allowed them to map out in detail the structure of the glowing gaseous remains of the dead star’s meal orbiting J1228+1040 for the first time.
Artist’s impression of the glowing disc of material around the white dwarf SDSS J1228+1040
While large stars — those more massive than around ten times the mass of the Sun — suffer a spectacularly violent climax as a supernova explosion at the ends of their lives, smaller stars are spared such dramatic fates. When stars like the Sun come to the ends of their lives they exhaust their fuel, expand as red giants and later expel their outer layers into space. The hot and very dense core of the former star — a white dwarf — is all that remains.
But would the planets, asteroids, and other bodies in such a system survive this trial by fire? What would be left? The new observations help to answer these questions.
It is rare for white dwarfs to be surrounded by orbiting discs of gaseous material — only seven have ever been found. The team concluded that an asteroid had strayed dangerously close to the dead star and been ripped apart by the immense tidal forces it experienced to form the disc of material that is now visible.
The orbiting disc was formed in similar ways to the photogenic rings seen around planets closer to home, such as Saturn. However, while J1228+1040 is more than seven times smaller in diameter than the ringed planet, it has a mass over 2500 times greater. The team learned that the distance between the white dwarf and its disc is also quite different — Saturn and its rings could comfortably sit in the gap between them.
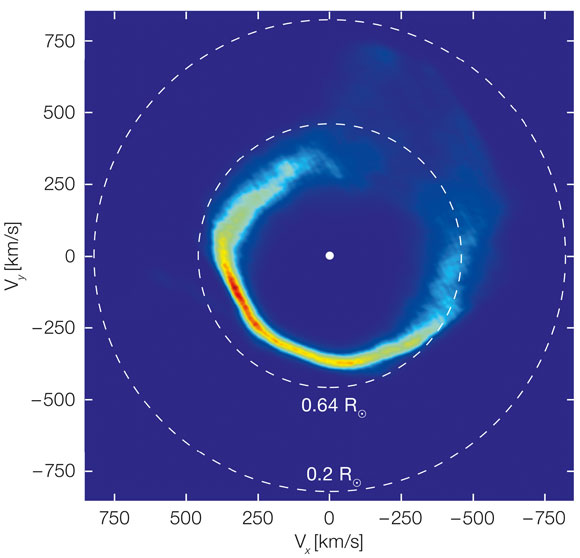
This plot is an unusual type of image, showing the velocities of the gas in the disc around the white dwarf SDSS J1228+1040, rather than its position. It was mapped out from Very Large Telescope observations over a period of twelve years and by applying a method called Doppler tomography. The dashed circles correspond to material in circular orbits at two different distances from the star. This appears “inside out” because material moves faster in close-in orbits. Credit: University of Warwick/C. Manser/ESO
The new long-term study with the VLT has now allowed the team to watch the disc precess under the influence of the very strong gravitational field of the white dwarf. They also find that the disc is somewhat lopsided and has not yet become circular.
“When we discovered this debris disc orbiting the white dwarf back in 2006, we could not have imagined the exquisite details that are now visible in this image, constructed from twelve years of data — it was definitely worth the wait,” added Boris Gänsicke, a co-author of the study.
Remnants such as J1228+1040 can provide key clues to understanding the environments that exist as stars reach the ends of their lives. This can help astronomers to understand the processes that occur in exoplanetary systems and even forecast the fate of the Solar System when the Sun meets its demise in about seven billion years.
Reference: “Doppler-imaging of the planetary debris disc at the white dwarf SDSS J122859.93+104032.9” by Christopher J. Manser, Boris T. Gaensicke, Thomas R. Marsh, Dimitri Veras, Detlev Koester, Elmé Breedt, Anna F. Pala, Steven G. Parsons and John Southworth, 6 November 2015, MNRAS.
DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stv2603
arXiv:1511.02230





Be the first to comment on "VLT Maps Out the Shattered Remains of an Asteroid Around a White Dwarf"