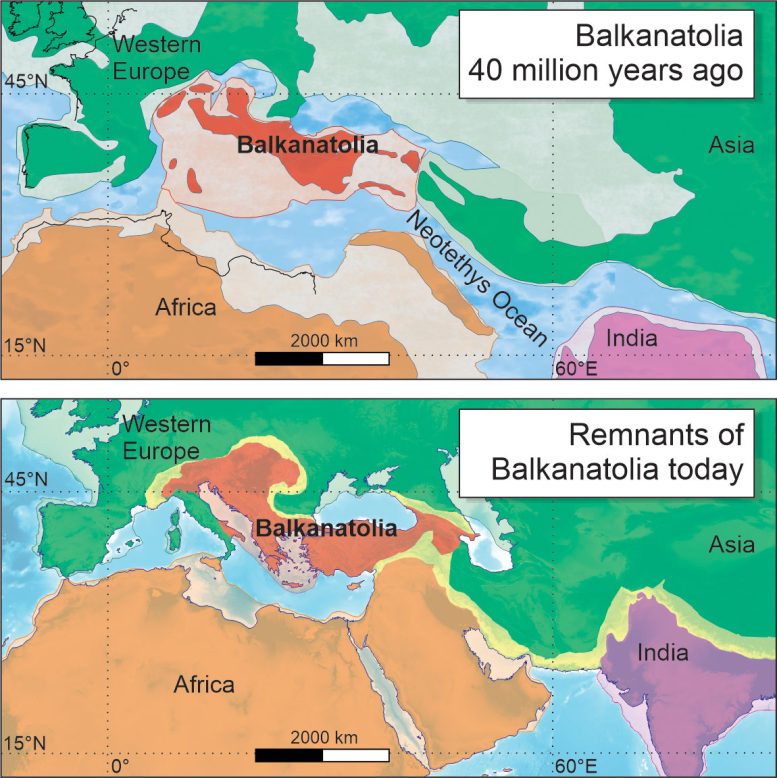
Map showing Balkanatolia 40 million years ago and at the present day. Balkanatolia is a forgotten low-lying continent wedged between Europe, Africa, and Asia, already in existence 50 million years ago and home to a unique fauna. Geographical changes 40 to 34 million years ago connected this continent to its two Eurasian neighbors, paving the way for the replacement of European mammals by Asian mammals. Credit: © Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais
Balkanatolia: The Forgotten Continent That Sheds Light on the Evolution of Mammals
- A team of geologists and paleontologists has discovered that, some 50 million years ago, there was a low-lying continent separating Europe from Asia that they have named Balkanatolia.
- At the time, it was inhabited by an endemic fauna that was very different from those of Europe and Asia.
- Geographical changes 40 to 34 million years ago connected this continent to its two neighbors, paving the way for the replacement of European mammals by Asian mammals.
A team of French, American, and Turkish paleontologists and geologists led by CNRS researchers[1] has discovered the existence of a forgotten continent they have dubbed Balkanatolia, which today covers the present-day Balkans and Anatolia. Formerly inhabited by a highly specific fauna, they believe that it enabled mammals from Asia to colonize Europe 34 million years ago. Their findings are published in the March 2022 volume of Earth-Science Reviews.
For millions of years during the Eocene Epoch (55 to 34 million years ago), Western Europe and Eastern Asia formed two distinct landmasses with very different mammalian faunas: European forests were home to endemic fauna such as Palaeotheres (an extinct group distantly related to present-day horses, but more like today’s tapirs), whereas Asia was populated by a more diverse fauna including the mammal families found today on both continents.
We know that, around 34 million years ago, Western Europe was colonized by Asian species, leading to a major renewal of vertebrate fauna and the extinction of its endemic mammals, a sudden event called the ‘Grande Coupure’. Surprisingly, fossils found in the Balkans point to the presence of Asian mammals in southern Europe long before the Grande Coupure, suggesting earlier colonization.
Now, a team led by CNRS researchers has come up with an explanation for this paradox. To do this, they reviewed earlier palaeontological discoveries, some of which date back to the 19th century, sometimes reassessing their dating in the light of current geological data. The review revealed that, for much of the Eocene, the region corresponding to the present-day Balkans and Anatolia was home to a terrestrial fauna that was homogeneous, but distinct from those of Europe and eastern Asia. This exotic fauna included, for example, marsupials of South American affinity and Embrithopoda (large herbivorous mammals resembling hippopotamuses) formerly found in Africa. The region must therefore have made up a single landmass, separated from the neighboring continents.
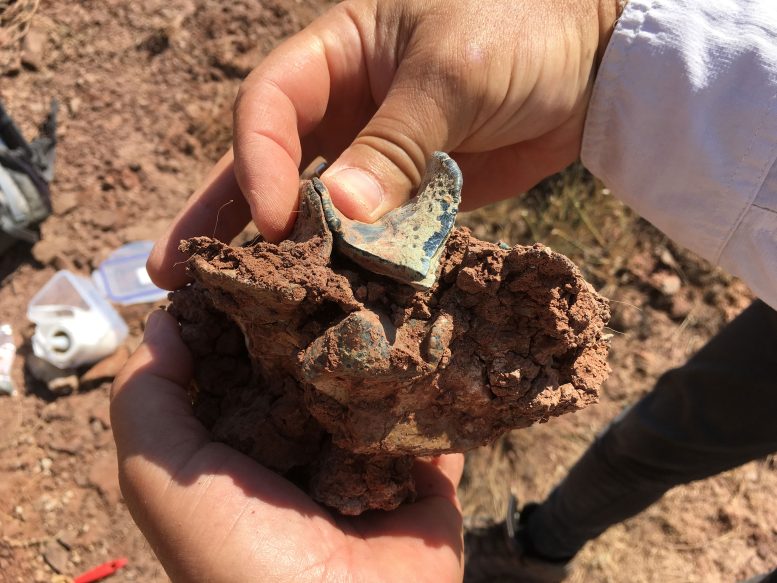

Upper molar of a Brontothere mammal of Asian origin. Alexis Licht et al. discovered a new fossil deposit in Turkey (Büyükteflek) dating from 38 to 35 million years ago, which yielded mammals whose affinity was clearly Asian, and are the earliest discovered in Anatolia until now. They found jaw fragments belonging to Brontotheres, animals resembling large rhinoceroses that died out at the end of the Eocene. Credit: © Alexis Licht & Grégoire Métais
The team also discovered a new fossil deposit in Turkey (Büyükteflek) dating from 38 to 35 million years ago, which yielded mammals whose affinity was clearly Asian, and are the earliest discovered in Anatolia until now. They found jaw fragments belonging to Brontotheres, animals resembling large rhinoceroses that died out at the end of the Eocene.
All this information enabled the team to outline the history of this third Eurasian continent, wedged between Europe, Africa, and Asia, which they dubbed Balkanatolia. The continent, already in existence 50 million years ago[2] and home to a unique fauna, was colonized 40 million years ago by Asian mammals as a result of geographical changes that have yet to be fully understood. It seems likely that a major glaciation 34 million years ago, leading to the formation of the Antarctic ice sheet and lowering sea levels, connected Balkanatolia to Western Europe, giving rise to the ‘Grande Coupure’.
Notes
- Working at the Centre for Research and Teaching in Environmental Geoscience (CNRS/Aix-Marseille Université/IRD/INRAE) and at the Centre for Research on Palaeontology – Paris (CNRS/Museum national d’Histoire naturelle/Sorbonne Université). Another French laboratory, Geosciences Rennes (CNRS/Université Rennes 1) also contributed to this study, along with Kütahya Dumlupınar and Eskişehir Osmangazi Universities (Turkey) and the universities of Washington, Connecticut, Kansas and Chicago (USA).
- Balkanatolia may be a relic of Greater Adria, another of the Mediterranean region’s ‘forgotten continents’, formed over 200 million years ago, and brought to light by reconstructions of the location of tectonic plates carried out by Douwe van Hinsbergen et al. and published in a 2019 paper.
Reference: “Balkanatolia: The insular mammalian biogeographic province that partly paved the way to the Grande Coupure” by Alexis Licht, Grégoire Métais, Pauline Coster, Deniz İbilioğlu, Faruk Ocakoğlu, Jan Westerweel, Megan Mueller, Clay Campbell, Spencer Mattingly, Melissa C. Wood and K. Christopher Beard, 21 January 2022, Earth-Science Reviews.
DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103929







Lets start at the Jurassic 220,000,000
Them there alps are formed not shown in your montage
are these low lying plains or mountain ranges at the Jurassic start
50,000,000
Balkanatolia/greater adria in existence forgotten low lying continent remnants in Greece and north Italy today 2022
Are the alps of western Europe formed already by now looking at your map i cant tell if its on the western Europe plate or the balkanatolia/greater adria plate
66,000,000
Scotland eire shear away from northern continent bringing western Europe withb them
40,000,000
Western Europe
Balkanatolia/greater adria in existence forgotten low lying continent remnants in Greece and north Italy today 2022
Neotethys ocean
Africa
Is balkanatolia the alp mountain range and if it is now it aint in western Europe according to your map
13,665,000,000 anno universo = 35,000,000 annual years ago eocene oligocene event 35,000,000 Siberia Popigon 100 kilometre crater impact
russia northern siberia taymyr peninsula 71 39 n 111.11 e popigia asteroid 5 to 8 kilometres impact causing 100 kilometre crater which wiped out many marine species the seventh largest impact crater identified on earth this flash formation of heat and pressure converted flakes of graphite in the archean graphite garnet gneiss into diamond 2mm in size suitable for abrasives
13,665,000,000 anno universo = 35,000,000 annual years ago late Eocene toms canyon impact crater struck the Atlantic continental shelf about 100 miles east of atlanti city new jersey the submarine canyon is the drowned glacial age mouth of toms river a glancing angle impact forming a long oval crater 200 miles 320 kilometres to the north east of of Chesapeake bay impact crater
13,665,000,000 anno universo = 35,000,000 annual years ago
united states virginia chesapeake bay 40 kilometre impact crater 37 17 n 76 1 w
the largest known impact crater in the usa and the 15th largest on earth
cape Charles central crater
Hampton annular trough
largest impact crater in the usa buried for 35 million years about 35 million years ago an asteroid hit the ocean off the east coast of north America its impact formed a 25 mile wide diameter crater that now lies buried beneath the Chesapeake bay an estuary in virginia and Maryland from this impact the nearby areas experienced fires earthquakes falling molten glass droplets an air blast and a devastating tsunami
when the asteroid hit it also produced an impact ejecta layer which includes tektites natural glass formed from debris during meteorite impacts and shocked zircon crystals which were thrown out of the impact area and it becomes known as the north American tektite strewn field which covers a region of about roughly 4 million square miles about 10 times the size of Texas some ejecta landed on land while the rest immediately cooled on contact with seawater and then sank to the ocean floor
uranium thorium helium technique samples from site 1073 400 kilometres 250 miles northeast of the impact site in the atlantic ocean
zircon crystals zirconium silicates preserve shock metamorphism caused by shock pressures and high temperatures
Chesapeak bay 36 kilometres crater impact
34,000,000 antarctic ice sheet and lowering sea levels
Grand coupoure extinction of its endemic mammals western Europe
Could one of them there impact craters be recalibrated by one million years to around this time
13,672,000,000 anno universo = 28,000,000 annual years ago sin sceal eile fado fado long long ago the landmass tectonic plate of spain docks and locks between the occident atlas mountains of african ham and the european plate of france and bolted in it causes the suture line and the pyrennes mountain range in spain and france
The doorstop effect keeping Africa and Europe ajar
and the fault lines of occident europe begin to realign themselves to centre on the orient lands of the fertile cresent of the middle east where the front rows scrum down north east african rift ham springboks versus
adria plate in the way
anatolian plate south of instanbul
the north anatolian fault separates both playing sides versus
eurasia the palestine philistine goliath giants who will give way first who will be driven backwards who will collapse the rolling maul who will drive the opposition into the ground under their power who might be submerged macconnee maccuaishla maccushla wait and see and tell me oer the waves i wait to hear your snarl and growling turn to yelping and barking across the white horse foamed waves macconnee come here beside me maccuaishla dont frisk your body down and spray me maccushla with your ocean foam all oer me lie down beside me and bide a while wag that tail of yours and hesst wheest listen to erins tale are we there yet are we there yet no we are not there yet wait another while shsst hisst hesst sheest listen and wait awhile more
hest Africa is now subducting the Mediterranean plate and the axis of tectonic alignment is torqueing again eastwards thanks to that door jamb of spain and the pyrennes
A FORGOTTEN place had to be known at some point. You might could say LOST but that even implies that someone knew where it was. Humans weren’t even a species when this was a place. A woolly rhino might have known about. A proto-whale perhaps. But not a human.