- Astronomers recently found the fastest spinning and possibly the youngest magnetar yet.
- J1818.0-1607 is located about 21,000 light-years away in the Milky Way galaxy.
- Magnetars are a special class of neutron stars with extremely powerful magnetic fields.
- Researchers needed Chandra and other telescopes to learn about this unusual object.
In 2020, astronomers added a new member to an exclusive family of exotic stars, with the discovery of a magnetar.
Magnetars are a type of neutron star, which are incredibly dense objects mainly made up of densely packed neutrons. They form from the collapsed core of a massive star during a supernova. What sets magnetars apart from the rest of their intriguing stellar clan is that they also have the most powerful known magnetic fields in the universe.
On March 12, 2020, astronomers detected a new magnetar with NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Telescope. After follow-up observations, researchers determined that this object, dubbed Swift J1818.0-1607 or J1818 for short, was special for a couple more reasons.
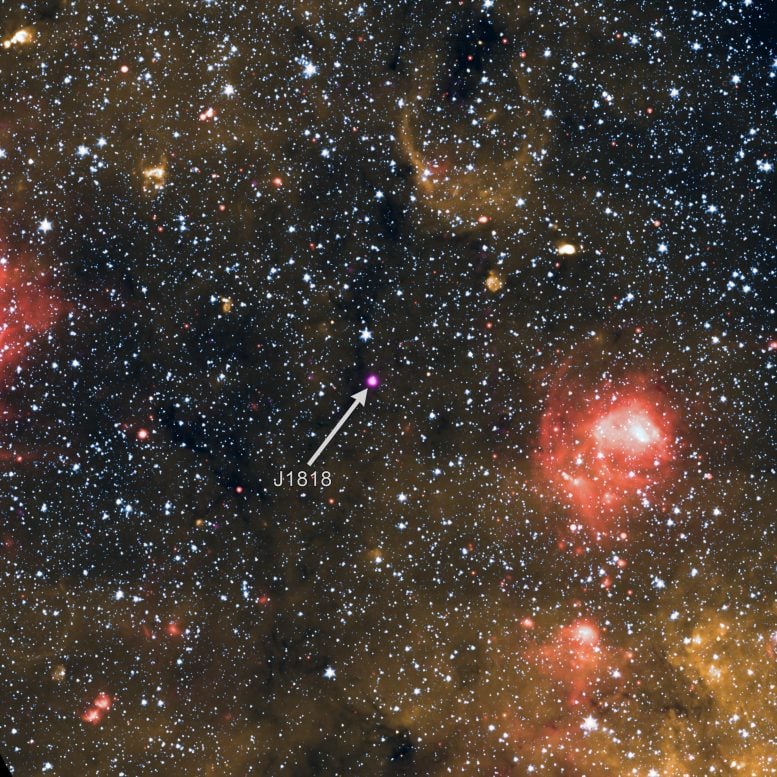

This image contains an exceptional magnetar, a type of neutron star with very powerful magnetic fields. Astronomers have found evidence that this object may be the youngest known magnetar (about 500 years old in Earth’s timeframe). It is also the fastest rotating one yet discovered (spinning about 1.4 times per second). This image shows the magnetar in X-rays from Chandra (purple) at the center of the image in combination with Spitzer and WISE infrared data showing the wider field of view. Magnetars form when a massive star runs out of nuclear fuel and its core collapses onto itself. Credit X-ray: NASA/CXC/University of West Virginia/H. Blumer; Infrared (Spitzer and Wise): NASA/JPL-Caltech/Spitzer
First, it may be the youngest known magnetar with an age estimated to be about 500 years old. Secondly, it also spins faster than any previously discovered magnetar, rotating once around every 1.4 seconds.
Observations with NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory of J1818 less than a month after the discovery with Swift gave astronomers the first high-resolution view of this object in X-rays. The Chandra data revealed a point source where the magnetar was located. This is surrounded by diffuse X-ray emission, likely caused by X-rays reflecting off dust located in its vicinity.
Astronomers expect that the explosion that created a magnetar of this age would have left behind a debris field, known as a supernova remnant. To search for this supernova remnant, a team of researchers looked at the X-rays from Chandra, infrared data from Spitzer, and radio data from the NSF’s Karl Jansky Very Large Array, or VLA. They may have found evidence for part of the remnant with the Spitzer and VLA data, but it is a relatively large distance away from the magnetar. In order to cover this distance the magnetar would need to have traveled at speeds far exceeding those of the fastest known neutron stars, even assuming it is much older than expected, which would allow more travel time.
Regardless, J1818 is only the 31st known magnetar, out of the approximately 3,000 known neutron stars. This means astronomers will continue to study it and its fellow magnetars as they strive to learn more about these extraordinary members of the cosmic family.
Read Chandra Studies Extraordinary Magnetar for more on this research.
Reference: “Chandra Observations of the Newly Discovered Magnetar Swift J1818.0–1607” by Harsha Blumer and Samar Safi-Harb, 26 November 2020, The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/abc6a2
arXiv: 2011.00324









Be the first to comment on "Chandra X-ray Observatory Studies Extraordinary Magnetar [Video]"