Today the Hamburg-based Cluster of Excellence “Climate, Climatic Change, and Society” (CLICCS) publishes a new, essential study on climate futures. The study represents the first systematic attempt to investigate whether a climate future with net-zero carbon emissions is not only possible but also plausible. The authors examine plausibility from a technical-economic perspective, but also with regard to the societal changes necessary for such a future. They conclude that deep decarbonization by 2050 is currently not plausible – the current efforts to bring about societal transformation need to be far more ambitious.
The European Union is now increasing the ambition of its climate goals, and the German Federal Constitutional Court has recently committed Germany to implementing more ambitious climate action. So, are we already on the path to a climate-neutral future? “Which climate futures are plausible is not only a physical question, it is at present especially a social one,” says CLICCS Speaker Prof. Detlef Stammer from Universität Hamburg. “In the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook we investigate the transformative power of social processes and have developed a completely new method for doing so. We’ll then combine the outcomes with findings from the natural sciences, allowing us to narrow down, step by step, what’s plausible.”
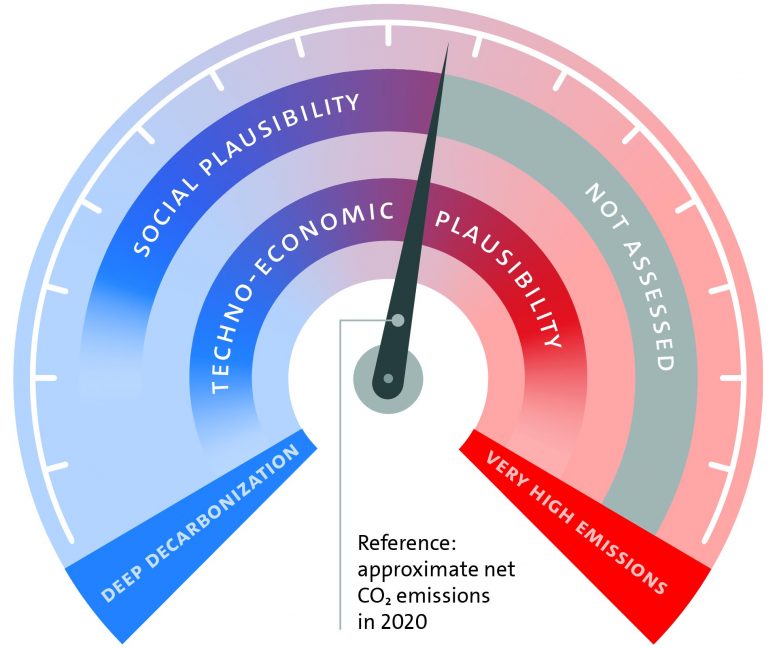
The speedometer shows the wide range of possible emissions in the year 2050 as described in existing emissions scenarios. Emissions could reach net-zero by 2050 (deep decarbonization) or could increase up to a doubling of current emissions (very high emissions). Approximate emissions in 2020 are indicated by the speedometer needle. Here we find a reduced range of plausible emissions scenarios, supported by a techno-economic plausibility assessment (Chapter 3) and a social plausibility assessment (Chapter 5), indicated by the shaded bands. Increasing emissions are not yet considered in the social plausibility assessment (gray band). Credit: University of Hamburg
The key factors being explored, also referred to as social drivers, include: United Nations’ climate policy, national climate legislation, protests and social movements, divesting from fossil fuel industries, and media coverage. Crucially, none of the ten social drivers assessed in the Outlook appear to have enough momentum to reach deep decarbonization by 2050. Yet reaching deep decarbonization by mid-century is vital if the climate targets laid out in the Paris Agreement are to be achieved.
However, six of the drivers could foster a gradual decarbonization: “The majority of the factors we evaluated certainly support the net-zero goal. For example, the factor ‘climate policy’ has been strengthened by the USA’s reentry into the Paris Agreement,” explains Prof. Anita Engels, a social scientist at Universität Hamburg and CLICCS Co-Chair. “At the same time, the extent to which climate protests can continue to put pressure on governments after COVID-19 will be an important aspect.” Another crucial driver is the divestment from fossil fuels. However, companies often operate under long investment cycles, which means the effects will only become apparent down the road.
The authors concluded that, at the moment, neither high-emissions nor low-emissions scenarios are plausible: “Studies show that very high CO2 emissions can produce tremendous economic costs. What’s more: global coal reserves are finite, and clean energy is becoming more affordable. As such, governments and companies alike will be forced to change course,” says CLICCS Co-Chair Prof. Jochem Marotzke from the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology. However, we’re still lacking the technologies needed for the rapid and large-scale removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere – an essential prerequisite for cutting emissions to net zero.
The authors further translated these findings about plausible emissions into an assessment of long-term warming, by incorporating the latest research on how CO2 emissions affect the climate: “Our results imply that global surface warming of less than 1.7 degrees Celsius (3.1 degrees Fahrenheit) by the year 2100 is not plausible, but nor is a rise of more than 4.9 degrees (8.8 degrees Fahrenheit).”
The Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook fills an important gap. Other studies-like the IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C (2.7°F) and the United Nations Emissions Gap Report-also assess which pathways might achieve the goals laid out in the Paris Agreement, but they focus more on the technical and practical requirements. “The Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook analyzes which social drivers can enable and motivate the change. We’re using this new analytical framework to systematically assess the available data with regard to the necessary decarbonization,” said Prof. Engels.
The study’s analytical approach is unique: “In the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook, we’re not looking into what would be necessary, feasible or desirable. We’re analyzing which climate futures are plausible – and which ones aren’t,” says Prof. Marotzke, who was also one of the key contributors to the upcoming IPCC report. “The social challenge is far greater than many people can imagine,” concludes Prof. Stammer. “As such, our findings represent a wake-up call for the political community and society at large.”
Reference: “Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook: Assessing the plausibility of deep decarbonization by 2050” by Stammer, Detlef; Engels, Anita; Marotzke, Jochem; Gresse, Eduardo; Hedemann, Christopher; Petzold, Jan; Held, Hermann; Aykut, Stefan; Li, Chao; Schneider, Uwe; Ratter, Beate; Oßenbrügge, Jürgen; Fröhle, Peter; Köhl, Michael; Wiener, Antje; Bassen, Alexander; Beyer, Jürgen; Brüggemann, Michael; Busch, Timo; d’Amico, Emilie; Frisch, Thomas; Guenther, Lars; Jarke-Neuert, Johannes; Johnson, Matthew; Lange, Andreas; Pavenstädt, Christopher; Perino, Grischa; Sander, Junis; Scheffran, Jürgen; Schenuit, Felix; Wickel, Martin; Wilkens, Jan; Zengerling, Cathrin; Neuburger, Martina; Datchoua-Tirvaudey, Alvine; Schnegg, Michael; Notz, Dirk; Lüdemann, Jana; Schmitt, Tobias; Singer, Katrin; Milinski, Sebastian; Suarez-Gutierrez, Laura; Gresse, Eduardo; Hedemann, Christopher; Petzold, Jan; Held, Hermann; Aykut, Stefan; Li, Chao; Schneider, Uwe; Ratter, Beate; Oßenbrügge, Jürgen; Fröhle, Peter; Köhl, Michael; Wiener, Antje; Bassen, Alexander; Beyer, Jürgen; Brüggemann, Michael; Busch, Timo; d’Amico, Emilie; Frisch, Thomas; Guenther, Lars; Jarke-Neuert, Johannes; Johnson, Matthew; Lange, Andres; Pavenstädt, Christopher; Perino, Grischa; Sander, Junis; Scheffran, Jürgen; Schenuit, Felix; Wickel, Martin; Wilkens, Jan; Zengerling, Cathrin; Neuburger, Martina; Datchoua-Tirvaudey, Alvine; Schnegg, Michael; Notz, Dirk; Lüdemann, Jana; Schmitt, Tobias; Singer, Katrin; Milinski, Sebastian and Suarez-Gutierrez, Laura, 9 June 2021.
DOI: 10.25592/uhhfdm.9104
About the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook:
More than 40 researchers from the Cluster of Excellence CLICCS are contributing authors of the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook. They hail from such diverse disciplines as the natural sciences, social sciences, economics and law. In addition, there are ca. 20 national and international reviewers. With the development of the Social Plausibility Assessment Framework, the Cluster has introduced a new scientific method for both assessing the status quo of social drivers and projecting their future trajectory.
From 2021 onwards, the Hamburg Climate Futures Outlook will be released annually. It analyzes both physical and social dynamics alike, and evaluates which climate futures are not only possible but also plausible.
The Cluster of Excellence Climate, Climatic Change, and Society (CLICCS) at Universität Hamburg is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG). Based at the Center for Earth System Research and Sustainability (CEN) at Universität Hamburg, it works in close cooperation with eleven partner institutes, including the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology in Hamburg, the Helmholtz Centre Hereon and the German Climate Computing Center.











I hope some people get arrested when the majority of the population realizes that the climate models are wrong and governments are basically stealing from citizens because you could have energy 3x as cheap in some countries.
Renewable energy is not that renewable and is not carbon neutral either, proper disposal of end of life infrastructures doesn’t exist, this is a well known fact.
You have to ask that if this was indeed a green agenda they would be speaking about pollution and promoting efficient consumption of resources… but no it’s all out invest and produce tons of new infrastructure and destroy the ones in place.