
After a massive seven-year Australian-led astronomy research project, the intricate mechanics governing the rotation, growth, clustering, and demise of galaxies have been unveiled with the release of comprehensive data.
Completion of the Australian-led astronomy project sheds light on the evolution of the Universe.
The complex mechanics determining how galaxies spin, grow, cluster and die have been revealed following the release of all the data gathered during a massive seven-year Australian-led astronomy research project.
The scientists observed 13 galaxies at a time, building to a total of 3068, using a custom-built instrument called the Sydney-AAO Multi-Object Integral-Field Spectrograph (SAMI), connected to the 4-meter Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) at Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales. The telescope is operated by the Australian National University.
Overseen by the ARC Center of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics in 3 Dimensions (ASTRO 3D), the project used bundles of optical fibers to capture and analyze bands of colors, or spectra, at multiple points in each galaxy.
The results allowed astronomers from around the world to explore how these galaxies interacted with each other, and how they grew, sped up, or slowed down over time.
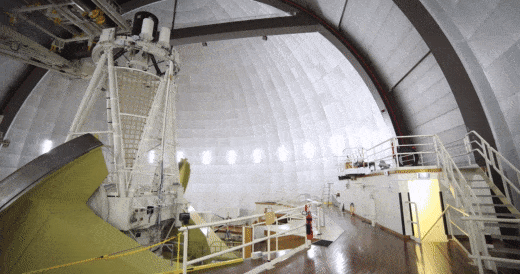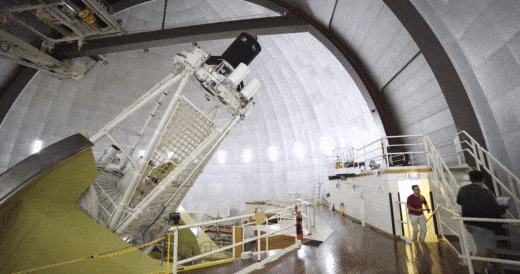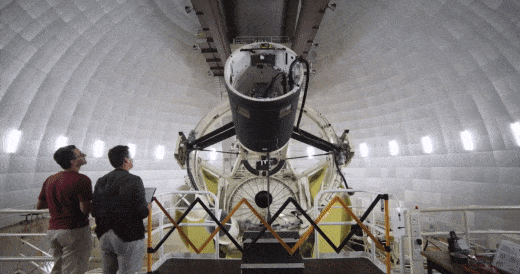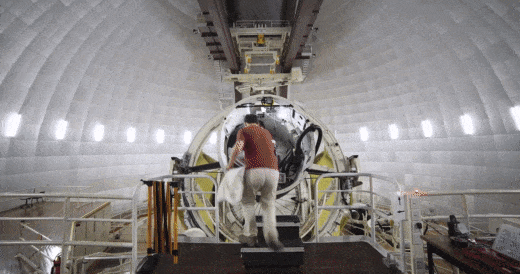
The SAMI instrument inside the Anglo Australian Telescope being readied for action. Credit: Ángel R. López-Sánchez (AAO-MQ)
No two galaxies are alike. They have different bulges, haloes, disks, and rings. Some are forming new generations of stars, while others haven’t done so for billions of years. And there are powerful feedback loops in them fuelled by supermassive black holes.
“The SAMI survey lets us see the actual internal structures of galaxies, and the results have been surprising,” said lead author Professor Scott Croom from ASTRO 3D and the University of Sydney.
“The sheer size of the SAMI Survey lets us identify similarities as well as differences, so we can move closer to understanding the forces that affect the fortunes of galaxies over their very long lives.”
The survey, which began in 2013, has already formed the basis of dozens of astronomy papers, with several more in preparation. A paper describing the final data release — including, for the first time, details of 888 galaxies within galaxy clusters — was published today (February 2, 2021) in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
“The nature of galaxies depends both on how massive they are and their environment,” said Professor Croom.
“For example, they can be lonely in voids, or crowded into the dense heart of galactic clusters, or anywhere in between. The SAMI Survey shows how the internal structure of galaxies is related to their mass and environment at the same time, so we can understand how these things influence each other.”
Research arising from the survey has already revealed several unexpected outcomes.
One group of astronomers showed that the direction of a galaxy’s spin depends on the other galaxies around it, and changes depending on the galaxy’s size. Another group showed that the amount of rotation a galaxy has is primarily determined by its mass, with little influence from the surrounding environment. A third looked at galaxies that were winding down star-making, and found that for many the process began only a billion years after they drifted into the dense inner-city regions of clusters.
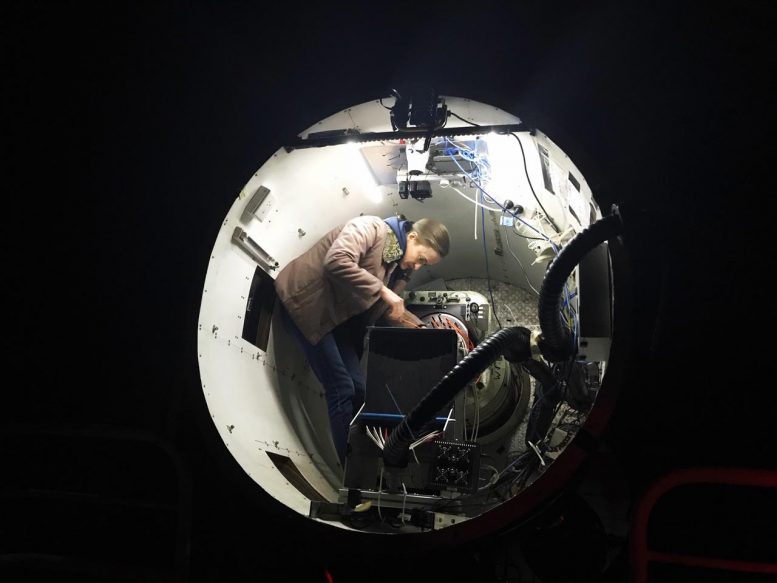

A/Prof Julia Bryant from the University of Sydney inside the SAMI instrument at the top end of the Anglo Australian Telescope. Credit: Scott Croom/University of Sydney
“The SAMI Survey was set up to help us answer some really broad top-level questions about galaxy evolution,” said co-author Dr Matt Owers from Macquarie University in Australia.
“The detailed information we’ve gathered will help us to understand fundamental questions such as: Why do galaxies look different depending on where they live in the Universe? What processes stop galaxies forming new stars and, conversely, what processes drive the formation of new stars? Why do the stars in some galaxies move in a highly ordered rotating disk, while in other galaxies their orbits are randomly oriented?”
Professor Croom added, “The survey is finished now, but by making it all public we hope that the data will continue to bear fruit from many, many years to come.”
Co-author Associate Professor Julia Bryant from ASTRO 3D and the University of Sydney said: “The next steps in this research will make use of a new Australian instrument — which we’ve called Hector — that will start operation in 2021, increasing the detail and number of galaxies that can be observed.”
When fully installed in the AAT, Hector will survey 15,000 galaxies.
Reference: “The SAMI Galaxy Survey: the third and final data release” by Scott M Croom, Matt S Owers, Nicholas Scott, Henry Poetrodjojo, Brent Groves, Jesse van de Sande, Tania M Barone, Luca Cortese, Francesco D’Eugenio, Joss Bland-Hawthorn, Julia Bryant, Sree Oh, Sarah Brough, James Agostino, Sarah Casura, Barbara Catinella, Matthew Colless, Gerald Cecil, Roger L Davies, Michael J Drinkwater, Simon P Driver, Ignacio Ferreras, Caroline Foster, Amelia Fraser-McKelvie, Jon Lawrence, Sarah K Leslie, Jochen Liske, Ángel R López-Sánchez, Nuria P F Lorente, Rebecca McElroy, Anne M Medling, Danail Obreschkow, Samuel N Richards, Rob Sharp, Sarah M Sweet, Dan S Taranu, Edward N Taylor, Edoardo Tescari, Adam D Thomas, James Tocknell and Sam P Vaughan, 1 February 2021, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stab229
The final data release paper has 41 authors, drawn from Australia, Belgium, the US, Germany, Britain, Spain and The Netherlands.
The full data set is available online through Australian Astronomical Optics (AAO) Data Central.









The only secret in physics is this. No one knows their ass from a hole in the ground. Its all speculation. Unless someone or an Ai develops better math, its going to stay that way.
Your comment is all speculation.
Staring 400 years ago, scientists figured out how classical mechanics work and starting 40 years ago how the universe works (inflationary hot big bang cosmology). That’s a lot of “not speculation” already there.
To be fair I don’t think most of these commenters can tell their own holes apart. Looking forward to where all this data leads, that may end up being interesting (sadly this article lacked in details on that front)
🙂
Unfortunately the paper isn’t much better than the article. It is mostly a data description and early survey, and the suggested trends are mostly wak and not quantified. The conclusion almost immediately go into suggestions of further data collection.
“wak” = weak.
El comentario de El Décimo Hombre es parcialmente acertado, según mi criterio, porque yo pienso que las muy respetables y extraordinarias Matemáticas NO APORTAN TODAS LAS SOLUCIONES, sino que, ampliando el horizonte de posibilidades, el Padre de las Matemáticas, el Razonamiento o Pensamiento Puro, Absoluto, tiene las Llaves del Conocimiento, del cual las Matemáticas son su más valioso instrumento!!
It all looks pretty obvious to me, the galaxies have drain holes at their center, and we are all going down the cosmic drain.
I know how it all began. God spoke it into existence. Let’s now move on to more important things; a relationship with our Lord and our Savior. Read Mere Christianity by C.S. Lewis and then read The Signature of God by Grant R. Jeffrey. You will come away with the deep conviction that God truly does exist. Shalom.
Superstition. You are not helping anyone understand nature by appealing to magic.
What STARTS with love, always ENDS with love
Your Welcome!
3301
How to overcome hereditary diseases like Diabetese blood pressure
Are you sure that God exist. I’ve not seen any proof. As a bunch of monkeys continues to search for that truth we wish and hope but only told faith is enough, faith in what, christ never was and all the wishing will not make it so. No God no christ, no faith. Believe in each other. Learn to live with each other, learn to care for each other. No need reaching for something that doesnt exists. Science has all the answers you are looking for.
This is good to study inter-relationahip among large numbets of galaxies present ina specìfic part of universe.We çan come to following conclusions in this rrgard-
1.The amount of rotation of a galaxy depends upon its mass and is directly proportional.
2.The inclination in direction of soin axis of a galaxy is dìrectĺy proportional to its moment of inertia.Spin of a galaxy interacts directly with spins of other galaxies in the surrounding and is proportional.
3.The internal structure of galaxy depends upon mass so that product of average radis and thickness is directly proportional to it.
This is good to study inter-relationahip among large numbets of galaxies present ina specìfic part of universe.We çan come to following conclusions in this rrgard-
1.The amount of rotation of a galaxy depends upon its mass and is directly proportional.
2.The inclination in direction of soin axis of a galaxy is dìrectĺy proportional to its moment of inertia.Spin of a galaxy interacts directly with spins of other galaxies in the surrounding and is proportional.
3.The internal structure of galaxy depends upon mass so that product of average radis and thickness is directly proportional to it.
Mass is the basic property that governs matter.Some other conditions lìke like effrcts of CMB radiations can be added to this.
This is good to study inter-relationahip among large numbets of galaxies present ina specìfic part of universe.We çan come to following conclusions in this rrgard-
1.The amount of rotation of a galaxy depends upon its mass and is directly proportional.
2.The inclination in direction of soin axis of a galaxy is dìrectĺy proportional to its moment of inertia.Spin of a galaxy interacts directly with spins of other galaxies in the surrounding and is proportional.
3.The internal structure of galaxy depends upon mass so that product of average radis and thickness is directly proportional to it.
Mass is the basic property that governs matter.Some other conditions lìke like effrcts of CMB radiations can be added to this.Hère relativity is sole internal proporty of a galaxy has noinfluence on other external galaxies.
Here in such circumstances relativity is the sole internal proporty of a galaxy havig no influence on other external galaxies.So how relativity is menifested in an isolated galaxy.
Here in such circumstances relativity is the sole internal proporty of a galaxy havig no influence on other external galaxies.So how relativity is menifested in an isolated galaxy.But since Bìg Bang from the very origin galaxies are inherently associated with space-time coordinates in the inertial frame of the Universe.Thanks to the aùthors for valuable works.
Here in such circumstances relativity is the sole internal proporty of a galaxy havig no influence on other external galaxies.So how relativity is menifested in an isolated galaxy.But since Bìg Bang from the very origin galaxies are inherently associated with space-time coordinates in the inertial frame of the Universe.Thanks to the aùthors for valuable works.Then galaxies are in a balanced state to operate with the inertial mass;side by CMB radiations are balanced as per necessary.