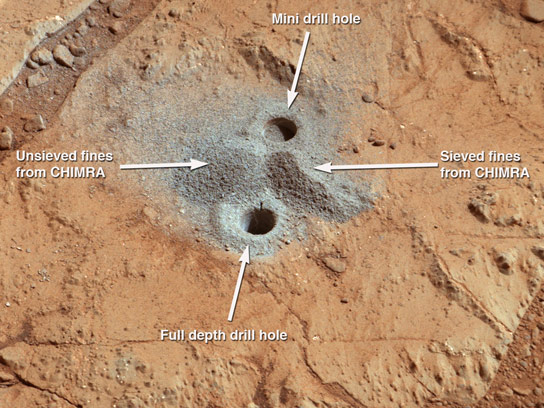

This image shows the first holes into rock drilled by NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity, with drill tailings around the holes plus piles of powdered rock collected from the deeper hole and later discarded after other portions of the sample had been delivered to analytical instruments inside the rover. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
New data from NASA’s Curiosity rover helped reveal changes in the Martian atmosphere, providing the most precise measurements ever made of isotopes of argon.
Mars has lost much of its original atmosphere, but what’s left remains quite active, recent findings from NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity indicate. Rover team members reported diverse findings today at the European Geosciences Union 2013 General Assembly, in Vienna.
Evidence has strengthened this month that Mars lost much of its original atmosphere by a process of gas escaping from the top of the atmosphere.
Curiosity’s Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument analyzed an atmosphere sample last week using a process that concentrates selected gases. The results provided the most precise measurements ever made of isotopes of argon in the Martian atmosphere. Isotopes are variants of the same element with different atomic weights. “We found arguably the clearest and most robust signature of atmospheric loss on Mars,” said Sushil Atreya, a SAM co-investigator at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
SAM found that the Martian atmosphere has about four times as much of a lighter stable isotope (argon-36) compared to a heavier one (argon-38). This removes previous uncertainty about the ratio in the Martian atmosphere from 1976 measurements from NASA’s Viking project and from small volumes of argon extracted from Martian meteorites. The ratio is much lower than the solar system’s original ratio, as estimated from argon-isotope measurements of the sun and Jupiter. This points to a process at Mars that favored preferential loss of the lighter isotope over the heavier one.
Curiosity measures several variables in today’s Martian atmosphere with the Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS), provided by Spain. While daily air temperature has climbed steadily since the measurements began eight months ago and is not strongly tied to the rover’s location, humidity has differed significantly at different places along the rover’s route. These are the first systematic measurements of humidity on Mars.
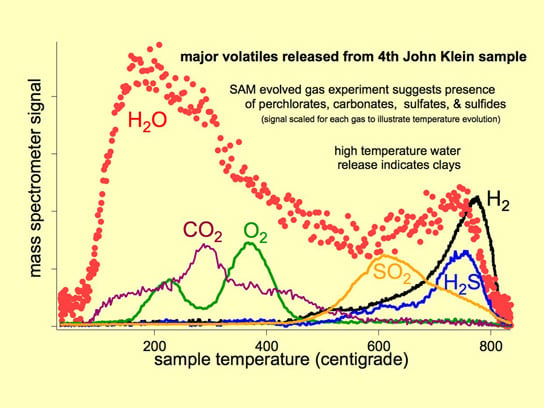
As the Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) suite of instruments on NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover heats a sample, gases are released (or “evolved”) from the sample and can be identified using SAM’s quadrupole mass spectrometer. This graphic shows the principal gases evolved from the fourth portion of powder delivered to SAM from the sample material collected when Curiosity first drilled into the “John Klein” target rock in the “Yellowknife Bay” area of Mars’ Gale Crater.
The mass spectrometer signal is scaled separately for each gas so that the same graph can illustrate the patterns for various gases showing what temperatures caused the gas to be released. These evolved gases and the temperatures at which they evolved suggest the presence of hydrated minerals, carbonates, perchlorates, sulfates and sulfides, and clays in the rock-powder sample. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Trails of dust devils have not been seen inside Gale Crater, but REMS sensors detected many whirlwind patterns during the first hundred Martian days of the mission, though not as many as detected in the same length of time by earlier missions. “A whirlwind is a very quick event that happens in a few seconds and should be verified by a combination of pressure, temperature, and wind oscillations and, in some cases, a decrease in ultraviolet radiation,” said REMS Principal Investigator Javier Gómez-Elvira of the Centro de Astrobiología, Madrid.
Dust distributed by the wind has been examined by Curiosity’s laser-firing Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument. Initial laser pulses on each target hit dust. The laser’s energy removes the dust to expose underlying material, but those initial pulses also provide information about the dust.
“We knew that Mars is red because of iron oxides in the dust,” said ChemCam Deputy Principal Investigator Sylvestre Maurice of the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie in Toulouse, France. “ChemCam reveals a complex chemical composition of the dust that includes hydrogen, which could be in the form of hydroxyl groups or water molecules.”
Possible interchange of water molecules between the atmosphere and the ground is studied by a combination of instruments on the rover, including the Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons (DAN), provided by Russia under the leadership of DAN Principal Investigator Igor Mitrofanov.
For the rest of April, Curiosity will carry out daily activities for which commands were sent in March, using DAN, REMS and the Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD). No new commands are being sent during a four-week period while Mars is passing nearly behind the sun, from Earth’s perspective. This geometry occurs about every 26 months and is called Mars solar conjunction.
“After conjunction, Curiosity will be drilling into another rock where the rover is now, but that target has not yet been selected. The science team will discuss this over the conjunction period,” said Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger, of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.
NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory Project is using Curiosity to investigate the environmental history within Gale Crater, a location where the project has found that conditions were long ago favorable for microbial life. Curiosity, carrying 10 science instruments, landed in August 2012 to begin its two-year prime mission. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, manages the project for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.






Still waiting for NASA to release that important hydrocarbons data…
Dear Sir
How can I get data for Mars Atmosphere specially ionosphere
the electron density and total electron content and the temperature
CO2 and H2O
regards
The data will eventually be published, but for now you can try these links or contact the article author with the info provided below. Thanks-
For more about the mission, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl . You can follow the mission on Facebook and Twitter at: http://www.facebook.com/marscuriosity and http://www.twitter.com/marscuriosity .
Guy Webster 818-354-6278
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
[email protected]