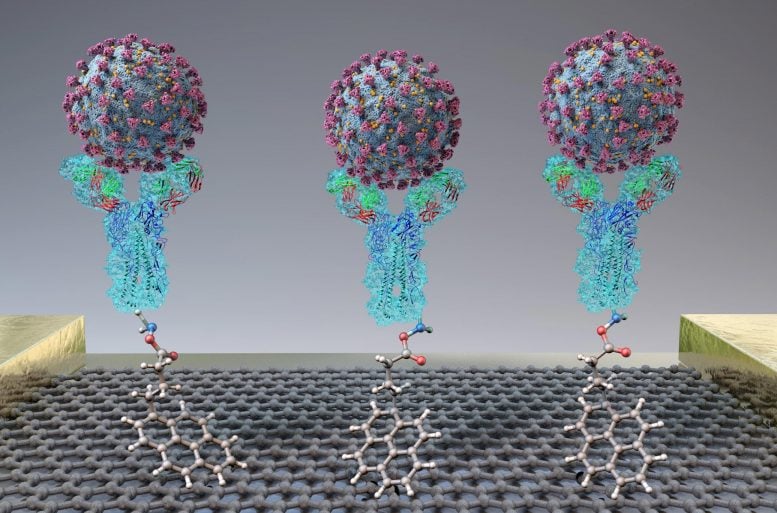
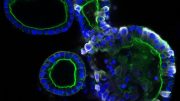
A new test quickly detects SARS-CoV-2 (spheres) through binding to antibodies (Y-shapes) on a field-effect transistor. Credit: Adapted from ACS Nano 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02823
According to many experts, early diagnosis and management are critical for slowing the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the new coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Therefore, the race is on to develop diagnostic tests for the virus that are faster, easier and more accurate than existing ones. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a field-effect transistor-based biosensor that detects SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs from patients with COVID-19, in less than one minute.
Currently, most diagnostic tests for COVID-19 rely on a technique called real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which amplifies SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient swabs so that tiny amounts of the virus can be detected. However, the method takes at least 3 hours, including a step to prepare the viral RNA for analysis. Edmond Changkyun Park, Seung Il Kim and colleagues wanted to develop a faster diagnostic test that could analyze patient samples directly from a tube of buffer containing the swabs, without any sample preparation steps.
The team based their test on a field-effect transistor — a sheet of graphene with high electronic conductivity. The researchers attached antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to the graphene. When they added either purified spike protein or cultured SARS-CoV-2 virus to the sensor, binding to the antibody caused a change in the electrical current. Next, the team tested the technique on nasopharyngeal swabs collected from patients with COVID-19 or healthy controls. Without any sample preparation, the sensor could discriminate between samples from sick and healthy patients. The new test was about 2-4 times less sensitive than RT-PCR, but different materials could be explored to improve the signal-to-noise ratio, the researchers say.
Reference: “Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor” by Giwan Seo, Geonhee Lee, Mi Jeong Kim, Seung-Hwa Baek, Minsuk Choi, Keun Bon Ku, Chang-Seop Lee, Sangmi Jun, Daeui Park, Hong Gi Kim, Seong-Jun Kim, Jeong-O Lee, Bum Tae Kim, Edmond Changkyun Park and Seung Il Kim, 15 April 2020, ACS Nano.
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02823
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Research Council of Science and Technology funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea.


Be the first to comment on "Diagnostic Biosensor Detects SARS-CoV-2 From Nasopharyngeal Swab in Less Than a Minute"