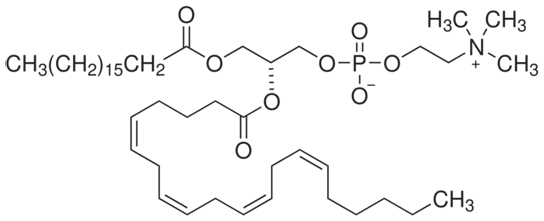
2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol (2-AG) plays a role in how the body uses energy.
New research published today in the journal Cell Metabolism indicates that endocannabinoids might enable organisms to stay thin without the need for exercise or diets. Endocannabinoids regulate how quickly the human body burns fat.
Previous research has shown that endocannabinoids play an important role in regulating energy metabolism. The new study shows that mice stayed thin without exercising or dieting. The mice were in a hypermetabolic state, in which their bodies were using up energy at a much higher rate.

The mice were resistant to obesity because they burned fat calories much more efficiently than normal mice did, states Daniele Piomelli, from the University of California, Irvine. The target is a compound named 2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol (2-AG), which is found in high levels in mammalian brains. Scientists think that it plays a role in how the body uses energy.
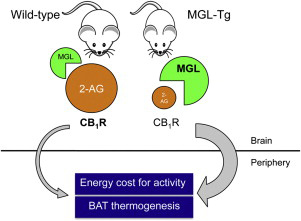 However, jumping from lab studies on mice to a health benefit in humans will take some time, since it’s difficult to make drugs that affect only one part of the brain. The drug in question would have to block 2-AG production in the brain, something that’s not yet possible.
However, jumping from lab studies on mice to a health benefit in humans will take some time, since it’s difficult to make drugs that affect only one part of the brain. The drug in question would have to block 2-AG production in the brain, something that’s not yet possible.
Reference: “2-Arachidonoylglycerol Signaling in Forebrain Regulates Systemic Energy Metabolism” by Kwang-Mook Jung, Jason R. Clapper, Jin Fu, Giuseppe D’Agostino, Ana Guijarro, Dean Thongkham, Agnesa Avanesian, Giuseppe Astarita, Nicholas V. DiPatrizio, Andrea Frontini, Saverio Cinti, Sabrina Diano and Daniele Piomelli, 7 March 2012, Cell Metabolism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.01.021








Be the first to comment on "Endocannabinoids Could Reduce or Eliminate Obesity"