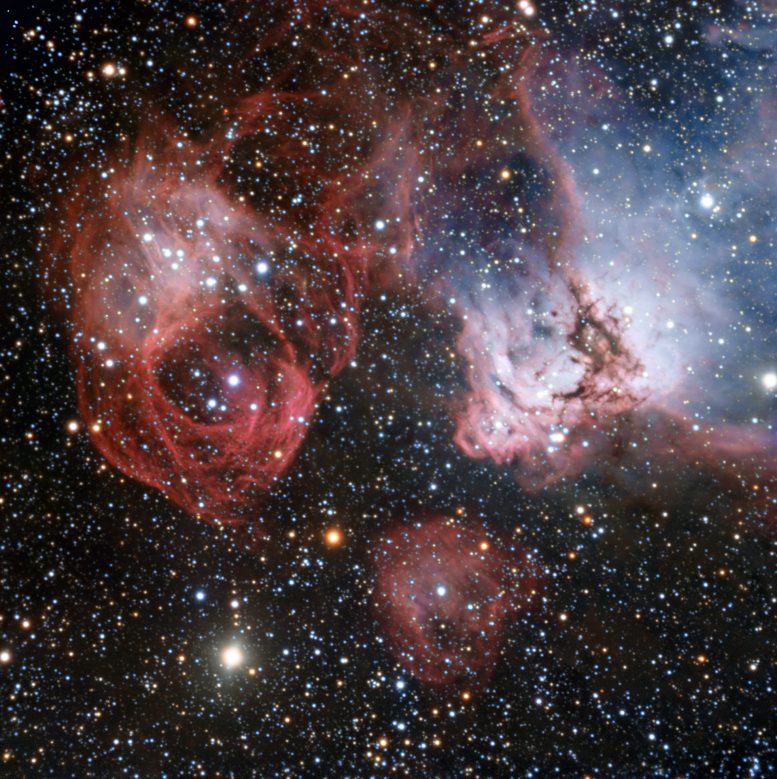

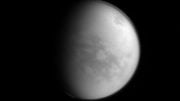
The Large Magellanic Cloud is one of the closest galaxies to our own. Astronomers have now used the power of the ESO’s Very Large Telescope to explore NGC 2035, one of its lesser known regions, in great detail. This new image shows clouds of gas and dust where hot new stars are being born and are sculpting their surroundings into odd shapes. But the image also shows the effects of stellar death — filaments created by a supernova explosion (left). Credit: ESO
A new ESO image explores the Large Magellanic Cloud and an area nicknamed the Dragon’s Head Nebula.
The Large Magellanic Cloud is one of the closest galaxies to our own. Astronomers have now used the power of ESO’s Very Large Telescope to explore one of its lesser known regions. This new image shows clouds of gas and dust where hot new stars are being born and sculpting their surroundings into odd shapes. But the image also shows the effects of stellar death — filaments created by a supernova explosion.
Located only about 160,000 light-years from us in the constellation of Dorado (The Swordfish), the Large Magellanic Cloud is one of our closest galactic neighbors. It is actively forming new stars in regions that are so bright that some can even be seen from Earth with the naked eye, such as the Tarantula Nebula. This new image, taken by ESO’s Very Large Telescope at the Paranal Observatory in Chile, explores an area called NGC 2035 (right), sometimes nicknamed the Dragon’s Head Nebula.
NGC 2035 is an HII region, or emission nebula, consisting of clouds of gas that glow due to the energetic radiation given off by young stars. This radiation strips electrons from atoms within the gas, which eventually recombine with other atoms and release light. Mixed in with the gas are dark clumps of dust that absorb rather than emit light, creating weaving lanes and dark shapes across the nebula.
The filamentary shapes to the left in the image are not the results of starbirth, but rather stellar death. It was created by one of the most violent events that can happen in the Universe — a supernova explosion [1]. These explosions are so bright that they often briefly outshine their entire host galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months.
From looking at this image, it may be difficult to grasp the sheer size of these clouds — they are several hundred light-years across. And they are not in our galaxy, but far beyond. The Large Magellanic Cloud is enormous, but when compared to our own galaxy it is very modest in extent, spanning just 14,000 light-years — about ten times smaller than the Milky Way.
This image was acquired using the FOcal Reducer and low dispersion Spectrograph instrument attached to ESO’s Very Large Telescope, which is located at the Paranal Observatory in Chile, as part of the ESO Cosmic Gems program [2].
Notes
[1] The remnant left over by the supernova explosion that can be seen in this image is called SNR 0536-67.6.
[2] The ESO Cosmic Gems program is an initiative to produce images of interesting, intriguing or visually attractive objects using ESO telescopes, for the purposes of education and public outreach. The program makes use of telescope time that cannot be used for science observations. All data collected may also be suitable for scientific purposes, and are made available to astronomers through ESO’s science archive.





My grandson is 10 years old and has a persuasive writing assignment to sell an object from space. He was allowed to choose from planets, stars, comets, moons, satellites, nebulas, dwarf planets and asteroids. After doing research, he chose the Dragon’s Head Nebula as his subject matter, because of it’s beauty and expansiveness.