
Quantum inertial sensors could serve as revolutionary, onboard navigational aids if they could be re-engineered into compact, rugged devices. When GPS signals are jammed or lost, they could safely guide vehicles.
High-tech quantum sensors could guide vehicles without satellites, if they can handle the ride.
When talking about quantum inertial sensors, words like “tough” or “rugged” are unlikely to be spoken. These remarkable scientific instruments can measure motion a thousand times more accurately than the devices that help navigate today’s missiles, drones, and aircraft. However, its delicate, table-sized array of components that includes a complex laser and vacuum system has essentially kept the technology grounded and confined to the controlled settings of a laboratory.
Jongmin Lee wants to change that.
The atomic physicist is part of a team at Sandia that envisions quantum inertial sensors as revolutionary, onboard navigational aids. The team is working to re-engineer the sensor into a compact, rugged device, where the technology could safely guide vehicles when GPS signals are jammed or lost.
In a major milestone toward realizing their vision, the team has successfully constructed a cold-atom interferometer. This is a core component of quantum sensors, and their version is designed to be much smaller and tougher than typical lab setups. The team describes their prototype in a paper that was recently published in the academic journal Nature Communications, showing how to integrate several normally separated components into a single monolithic structure. In doing so, they reduced the key components of a system that existed on a large optical table down to a sturdy package roughly the size of a shoebox.
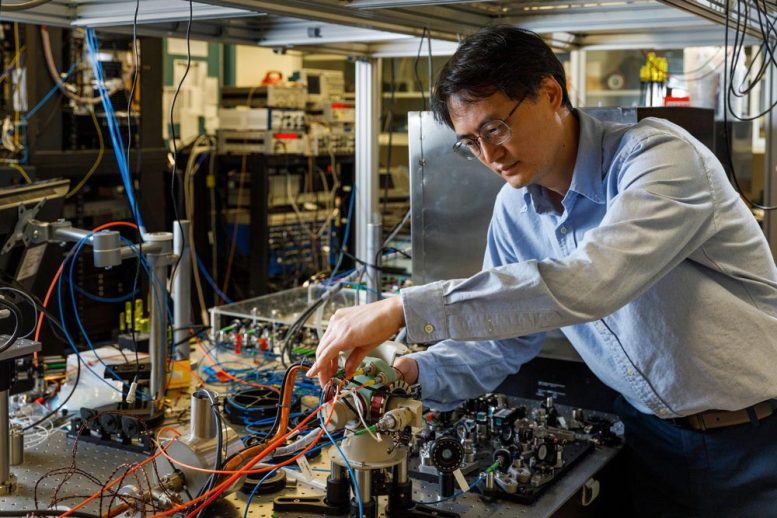
TOUGH ENOUGH? — Sandia atomic physicist Jongmin Lee examines the sensor head of a cold-atom interferometer that could help vehicles stay on course where GPS is unavailable. Credit: Photo by Bret Latter
“Very high sensitivity has been demonstrated in the lab, but the practical matters are, for real-world application, that people need to shrink down the size, weight, and power, and then overcome various issues in a dynamic environment,” Jongmin said.
The paper also describes a roadmap for further miniaturizing the system using technologies under development.
The prototype, funded by Sandia’s Laboratory Directed Research and Development program, demonstrates significant strides toward moving advanced navigation tech out of the lab and into vehicles on the ground, underground, in the air, and even in space.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a constellation of orbiting satellites that provides position, navigation, and timing data to military and civilian users around the world. GPS satellites orbit the Earth every 12 hours, continuously transmitting navigation signals. With the proper equipment, users can receive at least four satellite signals to calculate time, location, and velocity. The signals are so accurate that time can be figured to within a millionth of a second, velocity within a fraction of a mile per hour, and location to within 100 feet.
Ultrasensitive measurements drive navigational power
As a jet does a barrel roll through the sky, current onboard navigation tech can measure the aircraft’s tilts and turns and accelerations to calculate its position without GPS, for a time. Small measurement errors gradually push a vehicle off course unless it periodically syncs with the satellites, Jongmin said.
Quantum sensing would operate in the same way, but the much better accuracy would mean onboard navigation wouldn’t need to cross-check its calculations as often, reducing reliance on satellite systems.
Roger Ding, a postdoctoral researcher who worked on the project, said, “In principle, there are no manufacturing variations and calibrations,” compared to conventional sensors that can change over time and need to be recalibrated.
Aaron Ison, the lead engineer on the project, said to prepare the atom interferometer for a dynamic environment, he and his team used materials proven in extreme environments. Additionally, parts that are normally separate and freestanding were integrated together and fixed in place or were built with manual lockout mechanisms.
“A monolithic structure having as few bolted interfaces as possible was key to creating a more rugged atom interferometer structure,” Aaron said.
Furthermore, the team used industry-standard calculations called finite element analysis to predict that any deformation of the system in conventional environments would fall within the required allowances. Sandia has not conducted mechanical stress tests or field tests on the new design, so further research is needed to measure the device’s strength.
“The overall small, compact design naturally leads towards a stiffer more robust structure,” Aaron said.
Photonics light the way to a more miniaturized system
Most modern atom interferometry experiments use a system of lasers mounted to a large optical table for stability reasons, Roger said. Sandia’s device is comparatively compact, but the team has already come up with further design improvements to make the quantum sensors much smaller using integrated photonic technologies.
“There are tens to hundreds of elements that can be placed on a chip smaller than a penny,” said Peter Schwindt, the principal investigator on the project and an expert in quantum sensing.
Photonic devices, such as a laser or optical fiber, use light to perform useful work and integrated devices include many different elements. Photonics are used widely in telecommunications, and ongoing research is making them smaller and more versatile.
With further improvements, Peter thinks the space an interferometer needs could be as little as a few liters. His dream is to make one the size of a soda can.
In their paper, the Sandia team outlines a future design in which most of their laser setup is replaced by a single photonic integrated circuit, about eight millimeters on each side. Integrating the optical components into a circuit would not only make an atom interferometer smaller, it would also make it more rugged by fixing the components in place.
While the team can’t do this yet, many of the photonic technologies they need are currently in development at Sandia.
“This is a viable path to highly miniaturized systems,” Roger said.
Meanwhile, Jongmin said integrated photonic circuits would likely lower costs and improve scalability for future manufacturing.
“Sandia has shown an ambitious vision for the future of quantum sensing in navigation,” Jongmin said.
Reference: “A compact cold-atom interferometer with a high data-rate grating magneto-optical trap and a photonic-integrated-circuit-compatible laser system” by Jongmin Lee, Roger Ding, Justin Christensen, Randy R. Rosenthal, Aaron Ison, Daniel P. Gillund, David Bossert, Kyle H. Fuerschbach, William Kindel, Patrick S. Finnegan, Joel R. Wendt, Michael Gehl, Ashok Kodigala, Hayden McGuinness, Charles A. Walker, Shanalyn A. Kemme, Anthony Lentine, Grant Biedermann and Peter D. D. Schwindt, 1 September 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31410-4





These devices can be s thousand times more precise than the ones now in use, according to this article, but think about it: they don’t need to be. Even 10 times better would be great.