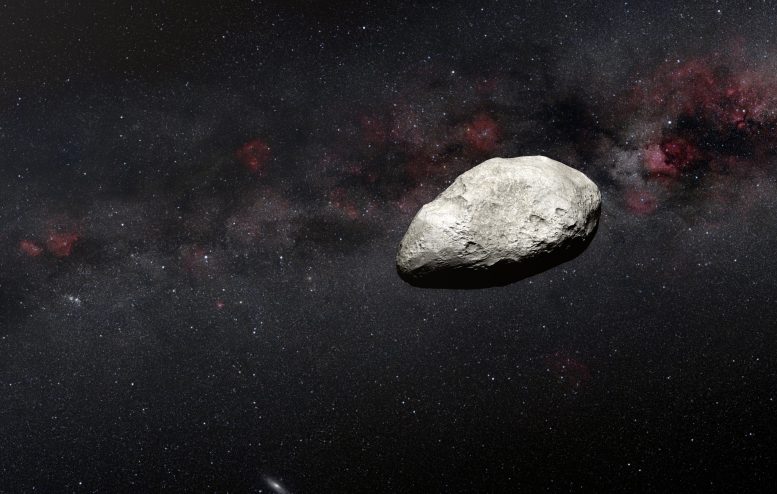

An asteroid roughly the size of Rome’s Colosseum — between 300 to 650 feet (100 to 200 meters) in length — has been detected by an international team of European astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. They used data from the calibration of the MIRI instrument, in which the team serendipitously detected an interloping asteroid. The object is likely the smallest observed to date by Webb and may be an example of an object measuring under 1 kilometer in length within the main asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter. More observations are needed to better characterize this object’s nature and properties. Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, N. Bartmann (ESA/Webb), Martin Kornmesser (ESA), Serge Brunier (ESO), Nick Risinger Photopic Sky Survey)
The object belongs to the poorly known sub-kilometer category of asteroids in the main belt.
An asteroid roughly the size of Rome’s Colosseum — between 300 to 650 feet (100 to 200 meters) in length — has been detected by an international team of European astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. The object, shown in this artist’s conception, is likely the smallest observed to date by Webb.
The detection was serendipitous — the asteroid was found in calibration images of a different asteroid. The lucky finding suggests Webb can detect many such objects.
James Webb Space Telescope Detects Extremely Small Main Belt Asteroid
An asteroid roughly the size of Rome’s Colosseum — between 300 to 650 feet (100 to 200 meters) in length — has been detected by an international team of European astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Their project used data from the calibration of the Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI), in which the team serendipitously detected an interloping asteroid. The object is likely the smallest observed to date by Webb and may be an example of an object measuring under 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) in length within the main asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter. More observations are needed to better characterize this object’s nature and properties.
“We — completely unexpectedly — detected a small asteroid in publicly available MIRI calibration observations,” explained Thomas Müller, an astronomer at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany. “The measurements are some of the first MIRI measurements targeting the ecliptic plane and our work suggests that many new objects will be detected with this instrument.”
These Webb observations, published on February 6 in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics, were not designed to hunt for new asteroids — in fact, they were calibration images of the main belt asteroid (10920) 1998 BC1, which astronomers discovered in 1998.[1] The observations were conducted to test the performance of some of MIRI’s filters, but the calibration team considered them to have failed for technical reasons due to the brightness of the target and an offset telescope pointing. Despite this, the data on asteroid 10920 were used by the team to establish and test a new technique to constrain an object’s orbit and to estimate its size. The validity of the method was demonstrated for asteroid 10920 using the MIRI observations combined with data from ground-based telescopes and ESA’s Gaia mission.[2]
In the course of the analysis of the MIRI data, the team found the smaller interloper in the same field of view. The team’s results suggest the object measures 100–200 meters, occupies a very low-inclination orbit, and was located in the inner main-belt region at the time of the Webb observations.
“Our results show that even ‘failed’ Webb observations can be scientifically useful, if you have the right mindset and a little bit of luck,” elaborated Müller. “Our detection lies in the main asteroid belt, but Webb’s incredible sensitivity made it possible to see this roughly 100-meter object at a distance of more than 100 million kilometers.”
The detection of this asteroid — which the team suspects to be the smallest observed to date by Webb and one of the smallest detected in the main belt — would, if confirmed as a new asteroid discovery, have important implications for our understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system. Current models predict the occurrence of asteroids down to very small sizes, but small asteroids have been studied in less detail than their larger counterparts owing to the difficulty of observing these objects. Future dedicated Webb observations will allow astronomers to study asteroids smaller than 1 kilometer in size.
What’s more, this result suggests that Webb will also be able to serendipitously contribute to the detection of new asteroids. The team suspects that even short MIRI observations close to the plane of the solar system will always include a few asteroids, most of which will be unknown objects.
In order to confirm that the object detected is a newly discovered asteroid, more position data relative to background stars is required from follow-up studies to constrain the object’s orbit.
“This is a fantastic result which highlights the capabilities of MIRI to serendipitously detect a previously undetectable size of asteroid in the main belt,” concluded Bryan Holler, Webb support scientist at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland. “Repeats of these observations are in the process of being scheduled, and we are fully expecting new asteroid interlopers in those images.”
Notes
- The main asteroid belt is a doughnut-shaped region that contains the majority of the Solar System’s asteroids. It lies roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter, and is closely aligned with the ecliptic plane, the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun, which is also the rough plane in which the other planets of the Solar System lie.
- RSA’s Gaia mission is in the process of precisely measuring the positions of astronomical objects to build up an extraordinarily precise three-dimensional map of more than a thousand million stars.
Reference: “Asteroids seen by JWST-MIRI: Radiometric size, distance, and orbit constraints” by T. G. Müller, M. Micheli, T. Santana-Ros, P. Bartczak, D. Oszkiewicz and S. Kruk, 6 February 2023, Astronomy and Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202245304
The James Webb Space Telescope, a collaborative international effort headed by NASA with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency, is the world’s leading space science observatory. With its cutting-edge capabilities, it will unravel the mysteries of our solar system, investigate distant exoplanets, and probe the unknown structures and origins of the universe and our place within it.
The Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), a joint project between NASA and ESA, was developed through a 50-50 partnership. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory drove the US efforts for MIRI, while a consortium of European astronomical institutes contributed on behalf of ESA. George Rieke of the University of Arizona leads the MIRI science team, and Gillian Wright serves as the MIRI European principal investigator.
Laszlo Tamas of the UK ATC manages the European Consortium. The cryocooler for MIRI was developed and managed by JPL in collaboration with Northrop Grumman in Redondo Beach, California, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.







Be the first to comment on "James Webb Space Telescope Detects Asteroid the Size of Rome’s Colosseum"