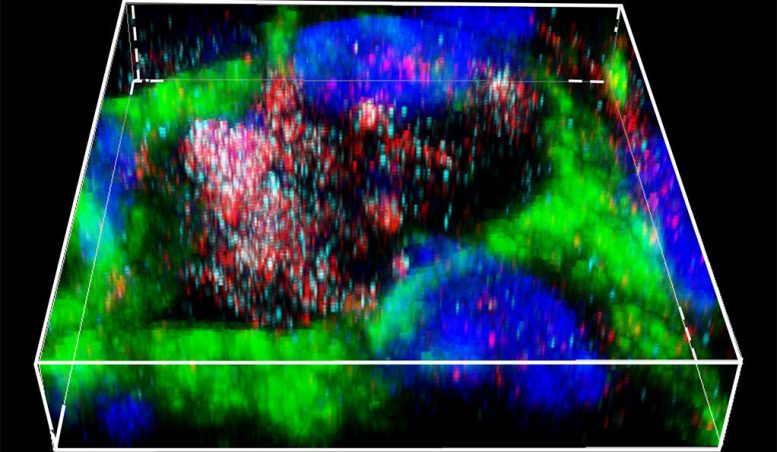
Stem cells can aid in healing spinal cord injuries by hitching a ride with anti-inflammatory cells called M2 macrophages, according to a study by Yale researchers.
In a new study, Yale researchers report the healing effects of stem cells in spinal cord injury can be aided by their ability to hitch intercellular rides to specific anti-inflammatory cells called M2 macrophages.
Yale University researchers had previously shown that mesenchymal stem cells harvested from bone marrow helped repair spinal cord injury in rats; however, many of the cells did not reach their target injury site.
The study by the Yale team, headed by neuroscientists Jeffery Kocsis and Karen Lankford, shows how properties from stem cells can be carried to the macrophages by intercellular cargo vesicles called exosomes. There, the stem cell-derived exosomes may aid macrophages to repair ruptures in the blood-brain barrier that can wreak havoc with the central nervous system.
The report appears on January 5 in the journal PLOS ONE.
Reference: “Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord” by Karen L. Lankford, Edgardo J. Arroyo, Katarzyna Nazimek, Krzysztof Bryniarski, Philip W. Askenase and Jeffery D. Kocsis, 2 January 2018, PLOS One.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190358


Be the first to comment on "Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Aid Spinal Cord Recovery"