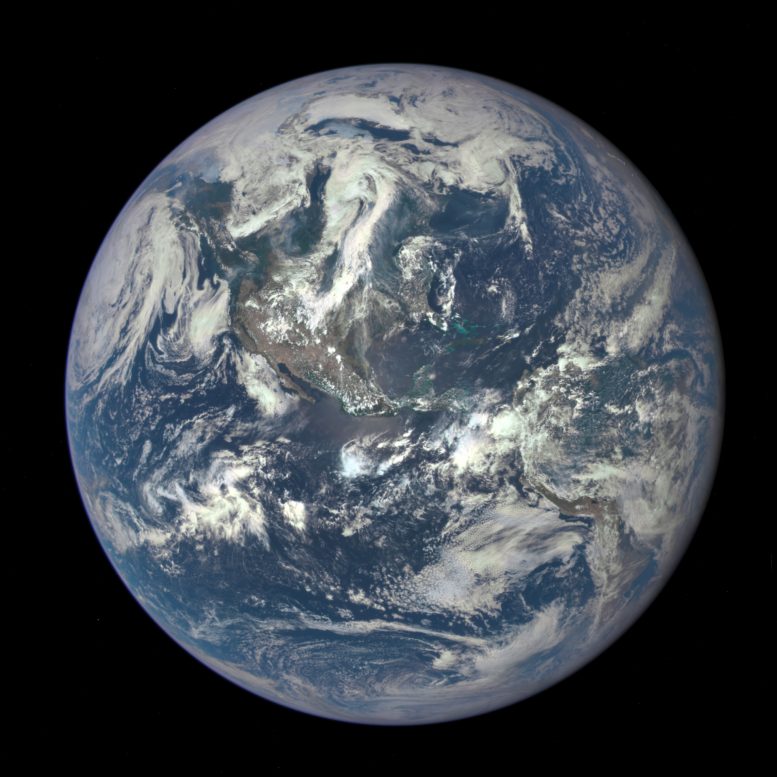

Deep Space Climate Observatory Satellite captures the first image of Earth from one million miles (1.6 kilometers) away.
NASA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory Satellite has captured its first view of Earth. The image shows the entire sunlit side from one million miles (1.6 kilometers) away.
This color image of Earth was taken by NASA’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC), a four megapixel CCD camera and telescope. The image was generated by combining three separate images to create a photographic-quality image. The camera takes a series of 10 images using different narrowband filters — from ultraviolet to near infrared — to produce a variety of science products. The red, green and blue channel images are used in these color images.
The image was taken on July 6, 2015, showing North and Central America. The central turquoise areas are shallow seas around the Caribbean islands. This Earth image shows the effects of sunlight scattered by air molecules, giving the image a characteristic bluish tint. The EPIC team is working to remove this atmospheric effect from subsequent images. Once the instrument begins regular data acquisition, EPIC will provide a daily series of Earth images allowing for the first time study of daily variations over the entire globe. These images, available 12 to 36 hours after they are acquired, will be posted to a dedicated web page by September 2015.






Be the first to comment on "NASA Deep Space Climate Observatory Satellite Captures Image of Earth"