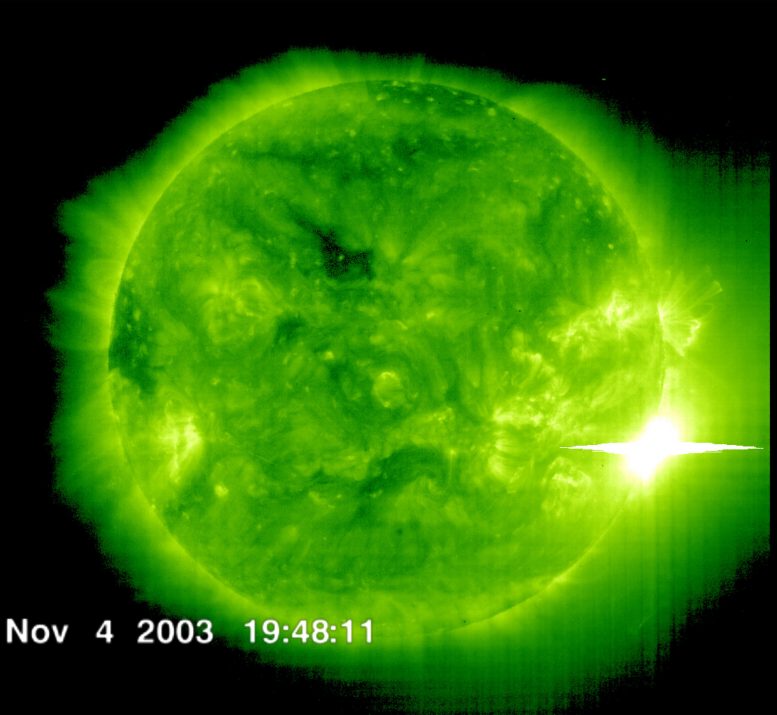
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory spacecraft captured this image of a solar flare as it erupted from the sun early on Nov 4, 2003. This was the most powerful flare measured with modern methods, classified as an X28. Credit: ESA and NASA/SOHO
As solar activity continues to build up toward what is known as solar maximum, NASA details the impacts of coronal mass ejections and space weather on Earth.
Given a legitimate need to protect Earth from the most intense forms of space weather — great bursts of electromagnetic energy and particles that can sometimes stream from the sun — some people worry that a gigantic “killer solar flare” could hurl enough energy to destroy Earth, but this is not actually possible.
Solar activity is indeed currently ramping up toward what is known as solar maximum, something that occurs approximately every 11 years. However, this same solar cycle has occurred over millennia so anyone over the age of 11 has already lived through such a solar maximum with no harm.
This is not to say that space weather can’t affect our planet. The explosive heat of a solar flare can’t make it all the way to our globe, but electromagnetic radiation and energetic particles certainly can. Solar flares can temporarily alter the upper atmosphere creating disruptions with signal transmission from, say, a GPS satellite to Earth causing it to be off by many yards. Another phenomenon produced by the sun could be even more disruptive. Known as a coronal mass ejection or CME these solar explosions propel bursts of particles and electromagnetic fluctuations into Earth’s atmosphere. Those fluctuations could induce electric fluctuations at ground level that could blow out transformers in power grids. A CME’s particles can also collide with crucial electronics onboard a satellite and disrupt its systems.
In an increasingly technological world, where almost everyone relies on cellphones, and GPS controls not just your in-car map system, but also airplane navigation and the extremely accurate clocks that govern financial transactions, space weather is a serious matter.
But it is a problem the same way hurricanes are a problem. One can protect oneself with advance information and proper precautions. During a hurricane watch, a homeowner can stay put … or he can seal up the house, turn off the electronics and get out of the way. Similarly, scientists at NASA and NOAA give warnings to electric companies, spacecraft operators, and airline pilots before a CME comes to Earth so that these groups can take proper precautions.
NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center is the U.S. government’s official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings. Improving these predictive abilities the same way weather prediction has improved over the last few decades is one of the reasons NASA studies the sun and space weather. We can’t ignore space weather, but we can take appropriate measures to protect ourselves.
And, even at their worst, the sun’s flares are not physically capable of destroying Earth.








Be the first to comment on "NASA Looks at the Impacts of Strong Solar Flares"