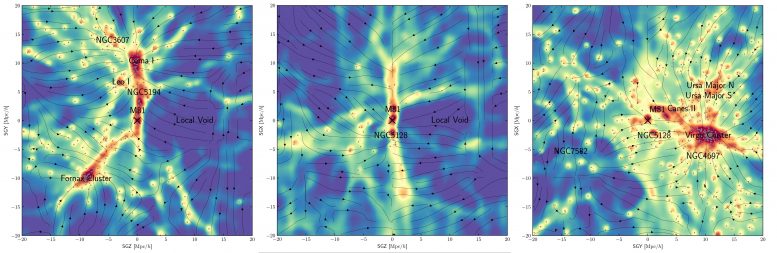
An international team of researchers has produced a map of the dark matter within the local universe, using a model to infer its location due to its gravitational influence on galaxies (black dots). These density maps — each a cross section in different dimensions — reproduce known, prominent features of the universe (red) and also reveal smaller filamentary features (yellow) that act as hidden bridges between galaxies. The X denotes the Milky Way galaxy and arrows denote the motion of the local universe due to gravity. Credit: Hong et. al., Astrophysical Journal
A new map of dark matter in the local universe reveals several previously undiscovered filamentary structures connecting galaxies. The map, developed using machine learning by an international team including a Penn State astrophysicist, could enable studies about the nature of dark matter as well as about the history and future of our local universe.
Dark matter is an elusive substance that makes up 80% of the universe. It also provides the skeleton for what cosmologists call the cosmic web, the large-scale structure of the universe that, due to its gravitational influence, dictates the motion of galaxies and other cosmic material. However, the distribution of local dark matter is currently unknown because it cannot be measured directly. Researchers must instead infer its distribution based on its gravitational influence on other objects in the universe, like galaxies.
“Ironically, it’s easier to study the distribution of dark matter much further away because it reflects the very distant past, which is much less complex,” said Donghui Jeong, associate professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State and a corresponding author of the study. “Over time, as the large-scale structure of the universe has grown, the complexity of the universe has increased, so it is inherently harder to make measurements about dark matter locally.”
Previous attempts to map the cosmic web started with a model of the early universe and then simulated the evolution of the model over billions of years. However, this method is computationally intensive and so far has not been able to produce results detailed enough to see the local universe. In the new study, the researchers took a completely different approach, using machine learning to build a model that uses information about the distribution and motion of galaxies to predict the distribution of dark matter.
The researchers built and trained their model using a large set of galaxy simulations, called Illustris-TNG, which includes galaxies, gasses, other visible matter, as well as dark matter. The team specifically selected simulated galaxies comparable to those in the Milky Way and ultimately identified which properties of galaxies are needed to predict the dark matter distribution.
“When given certain information, the model can essentially fill in the gaps based on what it has looked at before,” said Jeong. “The map from our models doesn’t perfectly fit the simulation data, but we can still reconstruct very detailed structures. We found that including the motion of galaxies — their radial peculiar velocities — in addition to their distribution drastically enhanced the quality of the map and allowed us to see these details.”
The research team then applied their model to real data from the local universe from the Cosmicflow-3 galaxy catalog. The catalog contains comprehensive data about the distribution and movement of more than 17 thousand galaxies in the vicinity of the Milky Way — within 200 megaparsecs. The resulting map of the local cosmic web is published in a paper appearing online on May 26, 2021, in the Astrophysical Journal.
The map successively reproduced known prominent structures in the local universe, including the “local sheet” — a region of space containing the Milky Way, nearby galaxies in the “local group,” and galaxies in the Virgo cluster — and the “local void” — a relatively empty region of space next to the local group. Additionally, it identified several new structures that require further investigation, including smaller filamentary structures that connect galaxies.
“Having a local map of the cosmic web opens up a new chapter of cosmological study,” said Jeong. “We can study how the distribution of dark matter relates to other emission data, which will help us understand the nature of dark matter. And we can study these filamentary structures directly, these hidden bridges between galaxies.”
For example, it has been suggested that the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies may be slowly moving toward each other, but whether they may collide in many billions of years remains unclear. Studying the dark matter filaments connecting the two galaxies could provide important insights into their future.
“Because dark matter dominates the dynamics of the universe, it basically determines our fate,” said Jeong. “So we can ask a computer to evolve the map for billions of years to see what will happen in the local universe. And we can evolve the model back in time to understand the history of our cosmic neighborhood.”
The researchers believe they can improve the accuracy of their map by adding more galaxies. Planned astronomical surveys, for example using the James Web Space Telescope, could allow them to add faint or small galaxies that have yet to be observed and galaxies that are further away.
Reference: “Revealing the Local Cosmic Web from Galaxies by Deep Learning” by Sungwook E. Hong, Donghui Jeong, Ho Seong Hwang and Juhan Kim, 26 May 2021, Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/abf040
In addition to Jeong, the research team includes Sungwook Hong at the University of Seoul/Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute in Korea, Ho Seong Hwang at the Seoul National University in Korea, and Juhan Kim at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study.
This research was supported in part by the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean Ministry of Education, the Korean Ministry of Science, the U.S. National Science Foundation, the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration Astrophysics Theory program, and the Center for Advanced Computation at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study.







It could also be non-luminous gas distributed between galaxies.
That is mostly dark matter, see the LCDM model.
It could happen, but is unlikely and not a general explanation of these bridges – see the map derivation.
Could some of the Dark Mater be in Black Holes (how about SMBHs)? Could some be under my carpet? There are a lot of possibilities. Don’t forget all this is so speculative.
Black hole matter is speculative, but has been constrained so the answer is “no”.
Late time stars aren’t enough and primordial black holes have been excluded by microlensing observations and what not. I lost interest at the last review that said something like at most 30 % of dark matter could be primordial black hole – meaning there is non-baryonic dark matter. [I don’t have it handy – lost interest – but you can search for it.]
This reminds me of statistics. Accurracy of results reaching six figures when calculations are made.
But statistics cannot predict the behavior of a single stimulus.
The rules of the game insist on the larger the statistical sample the less it applies to individuals.
Where the Milky Way is going and when it will get there is known without doubt, but where our sun will be inside the Milky Way is a complete unknown.
? Modern cosmology has gone from 100 % uncertainty – a factor two in universe age – before the discovery of dark energy – and now with eBOSS galaxy survey the inflationary hot big bang cosmology produces high precision results at 1 % remaining uncertainty (apart from the expansion rate tension, which is at 10 %).
Dark matter/energy,in one of its form ĺinked with common visible matter of the galaxy milkyway by very minute magnetic particles,which are indistinguishable as wave or particle.Heat particles thermions are annexed to these.Unknown form of gravity is present with this make it Dark in nature.
Dark matter doesn’t seem to interact with normal matter as yuo ad hoc propose [ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dark_matter ].
Dark matter/energy,in one of its form ĺinked with common visible matter of the galaxy milkyway by very minute magnetic particles,which are indistinguishable as wave or particle.Heat particles thermions are annexed to these.Unknown form of gravity is present with this make it Dark in nature.Gravity is common to both FORM of MATTER Visible(that which are in view) and Dark.
Dark matter/energy,in one of its form ĺinked with common visible matter of the galaxy milkyway by very minute magnetic particles,which are indistinguishable as wave or particle.Heat particles thermions are annexed to these.Unknown form of gravity is present with this make it Dark in nature.Gravity is common to both FORM of MATTER Visible(that which are in view) and Dark.Dark matter particles which constitute the FINAL minute particle of visiblè universe.So thouh they can present in both wave particĺe states simultaneously,measured as waves.
Dark matter/energy,in one of its form ĺinked with common visible matter of the galaxy milkyway by very minute magnetic particles,.Heat particles thermions havè źero balanceď contribution to these.Unknown form of gravity is present with this make it Dark in nature.Gravity is common to both FORM of MATTER Visible(that which are in view) and Dark.Dark matter particles which constitute the FINAL minute particle of visiblè universe.
… was the amount of the dark matter always the same, or does it change, …
It is likely a temporary phenomena.
“But there are more ways to tackle the problem than trying to cook up a new particle to inhabit the universe. A pair of physicists recently used the language of quantum gravity to put down some strong constraints on the nature of the dark matter particle. The research appeared recently in Physics Letters B.”
“The research looked at both ends of the dark matter mass range. On the light end, we know that it has to be above a certain mass threshold, otherwise experiments that have examined the possible existence of a fifth force of nature would rule it out (alternatively, the dark matter could respond to that fifth force). On the heavy end, massive particles tend to decay, and we know that the dark matter has to have been in the universe for essentially its entire existence – that puts an upper bound on its size.”
[ https://www.universetoday.com/149925/narrowing-down-the-mass-of-dark-matter/ ].
So interaction with gravity says it will eventually go away. It seems part of the apparent finetuning that put our vacuum (“dark”) energy at low value so galaxies would have time to form, and the mass-decay time relationship of dark matter says that it too may be “Goldilocks” for galaxy clusters which can have life (in our universe).
It’s best not to pry too deeply into the dark is and what matter is energy and what matter doesn’t matter. Which is throwing an educated guess out there I’d say the brain accumulates Dark matter to a degree in which it makes the gravity and sleepiness almost the same until you go to sleep and then the transmutes it into dark energy and the more conscious beings are and it said location the fastest space spreads around it. There are beings you can see dark matter and there are beings who cannot and they are beings who cannot tell the difference between an orange. We should probably leave the very highly complex equations up to things like the ship on or should we call the AI Cortana?? Or are we on Aletheia?! These are questions that should be best left to people you know when it’s like to not be a person. Now if you all excuse me I have to go back to sleep in the starset society. Or what you all call the oldest house what’s the difference?! Thank Dustin Bates for everything. Tell him I said that I’m sorry I’m not a she only my soul is a dark star I guess I do kind of suck. She’s too bad I didn’t drink blood. I really liked him. I mean like I really I really did.
? In any case, dark matter is passing through us all the time, and nothing stays (no interaction apart from gravity – and we are low mass compered to the galaxy scales where lots of dark matter lumps forms).
Don’t forget that this was just a computer simulation with the assumption that Dark Matter was causing all the fuss. But Dark Matter, which is supposed to be everywhere, would cause galaxy clusters to form in all directions, but they don’t. They form in stringy lines. All of that is explained in my YouTube on the formation of dwarf galaxies, which eventually expand. See https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HZaTxgY8NQI&t=3s. And if you’re interested in Dark Matter, see https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N84yISQvGCk&t=4s.
Is it possible that the scaffolding is created by magnetic lines of flux?
The map was made purely with gravity I believe – that is the dominant interaction at those scales.
Um, who watches Star Trek: Discovery?
Incredible work
My opinion, all the evil blocking the galaxies, that’s what I think dark matter is. Negativity matter
For a possibly interesting correlation with so called “galactic conformity”, see here: https://phys.org/…aby.html .
“Three dozen dwarf galaxies far from each other had a simultaneous ‘baby boom’ of new stars, an unexpected discovery that challenges current theories on how galaxies grow and may enhance our understanding of the universe.”
Their 2013 reference on galactic conformity notes:
“The scale dependence and the precise nature of the effect depend on the mass of the central. In central galaxies with masses less than 1010 M, conformity extends out to scales in excess of 4 Mpc, well beyond the virial radii of their dark matter haloes. For low-mass central galaxies, conformity with neighbours on very large scales is only seen when they have low star formation rate or gas content. In contrast, at high stellar masses, conformity with neighbours applies in the gas-rich regime and is clearly confined to scales comparable to the virial radius of the dark matter halo of the central galaxy.”
“We speculate that the conformity between low-mass, gas-poor central galaxies and their distant neighbours may be a signature of ‘pre-heating’ of the intergalactic gas at an earlier epoch. The smaller scale conformity between high-mass, gas-rich central galaxies and their close neighbours may be a signature of ongoing gas accretion on to central galaxies in a minority of massive dark matter haloes.”
So for these dwarf galaxies putatively “pre-heating” of the environment gas applies. The cosmic web filament where the Milky Way sits seems to be a large, presumably old one as the article here describes.
“Could it be? A spider web? A gaseous entity lying at the center of the Universe. It chooses it’s victims. Could it be?” Said Charlotte.
It’s all those things and more. Limitless dimensions ever evolving dark and light matter. The more you discover and learn the more you find the vastness. These bridges act to short cut distances to make travel almost instantaneous. It won’t be long till we reach an Earth of goodness and not evil when we control population and eliminate crime. We then will be in touch with the intelligence that has succeeded in being part of the universal community.
My question would be whether these bridges could be used as a basis for an Einstein-Rosen bridge
No wonder the dark matter concept is one of the most puzzling and dramatic in contemporary cosmology. However we need a new concept of the ultimate origin and nature of the universe to put things together. So now, four years after my first book entitled In Search of Consciousness and the Theory of Everything my second book will soon be published under the title: Theory of Everything: The Ultimate Origin and Nature of the Universe and of Consciousness and Solving the Dark Matter Dark Energy Mystery. It will demonstrate the huge smount of intelligence that went into the conception of the Big Bang.
Space is Fake. None of the discoveries or theories presented are anything but mathemagical concepts formed by starting with nothing assumptions and then layering upon that nonexistent and unprovable nonsense as needed… No one ever has nor ever will observe (in the real sense of the wordl) any of this fantasy land ridiculousness. Wake up, people. Space is Fake.
Its philotic twining of the galaxies!
Why can’t I see the picture up close…
Most points on the map are the vacuum, a dynamic process we call Time. Arrows point in the direction of a lower rate of time; These arrows are gradient in the rate of time we call Gravity. RECAP: Dark matter is the stuff out there, a dynamics process (Time) which rate of evolution varies here and there as gradients or Dark Energy. This dynamic time process is both “spontaneous” and “generating”, i.e., explosive in nature.