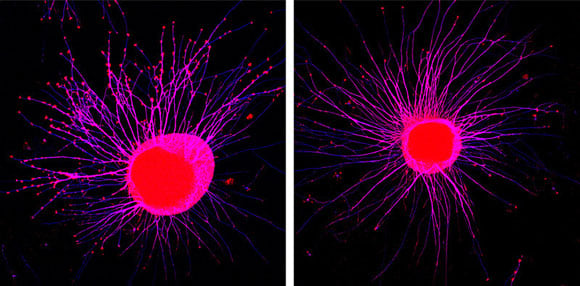
Membrane-attached signaling molecules make nerve cell filaments retract over a distance. Axonal growth cones of young neurons (left, red swellings) collapse after coming in contact with Eph receptors from exosomes (right). MPI of Neurobiology / Gong
New research reveals how cells can pack and release active ephrins and Eph receptors through extracellular vesicles, improving our understanding of intercellular communication and paving the way for new therapeutic strategies.
Eph receptors and their partner proteins, the ephrins, are vital for intercellular communication. In the developing brain, they guide young neurons to the right partner cells by repulsion. They also play important roles in cell migration, regeneration, neurodegenerative diseases and the development of cancer. Until recently, scientists assumed that ephrin/Eph signal transmission could only occur through direct cell-cell contact. However, Rüdiger Klein and his team at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology have now shown that cells can also pack and release active ephrins and Eph receptors through extracellular vesicles. Not only does this discovery improve our understanding of this communication system, it may also pave the way for new therapeutic strategies.
The human body contains up to 100 billion cells. As they grow, migrate, replicate and move, these cells come into contact with countless other cells and exchange information with them. One way this communication happens is through the ephrin/Eph-receptor system, which is able to guide cell migration and the growth of neuronal extensions. In addition, the ephrin-Eph system also plays a role in plastic processes, such as learning and regeneration, as well as in tumor growth and neurodegenerative diseases.
Eph receptors and their binding partners, the ephrins, are found on the surface of almost all cell types. When an ephrin meets the Eph receptor of another cell, they join to form an ephrin-Eph complex. This triggers processes in one or both cells that generally lead to internalization of the complex and repulsion of one cell away from the other. The repelled cell then moves or grows in another direction. In the nervous system, many such interactions guide the extensions of young neurons to their right destinations.
“This is why it’s so fundamentally important to understand how cells use this system to communicate”, says Rüdiger Klein, whose Department at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology is studying ephrins and Eph receptors. It had always seemed clear that ephrins and Ephs could only trigger a signaling process by direct contact between two cells. Recently, however, ephrins and Eph receptors have also been found in extracellular vesicles/exosomes – small droplets of fat released by cells, used as transport vehicles, signal transmitters, or for eliminating cell components. “This has thrown up the interesting question of what business Ephs and ephrins have in exosomes”, says Klein.
Intrigued, the Martinsried-based team set up an elaborate experimental study to purify the exosomes from different cell types, including neurons, and analyze their contents. They revealed that many of these exosomes contained ephrins and Ephs, and decoded the cellular mechanism by which they were packed into the exosomes. Interestingly, further analysis showed that the Eph receptors had not been dumped as waste products, but remained active on the exosomes. Eph receptors on the exosomes were able to bind to ephrin molecules on the surface of growing neurons and repel the neuronal extensions. This proves, for the first time, that cells can send ephrins and Ephs out to transmit signals over a distance. “It opens up a whole range of new possibilities”, says Rüdiger Klein. Ephrins and Eph receptors have also been found in the exosomes of cancer cells. “This might mean that strategies to control exosome release could be used to interrupt the ephrin-Eph signaling pathway and thereby disrupt tumor growth”, he surmises.
Reference: “Exosomes mediate cell contact–independent ephrin-Eph signaling during axon guidance” by Jingyi Gong, Roman Körner, Louise Gaitanos and Rüdiger Klein, 27 June 2016, Journal of Cell Biology.
DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201601085







It is correct to assume the nerve cell information transmission through Ephrins and Eph receptors in the initial stages of formation of brain and its development through actual contact since the nerve axons are not so elongated initially. After growth neurotransmitter chemicals are formed and transferred through axon ends for communication to each nerve cell and thereby to other tissues through them for motor or sensory functions. The article states that intercellular communication is through membrane attached signalling molecules through nerve filaments in the young neurons. This is an evolution of nerve signals, no doubt. Thank You.