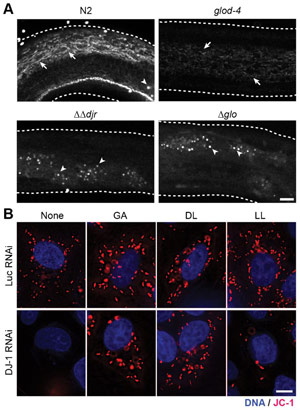
Glycolate and D-lactate are required for mitochondrial membrane potential. (A) Disruption of the mitochondrial network upon desiccation at 98% RH and rehydration in mutants for glyoxalases. Arrow, mitochondrial networks stained with MitoTracker. Arrowhead, non-specific staining of the gut granules. (B) JC-1 staining in live HeLa cells with 1 mM of glycolate (GA), D-lactate (DL), and L-lactate (LL). Red, JC-1; blue, DNA. For merged images and quantification, see Fig. 4. Scale bars: 10 µm. Credit: Yusuke Toyoda, et al.
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics show that two products of the gene DJ-1 can stop and even counteract the degeneration of neurons caused by Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease affects neurons in the Substantia nigra brain region – their mitochondrial activity ceases and the cells die. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics show that supplying D-lactate or glycolate, two products of the gene DJ-1, can stop and even counteract this process: Adding the substances to cultured HeLa cells and to cells of the nematode C. elegans restored the activity of mitochondria and prevented the degeneration of neurons. They also showed that the two substances rescued the toxic effects of the weed killer Paraquat. Cells that had been treated with this herbicide, which is known to cause a Parkinson’s like harm to mitochondria, recovered after the addition of the two substances. Both glycolic and D-lactic acids occur naturally in unripe fruits and certain kinds of yogurt.
Teymuras Kurzchalia and Tony Hyman both have labs at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics with rather different research programs – but both happened to stumble upon the gene DJ-1 and joined forces. This gene, originally thought of as an oncogene, has been linked to Parkinson’s disease since 2003. Recent studies showed that DJ-1 belongs to a novel glyxolase family. The major function of these genes is assumed to detoxify aggressive aldehyde by-products from mitochondrial metabolism. The Dresden research team now showed that the products of DJ-1, D-lactate, and glycolate, are actually required to maintain the high mitochondrial potential and thus can prevent the degeneration of neurons implicated in Parkinson’s disease.
Their experiments proved that both substances are lifesavers for neurons: Adding them to affected cells, in other words cells treated with the environmental poison Paraquat or with a down-regulated DJ-1, decreased the toxic effect of the herbicide, restored the activity of the mitochondria and thus ensured the survival of the neurons.
“We do not yet understand how exactly D-lactate and glycolate achieve this curative and preventive effect, but the next step will be to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying this process”, say Hyman and Kurzchalia. In addition to further molecular investigation, they also have more concrete plans for the future: As Kurzchalia says “We can develop a yogurt enriched with D-lactate: It could serve as a protection against Parkinson’s and is actually very tasty at the same time!“ This is why the researchers have filed a patent for their finding.
Many diseases are associated with a decline in mitochondrial activity, not only Parkinson’s. Thus, the researchers believe that the DJ1-products could have a general role in protecting cells from decline.
Reference: “Products of the Parkinson’s disease-related glyoxalase DJ-1, D-lactate and glycolate, support mitochondrial membrane potential and neuronal survival” by Yusuke Toyoda, Cihan Erkut, Francisco Pan-Montojo, Sebastian Boland, Martin P. Stewart, Daniel J. Müller, Wolfgang Wurst, Anthony A. Hyman and Teymuras V. Kurzchalia, 25 July 2014, The Company of Biologists.
DOI: 10.1242/bio.20149399




Many diseases are associated with a decline in mitochondrial activity and a dead cell cannot be rejuvenated. To stop the death something can be done prior to the onset of disease. Otherwise Levidopa is the medicine as on date and it will kindle Dopamine secretion to some extent for some time.However death of the cell is certain and it can only be delayed and nothing more. Even in Diabetes Melitus 2 , the Beta cells secrete insulin and more and more pressing them to produce insulin results in gradual depletion of its life and the disease is only progressing. An elixir has not been found so far to bring back to life the dead. Thank You.
Great post. Thanks for sharing this information