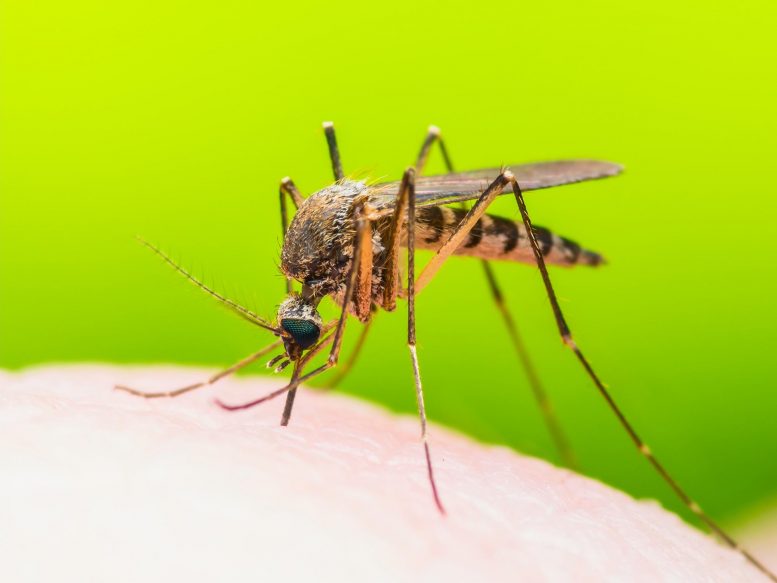

According to new research, Zika and dengue fever viruses make infected mice and humans smell more attractive to mosquitoes, causing increased spread of disease.
Dengue and Zika viruses alter the microbiome in both humans and mice to attract mosquitoes and spread to new hosts.
Zika and dengue fever viruses modify the scent of mice and humans they infect, scientists reveal in today’s (June 30) issue of the journal Cell. The altered scent attracts mosquitoes, which bite the host, drink their infected blood, and then spread the virus to its next victim.
Dengue fever is carried by mosquitoes in tropical areas around the world, and occasionally in subtropical areas such as the southeastern United States. Infected humans suffer from fever, rash, and painful aches, and it sometimes results in hemorrhage and death. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID), more than 50 million dengue cases occur every year, resulting in about 20,000 deaths, most of them in children.
Zika is another mosquito-borne viral disease in the same family as dengue. Although it is uncommon for Zika to cause serious disease in adults, a recent outbreak in South America caused serious birth defects in the unborn children of infected pregnant women. This viral family also includes yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and West Nile.
These viruses require ongoing infections in animal hosts as well as mosquitoes in order to spread. If either of these is missing—if all the susceptible hosts clear the virus, or all the mosquitoes die—the virus disappears. For example, during the yellow fever outbreak in Philadelphia in 1793, the coming of the fall frosts killed the local mosquitoes, and the outbreak ended.
In tropical climates without killing frosts, there are always mosquitoes; the virus just needs one to bite an infected host animal in order to spread. Zika and dengue viruses seem to have developed a sneaky way of increasing the odds.
A team of researchers from University of Connecticut (UConn) Health, Tsinghua University in Beijing, the Institute of Infectious Diseases in Shenzhen, the Ruili Hospital of Chinese Medicine and Dai Medicine, the Yunnan Tropical and Subtropical Animal Virus Disease Laboratory, and the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, suspected that dengue and Zika might be manipulating the hosts in some way to attract mosquitoes. Both malaria and general inflammation can change people’s scent. Viral infection by dengue and Zika, they thought, might do the same thing.
First the team tested whether mosquitoes showed a preference for infected mice. And indeed, when mosquitoes were offered a choice of healthy mice or mice sick with dengue, the mosquitoes were more attracted to the dengue-infected mice.
Then they analyzed the smelly molecules on the skin of infected and healthy mice. They identified several molecules that were more common on infected animals, and tested them individually. They applied them both to clean mice, and to the hands of human volunteers, and found that one odoriferous molecule, acetophenone, was especially attractive to mosquitoes. Skin odorants collected from human dengue patients showed the same thing: more attractive to mosquitoes and more acetophenone production.
Acetophenone is made by some Bacillus bacteria that grow on human (and mouse) skin. Normally skin produces an antimicrobial peptide that keeps Bacillus populations in check. But it turns out that when mice are infected with dengue and Zika, they don’t produce as much of the antimicrobial peptide, and the Bacillus grows faster.
“The virus can manipulate the hosts’ skin microbiome to attract more mosquitoes to spread faster!” says Penghua Wang, an immunologist at UConn Health and one of the study authors. The findings could explain how mosquito viruses manage to persist for such a long time.
Wang and his coauthors also tested a potential preventative. They gave mice with dengue fever a type of vitamin A derivative, isotretinoin, known to increase the production of the skin’s antimicrobial peptide. The isotretinoin-treated mice gave off less acetophenone, reducing their attractiveness to mosquitoes and potentially reducing the risk of infecting others with the virus.
Wang says the next step is to analyze more human patients with dengue and Zika to see if the skin odor-microbiome connection is generally true in real world conditions, and to see if isotretinoin reduces acetophenone production in sick humans as well as it does in sick mice.
Reference: “A volatile from the skin microbiota of flavivirus-infected hosts promotes mosquito attractiveness” by Hong Zhang, Yibin Zhu, Ziwen Liu, Yongmei Peng, Wenyu Peng, Liangqin Tong, Jinglin Wang, Qiyong Liu, Penghua Wang and Gong Cheng, 30 June 2022, Cell.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.016





IMHO, completely/permanently eradicating all diseases & parasites should/must be a common shared long term goal for whole humanity!
Each disease/parasite keep causing massive damage/loss/cost/labor to humanity, absolutely for sure!
Keep fighting against each/all (& keep suffering/losing) “for rest of eternity” is NOT a good/smart option, very obviously!
Especially, mosquitoes are carriers of many extremely dangerous diseases & parasites
& they do NOT have any essential function in nature (which cannot be done by many other insects)!
& so they should/must be one of highest priority targets to completely/permanently/globally eradicate!
(& of course, it would not be easy/quick/cheap! But, it is vitally important that we keep trying new ideas/solutions!)
(Also, the situation w/ mosquitoes is already bad enough that there is no reason to be scared of making it any worse, IMHO!)