
Simulated Photonic Reinforcement Learning Method Learns Faster and Aims Higher
How does a gambler maximize winnings from a row of slot machines? This question inspired the “multi-armed bandit problem,” a common task in reinforcement learning in which “agents” make choices to earn rewards. Recently, an international team of researchers, led by Hiroaki Shinkawa from the University of Tokyo, introduced an advanced photonic reinforcement learning method that transitions from the static bandit problem to a more intricate dynamic setting. Their findings were recently published in the journal, Intelligent Computing.
The success of the scheme relies on both a photonic system to enhance the learning quality and a supporting algorithm. Looking at a “potential photonic implementation,” the authors developed a modified bandit Q-learning algorithm and validated its effectiveness through numerical simulations. They also tested their algorithm with a parallel architecture, where multiple agents operate at the same time, and found that the key to accelerating the parallel learning process is to avoid conflicting decisions by taking advantage of the quantum interference of photons.
Although using the quantum interference of photons is not new in this field, the authors believe this study is “the first to connect the notion of photonic cooperative decision-making with Q-learning and apply it to a dynamic environment.” Reinforcement learning problems are generally set in a dynamic environment that changes with the agents’ actions and are thus more complex than the static environment in a bandit problem.
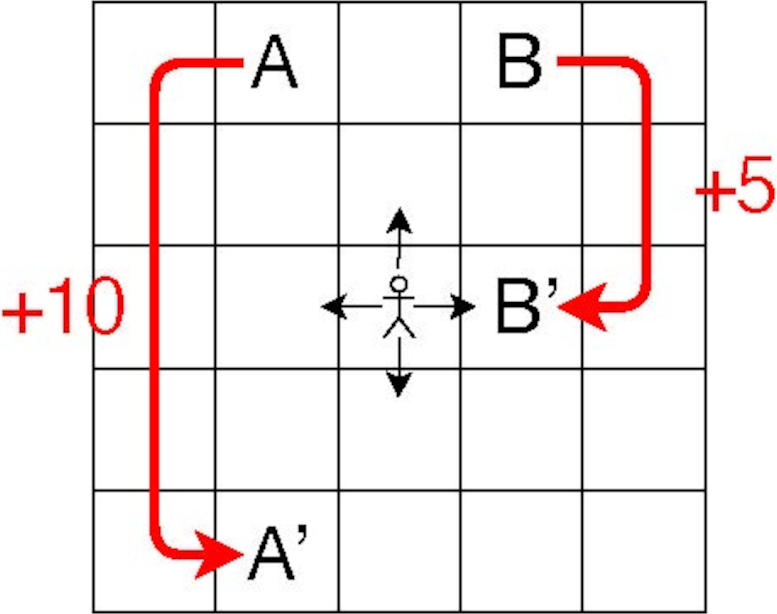
This study targets a grid world, a collection of cells holding varying rewards. Each agent can go up, down, left, or right and get a reward based on its current move and location. In this environment, the agent’s next move is determined entirely by its current move and location.
The simulations in this study use a 5 × 5 cell grid; each cell is called a “state,” every move made by an agent at each time step is called an “action,” and the rule determining how an agent selects a certain action in each state is called a “policy.” The decision-making process is designed as a bandit problem scenario, where each state-action pair is regarded as a slot machine and the changes in Q value — the values of the state-action pairs — are regarded as the rewards.
Unlike basic Q-learning algorithms, which generally focus on finding the optimal path to maximize rewards, the modified bandit Q-learning algorithm aims to learn the optimal Q value for every state-action pair in the entire environment, efficiently and accurately. Therefore, it is essential for an agent to keep a good balance between “exploiting” the familiar pairs with high values for faster learning and “exploring” unfrequented pairs for potentially higher values. The softmax algorithm, a popular model that excels in this kind of balancing, is used as the policy.
The authors’ future priority is to design a photonic system supporting conflict-free decision-making among at least three agents, hoping its addition to their proposed scheme will help agents avoid making conflicting decisions. Meanwhile, they are planning to develop algorithms that allow agents to act continuously and to apply their bandit Q-learning algorithm to more complicated reinforcement learning tasks.
Reference: “Bandit Approach to Conflict-Free Parallel Q-Learning in View of Photonic Implementation” by Hiroaki Shinkawa, Nicolas Chauvet, André Röhm, Takatomo Mihana, Ryoichi Horisaki, Guillaume Bachelier and Makoto Naruse, 25 July 2023, Intelligence Computing.
DOI: 10.34133/icomputing.0046
The study was funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.