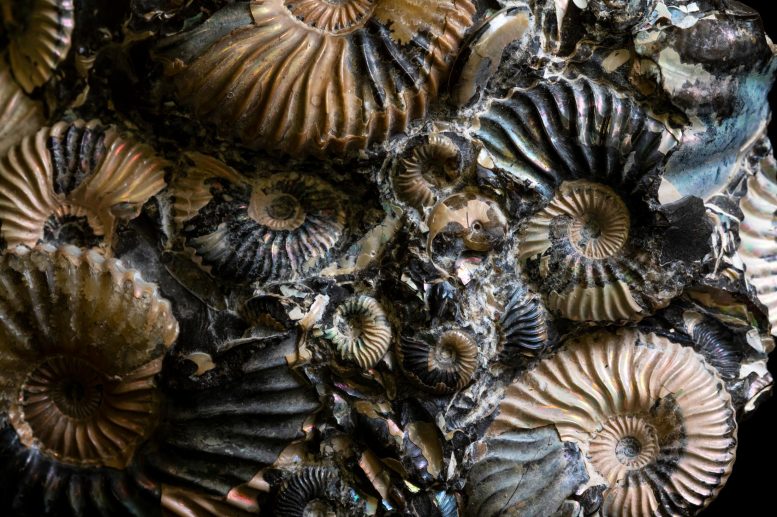

Predator-prey interactions reshaped ocean life, adding a fourth evolutionary phase to the fossil record’s three-fauna model.
Evolutionary arms races between marine animals overhauled ocean ecosystems on scales similar to the mass extinctions triggered by global disasters, a new study shows.
Scientists at Umeå University in Sweden and the Florida Museum of Natural History used paleontological databases to build a multilayered computer model of the history of marine life over the last 500 million years. Their analysis of the fossil record closely echoed a seminal 1981 study by paleontologist J. John Sepkoski – with one key difference.
Sepkoski’s ground-breaking statistical work showed abrupt ocean-wide changes in biodiversity about 490 and 250 million years ago, corresponding to two mass extinction events. These events divided marine life into what he called “three great evolutionary faunas,” each dominated by a unique set of animals.
But the new model reveals a fourth.
The fierce fight for survival that played out between predatory marine animals and their prey about 250 to 66 million years ago may have been an equally powerful force, reshaping ocean diversity into what we see today. This third grand transition was much more gradual than its predecessors and driven by organisms, rather than external processes.

Biology, Not Catastrophe, Reshaped Ocean Life
“What we learned is that not all major shifts in animal life have been related to mass extinction events,” said study lead author Alexis Rojas, who earned his Ph.D. at the University of Florida. Rojas is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Integrated Science Lab, a hub dedicated to interdisciplinary research at Umeå University.
Many scientists have long held the view that external factors such as volcanic activity, asteroid impacts or changes in climate are the primary drivers of major shifts in the Earth’s biosphere, said study co-author Michal Kowalewski, Rojas’ doctoral adviser and the Florida Museum Thompson Chair of Invertebrate Paleontology.
“The fossil record tells us that some of the key transitions in the history of life were rapid changes triggered by abrupt external factors. But this study shows that some of those major transitions were more gradual and may have been driven by biological interactions between organisms,” he said.

Sepkoski’s Vision: Simplifying the Complexity of the Fossil Record
One reason Sepkoski’s work was so revolutionary was that he took a mathematical approach to a practical problem: The fossil record is too big and complex for one person to be able to discern life’s underlying patterns by looking at specimens alone.
“When its components are examined individually or in small groups, the complexity of their form, function, interaction, and history often seems overwhelming, and almost infinite,” he wrote in the introduction to his 1981 study.
Organizing these components into a hierarchy of systems, he argued, presented a more complete view. Sepkoski’s modeling divided 500 million years of ocean life into three great dynasties, each separated by a mass extinction that cleared the way for new groups to flourish and dominate. After the reign of trilobites, clamlike animals known as brachiopods and certain ancient corals and ammonites rose to prominence. After the cataclysmic end-Permian extinction, sometimes known as the “Great Dying,” they were in turn replaced by snails, clams, crustaceans, modern corals, and various kinds of bony fishes.

Sepkoski’s hypothesis fundamentally changed how scientists thought about the history of life, Kowalewski said. It offered an organized way of understanding the history of marine ecosystems – the overarching storyline and plot twists.
But as our knowledge of the fossil record grows, so does Sepkoski’s dilemma of how to analyze such vast and complex information, said Kowalewski.
“With millions of fossil specimens now documented, there is simply no feasible way for our brains to process such massive archives of paleontological data,” he said. “Fortunately, analytical methods continue to improve, giving us better ways to extract and examine information hidden inside these immensely complex data.”
A Modern Lens on Ancient Life
Rojas took on this challenge by using the latest advancements in data modeling. Specifically, he was interested in using complex network tools to create a better representation of the fossil record. Unlike other approaches in paleobiology, complex networks use a linked structure of nodes representing physical and abstract variables to uncover underlying patterns in a given system. Network approaches can be applied to social phenomena – for example, showing a Facebook user’s patterns of interactions with friends on the platform – but they can also be applied to complex natural systems. Like Sepkoski, Rojas is a classically trained paleontologist looking for a fresh perspective on the fossil record.

“There are many processes happening at the same time at multiple scales: in your neighborhood, your country, and across the entire planet. Now imagine the processes that occur in one day, one year, or 500 years. What we are doing is trying to understand all these things across time,” he said.
A simple network might consist of a single layer – all records of animal life and where they lived. But Rojas and his colleagues’ network incorporates different intervals of time as individual layers, a feature lacking in previous research on macroevolution. The result is what Rojas described as a new, abstracted fossil record, a complement to the physical fossil record represented by the specimens in museum collections.

“It’s important because the questions we are asking, the processes we are studying, occur at different scales in time and space,” Rojas said. “We’ve taken some steps back so we can look at the entire fossil record. By doing that, we can explore all sorts of questions.”
Think of it like navigating a Google Earth that represents the oceans over the last 500 million years. When and where would you go?
“Our interactive map of marine life shows smaller groups of animals and their interactions within each evolutionary fauna,” Rojas said. “At the most basic levels, this map shows ocean regions with particular animals. The building blocks of our study are the individual animals themselves.”
The Mesozoic Marine Revolution: A Gradual Overhaul
This complex network shows what Sepkoski’s model could not capture: a gradual transition in ocean life coincident with the Mesozoic Marine Revolution, which began about 150 million years ago. First hypothesized in the 1970s, this revolution was caused by the rapid increase of marine predators such as bony fish, crustaceans and snails, which have dominated oceans ever since. Their proliferation drove prey to become more mobile, hide beneath the ocean floor or enhance their defenses by thickening their armor, developing spines, or improving their ability to regenerate body parts.
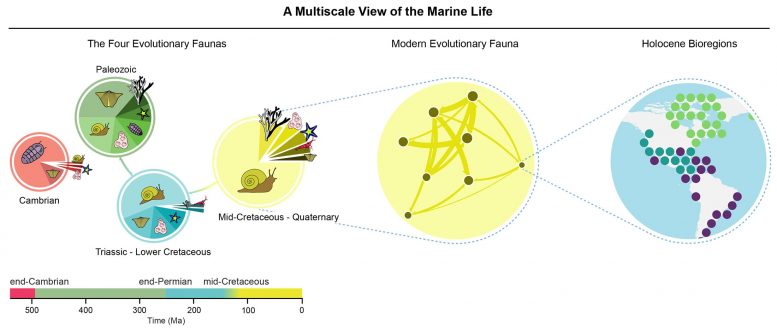
Sepkoski knew about the Mesozoic Marine Revolution, but his model, limited by the methods and data available at the time, was unable to delineate the ocean ecosystems preceding and following this gradual transition. The study by Rojas and his colleagues demonstrates that both physical and biological processes play key roles in shaping ocean life at the highest levels.
“We are integrating the two hypotheses – the Mesozoic Marine Revolution and the three great evolutionary faunas into a single story,” Rojas said. “Instead of three phases of life, the model shows four.”
Reference: “A multiscale view of the Phanerozoic fossil record reveals the three major biotic transitions” by Alexis Rojas, Joaquin Calatayud, Michał Kowalewski, Magnus Neuman and Martin Rosvall, 8 March 2021, Communications Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01805-y
Joaquin Calatayud, Magnus Neuman and Martin Rosvall of Umeå University also co-authored the study.
The team published its results in Communications Biology.
Support for the research was provided by the Olle Engkvist Byggmästare Foundation, the Carl Trygger Foundation and the Swedish Research Council.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.