After the breach of Kakhovka Dam and the flood that ensued, farmers in the area are coping with depleted water supplies.
The breach of the Kakhovka Dam in June 2023 has led to a water crisis in southern Ukraine, threatening farmland and global food supplies. NASA’s Harvest Consortium is monitoring the situation and developing satellite-based tools to assess the impact, while authorities warn of potential desertification by 2024.
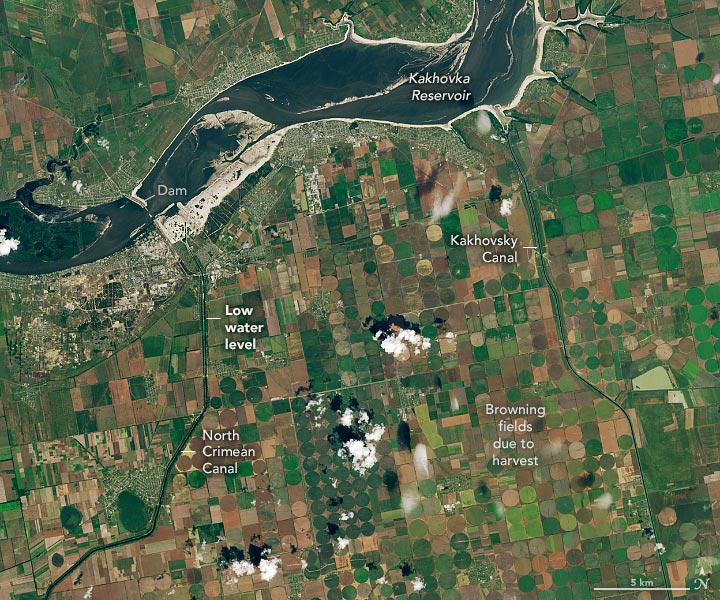


The Breach of Kakhovka Dam
On June 6, 2023, when the Kakhovka Dam was breached, water surged from the adjacent reservoir into the Dnipro River towards the city of Kherson and the Black Sea. This caused severe downstream flooding. Although the floodwaters began to recede after a few weeks, a slower-moving water crisis unfolded in southern Ukraine, where canals previously fed by the Kakhovka Reservoir are running dry.
Monitoring the Impact
Scientists with NASA’s Harvest Consortium have been closely monitoring the situation. Their primary focus is to understand the impact of this event on farmers. The research is part of a broader effort to develop analytical tools, based on satellite observations, to quickly assess how crop conditions and the war in Ukraine are affecting global food supplies.
“The major challenge for farmers now is lack of water,” said Inbal Becker-Reshef, NASA Harvest’s director. “Networks of canals that are normally fed by the Kakhovka Reservoir have become disconnected from the reservoir and are drying out.”
Analysis by NASA Harvest shows that all four of the major inlets that supply the canal networks have been disconnected. While abundant rainfall in spring and early summer prevented the canals from going completely dry, satellite observations show a narrowing of the canals suggesting large reductions in the amount of water.

Potential Desertification
The Ministry of Agrarian Policy and Food of Ukraine noted that the loss of water for hundreds of thousands of hectares could turn farmland in this area into “deserts” by 2024. The lack of irrigation could also have ripple effects that cause farmers to produce fewer crops on non-irrigated fields due to loss of income, according to the ministry. “A million and a half hectares will not be used to their full potential,” said Mykola Solskyi, the minister of agrarian policy and food of Ukraine.
Visual Documentation
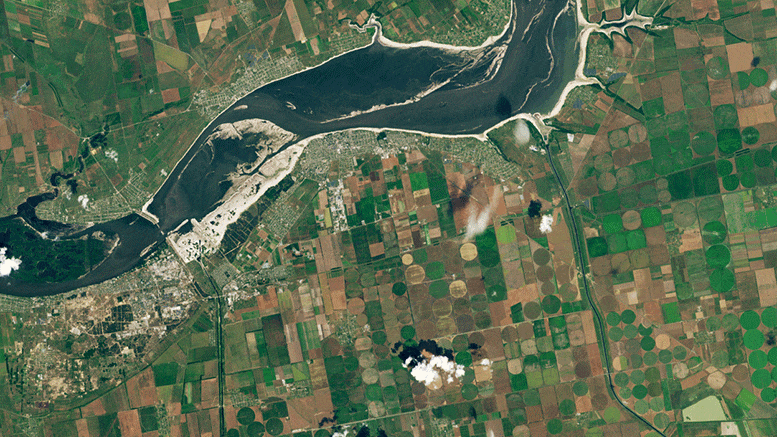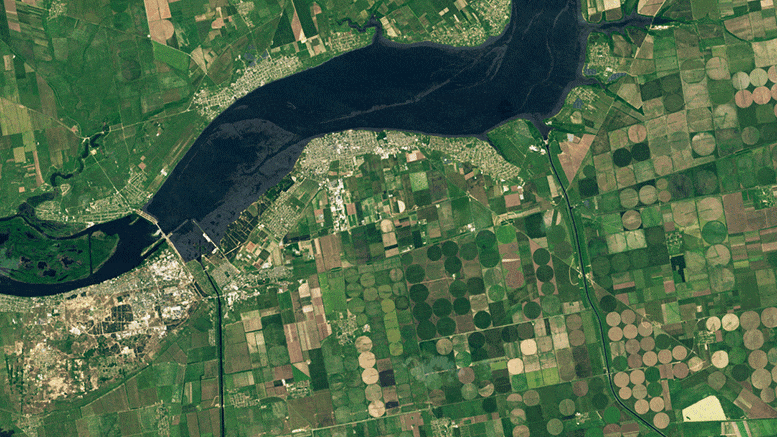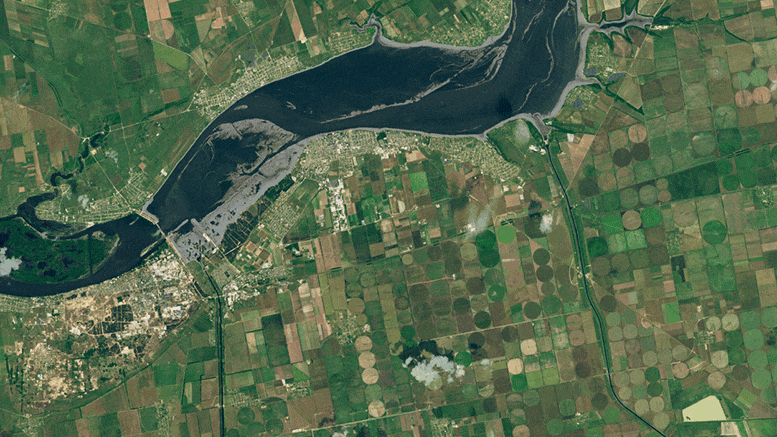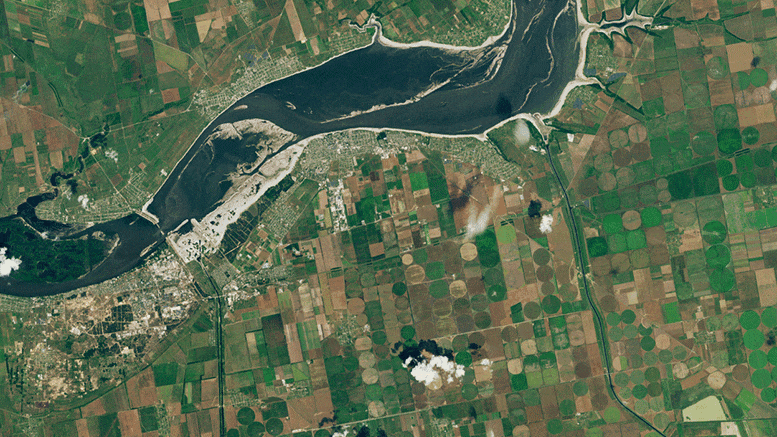
Inlets to the North Crimean Canal and the Kakhovsky Canal—two of the four major canal networks fed by the Kakhovka Reservoir—are visible in the images at the top of the page. The left image shows the inlets on May 17, 2023, when they were full of water. The second image shows the same canals on June 18, after water levels in the reservoir had dropped below what is required for water to enter the canals. Both images were acquired with Landsat 9’s Operational Land Imager-2 (OLI-2). (Note that the apparent browning in the center-pivot fields is due to the normal harvest cycle, not lack of water. As winter wheat and other crops are harvested and tilled, the fields appear brown before the next crop is planted.)
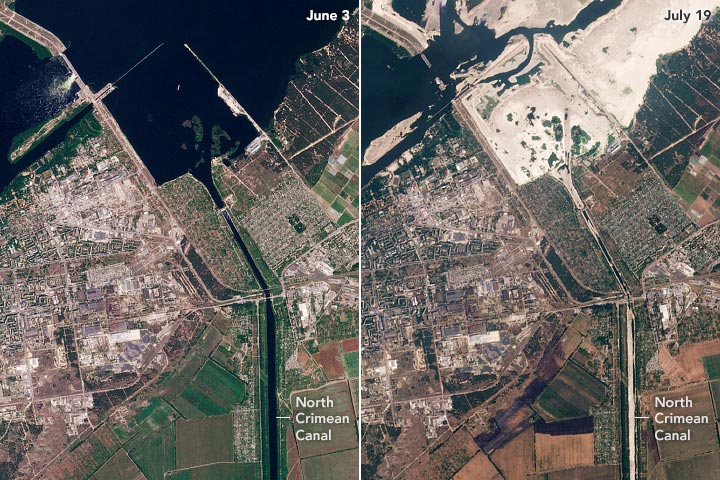
The pair of images above, from Planet Labs, shows a closer view of changes at the inlet of the North Crimean Canal. The left image shows the canal on June 3, 2023. The second image shows the same area on July 19, 2023, as the inlet and canal were drying up.
Crops at Risk
“Many of the summer crops grown in Kherson—such as corn, wheat, sunflower, tomatoes, and melons—are heavily reliant on irrigation, and summer rains are unlikely to be sufficient to maintain crop health and average yields of irrigated crops,” said Becker-Reshef.
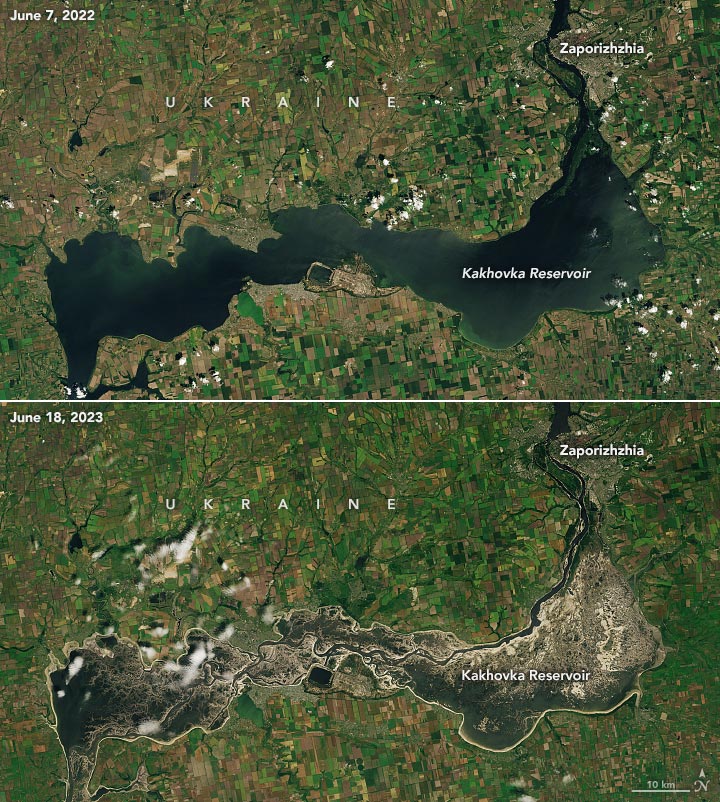

Satellite Imaging
The reason for the irrigation challenges is apparent in the pair of satellite images above. After the dam breach, the reservoir that once sustained the canals mostly emptied, exposing broad expanses of mud. The top image of the pair was acquired by OLI on Landsat 8 on June 7, 2022, about one year before the dam was damaged. The bottom image, acquired by OLI-2 on Landsat 9, shows the same area on June 18, after roughly 75 percent of the water in the reservoir had drained—a volume of water roughly equivalent to Utah’s Great Salt Lake.
Satellite altimetry data provided by the U.S. Foreign Agriculture Service and the French data services center (Theia) confirmed that water levels dropped by several meters over a few days soon after the dam failed. This came after water levels had climbed to a 30-year high following a wet spring.
Flooding Impacts
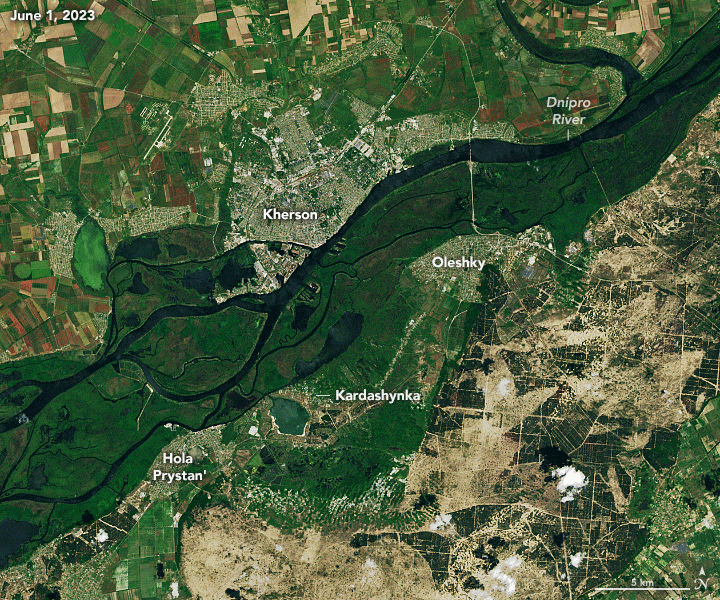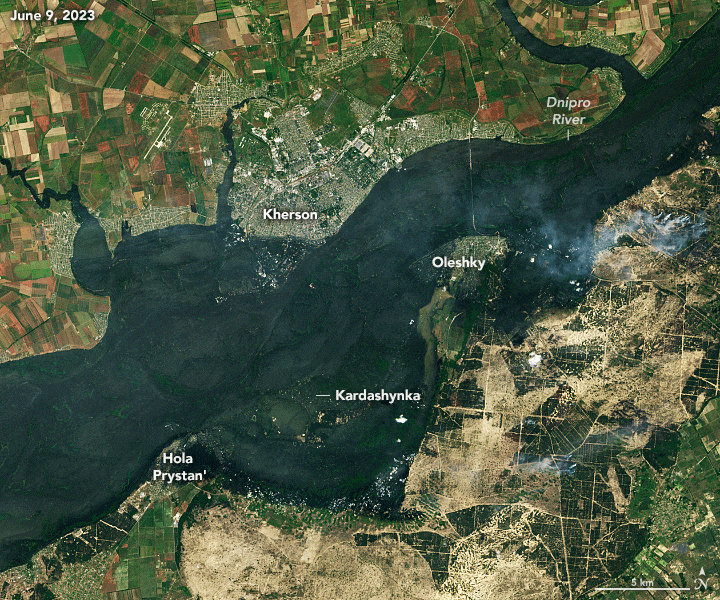
The image below shows flooding along the Dnipro River on June 9, 2023, three days after the dam was breached. For comparison, the other image shows the same area on June 1, 2023. The most severe flooding was on the east side of the river, which is at an overall lower elevation and more flood prone than the west side. During the worst of the flooding, several thousand homes were inundated, tens of thousands of people lost power, and more than 40,000 were forced to evacuate. Images before and during the flooding were acquired by the OLI on Landsat 8 and OLI-2 on Landsat 9, respectively.
Efforts by NASA Harvest
The NASA Harvest team—in partnership with Sertit (University of Strasbourg)—used Planet and Sentinel-3 data to produce a comprehensive map of flooded croplands, flooded villages, and open water that they provided to the Ukrainian Ministry of Agriculture as part of the humanitarian response efforts following the dam breach. They also continue to monitor the main canal inlets from the Kakhovka Reservoir and are developing methods to use satellites to track how much irrigation water fields receive throughout the summer.
Crop Health Monitoring
NASA Harvest analysts will also be monitoring the health of crops using tools such as the GIMMS Global Agricultural Monitoring tool and the AGMET EO Indicator dashboard. These tools had not yet shown a major drop in the greenness of crops by early July 2023 due to regular rains, though the loss of irrigation water could begin to brown crops in the future.
Effects on Ukraine’s Agriculture
The semiarid steppe ecosystems found in the Kherson, Zaporizhzhia, and Dnipropetrovsk oblasts generally receive 100 to 120 millimeters (4 to 5 inches) of rain during the summer growing season—not typically enough for some crops to thrive without irrigation. More than 12,000 kilometers of canals constructed since the 1960s have provided irrigation water for up to 500,000 hectares (1,900 square miles) of croplands, turning the region into one of the most productive farming regions in Ukraine. Canal water is also used for drinking water, industry, and other public uses.
Grain Exports Affected
According to estimates from the Ukrainian Grain Council, the flood could lead to a 14 percent reduction in the volume of Ukraine’s grain exports. In late June 2023, NASA Harvest estimated that Ukraine would produce 25 million tons of wheat this year, about two million tons lower than the five-year average. NASA Harvest will continue to monitor the situation in the coming months and will post updates in its news feed.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Lauren Dauphin using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey, and Planet Labs images courtesy of Inbal Becker-Reshef.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.