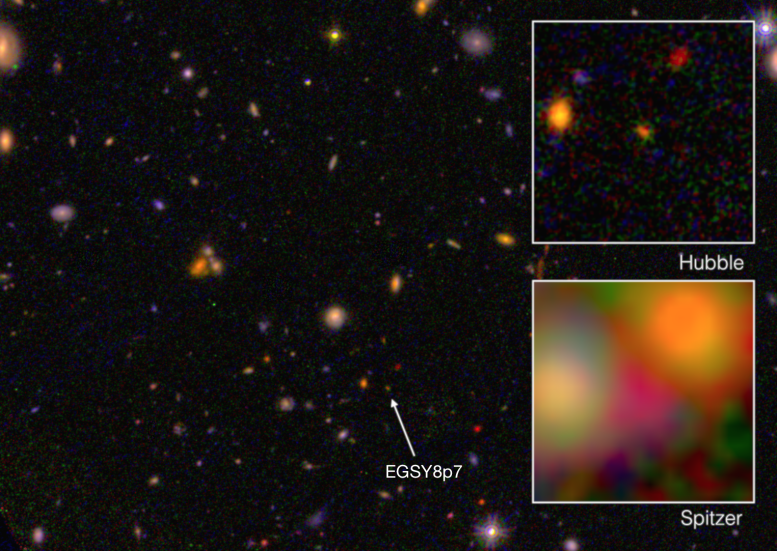
Using the multi-object spectrometer for infrared exploration at the W.M. Keck Observatory, astronomers have discovered the farthest galaxy to date – EGS8p7.
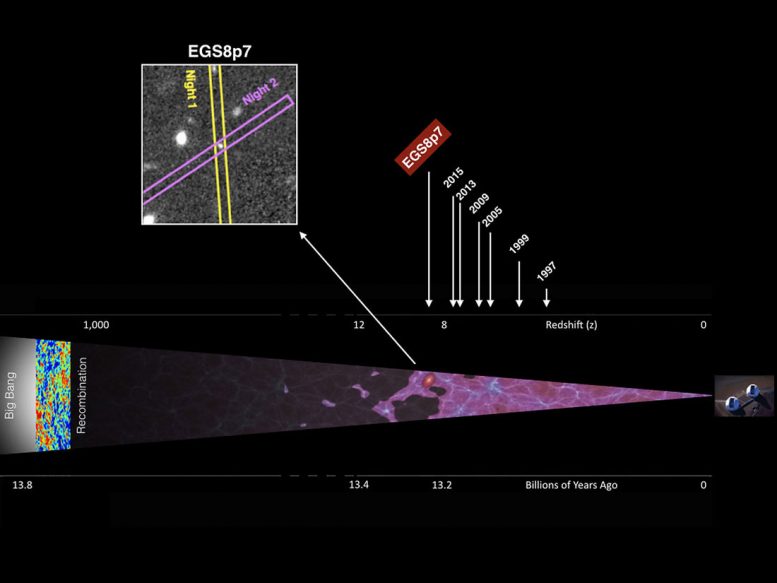
A team of Caltech researchers that has spent years searching for the earliest objects in the universe now reports the detection of what may be the most distant galaxy ever found. In an article published August 28, 2015 in Astrophysical Journal Letters, Adi Zitrin, a NASA Hubble Postdoctoral Scholar in Astronomy, and Richard Ellis—who recently retired after 15 years on the Caltech faculty and is now a professor of astrophysics at University College, London—describe evidence for a galaxy called EGS8p7 that is more than 13.2 billion years old. The universe itself is about 13.8 billion years old.
Earlier this year, EGS8p7 had been identified as a candidate for further investigation based on data gathered by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the Spitzer Space Telescope. Using the multi-object spectrometer for infrared exploration (MOSFIRE) at the W.M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii, the researchers performed a spectrographic analysis of the galaxy to determine its redshift. Redshift results from the Doppler effect, the same phenomenon that causes the siren on a fire truck to drop in pitch as the truck passes. With celestial objects, however, it is light that is being “stretched” rather than sound; instead of an audible drop in tone, there is a shift from the actual color to redder wavelengths.
Redshift is traditionally used to measure distance to galaxies, but is difficult to determine when looking at the universe’s most distant—and thus earliest—objects. Immediately after the Big Bang, the universe was a soup of charged particles—electrons and protons—and light (photons). Because these photons were scattered by free electrons, the early universe could not transmit light. By 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe had cooled enough for free electrons and protons to combine into neutral hydrogen atoms that filled the universe, allowing light to travel through the cosmos. Then, when the universe was just a half-billion to a billion years old, the first galaxies turned on and reionized the neutral gas. The universe remains ionized today.
Prior to reionization, however, clouds of neutral hydrogen atoms would have absorbed certain radiation emitted by young, newly forming galaxies—including the so-called Lyman-alpha line, the spectral signature of hot hydrogen gas that has been heated by ultraviolet emission from new stars, and a commonly used indicator of star formation.
Because of this absorption, it should not, in theory, have been possible to observe a Lyman-alpha line from EGS8p7.
“If you look at the galaxies in the early universe, there is a lot of neutral hydrogen that is not transparent to this emission,” says Zitrin. “We expect that most of the radiation from this galaxy would be absorbed by the hydrogen in the intervening space. Yet still we see Lyman-alpha from this galaxy.”
They detected it using the MOSFIRE spectrometer, which captures the chemical signatures of everything from stars to distant galaxies at near-infrared wavelengths (0.97-2.45 microns, or millionths of a meter).
“The surprising aspect about the present discovery is that we have detected this Lyman-alpha line in an apparently faint galaxy at a redshift of 8.68, corresponding to a time when the universe should be full of absorbing hydrogen clouds,” Ellis says. Prior to their discovery, the farthest detected galaxy had a redshift of 7.73.
One possible reason the object may be visible despite the hydrogen-absorbing clouds, the researchers say, is that hydrogen reionization did not occur in a uniform manner. “Evidence from several observations indicate that the reionization process probably is patchy,” Zitrin says. “Some objects are so bright that they form a bubble of ionized hydrogen. But the process is not coherent in all directions.”
“The galaxy we have observed, EGS8p7, which is unusually luminous, may be powered by a population of unusually hot stars, and it may have special properties that enabled it to create a large bubble of ionized hydrogen much earlier than is possible for more typical galaxies at these times,” says Sirio Belli, a Caltech graduate student who worked on the project.
“We are currently calculating more thoroughly the exact chances of finding this galaxy and seeing this emission from it, and to understand whether we need to revise the timeline of the reionization, which is one of the major key questions to answer in our understanding of the evolution of the universe,” Zitrin says.
The paper was co-authored by Ivo Labbe, Rychard Bouwens, Guido Roberts-Borsani, Daniel P. Stark, Pascal A. Oesch, and Renske Smit. The research was sponsored by NASA through a Hubble Fellowship, the Institute of Astronomy at the University of Edinburgh, and the National Science Foundation. MOSFIRE was made possible by funding provided by the National Science Foundation and astronomy benefactors Gordon and Betty Moore. Cooperating institutions include Yale University, the University of Arizona, University College London, Leiden University (Netherlands), and the University of Durham (UK).
Reference: “Lyman-alpha Emission from a Luminous z=8.68 Galaxy: Implications for Galaxies as Tracers of Cosmic Reionization” by Adi Zitrin, Ivo Labbe, Sirio Belli, Rychard Bouwens, Richard S. Ellis, Guido Roberts-Borsani, Daniel P. Stark, Pascal A. Oesch and Renske Smit, 28 August 2015, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.1088/2041-8205/810/1/L12
arXiv: 1507.02679
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
1 Comment
That would be 775 nonillion miles more or less, yes?