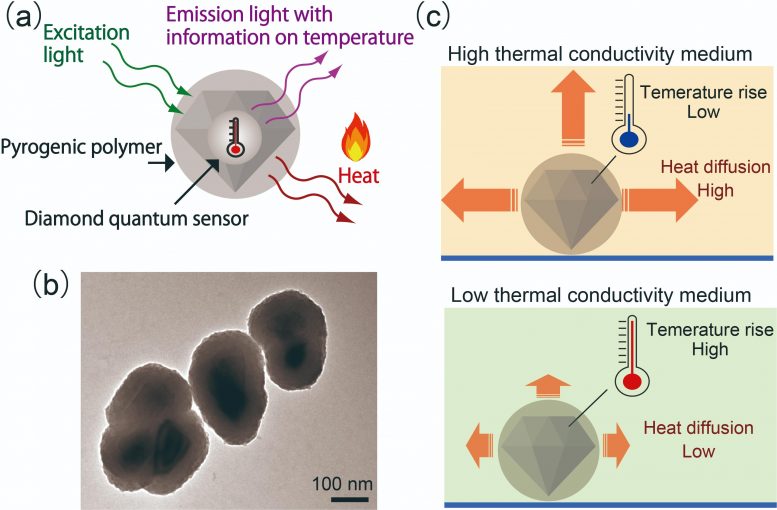
An international team of researchers created nanodiamond sensors that can act as both heat sources and thermometers, and is using them to measure the thermal conductivity inside living cells, which may lead to new diagnostics tools and cancer therapies.
A team of scientists from Osaka University, The University of Queensland, and the National University of Singapore’s Faculty of Engineering used tiny nanodiamonds coated with a heat-releasing polymer to probe the thermal properties of cells. When irradiated with light from a laser, the sensors acted both as heaters and thermometers, allowing the thermal conductivity of the interior of a cell to be calculated. This work may lead to a new set of heat-based treatments for killing bacteria or cancer cells.
The Mystery of In-Cell Thermal Conductivity
Even though the cell is the fundamental unit of all living organisms, some physical properties have remained difficult to study in vivo. For example, a cell’s thermal conductivity, as well as the rate that heat can flow through an object if one side is hot while the other side is cold, remained mysterious. This gap in our knowledge is important for applications such as developing thermal therapies that target cancer cells, and for answering fundamental questions about cell operation.
Creating Smart Nanodiamond Sensors
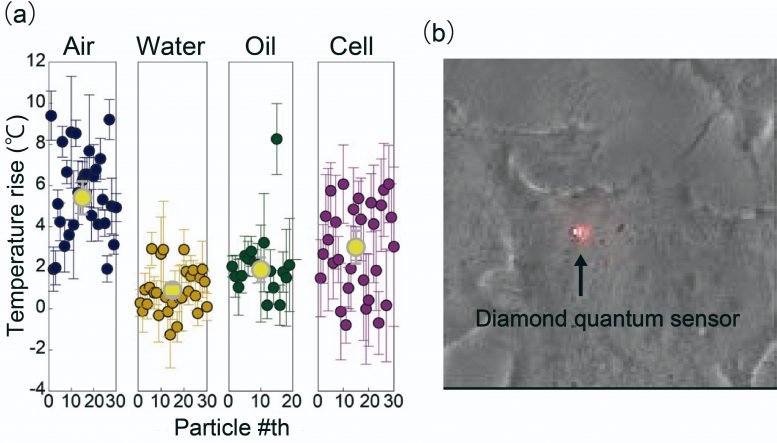
Now, the team has developed a technique that can determine the thermal conductivity inside living cells with a spatial resolution of about 200 nm. They created tiny diamonds coated with a polymer, polydopamine, that emit both fluorescent light as well as heat when illuminated by a laser. Experiments showed that such particles are non-toxic and can be used in living cells. When inside a liquid or a cell, the heat raises the temperature of the nanodiamond. In media with high thermal conductivities, the nanodiamond did not get very hot because heat escaped quickly, but in an environment of low thermal conductivity, the nanodiamonds became hotter. Crucially, the properties of the emitted light depend on the temperature, so the research team could calculate the rate of heat flow from the sensor to the surroundings.
Having good spatial resolution allowed measurements in different locations inside the cells. “We found that the rate of heat diffusion in cells, as measured by the hybrid nanosensors, was several times slower than in pure water, a fascinating result which still waits for a comprehensive theoretical explanation and was dependent on the location,” senior author Taras Plakhotnik says.
“In addition to improving heat-based treatments for cancer, we think potential applications for this work will result in a better understanding of metabolic disorders, such as obesity,” senior author Madoka Suzuki says. This tool may also be used for basic cell research, for example, to monitor biochemical reactions in real time.
Reference: “In situ measurements of intracellular thermal conductivity using heater thermometer hybrid diamond nanosensors” by Shingo Sotoma, Chongxia Zhong, James Chen Yong Kah, Hayato Yamashita, Taras Plakhotnik, Yoshie Harada and Madoka Suzuki, 15 January 2021, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd7888
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.