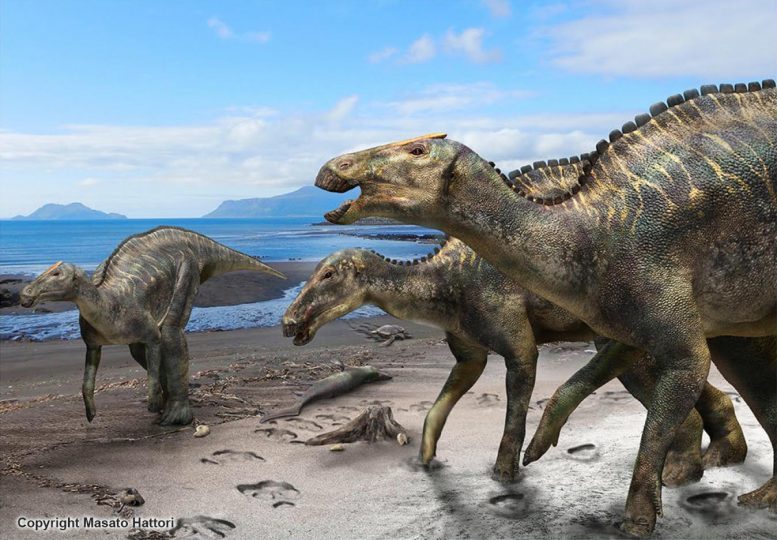

This is a reconstruction of Kamuysaurus japonicus. Credit: Kobayashi Y., et al, Scientific Reports, September 5, 2019
The dinosaur, whose nearly complete skeleton was unearthed from 72 million-year-old marine deposits in Mukawa Town in northern Japan, belongs to a new genus and species of herbivorous hadrosaurid dinosaur, according to the study published in Scientific Reports. The scientists named the dinosaur Kamuysaurus japonicus.
A partial tail of the dinosaur was first discovered in the outer shelf deposits of the Upper Cretaceous Hakobuchi Formation in the Hobetsu district of Mukawa Town, Hokkaido, in 2013. Ensuing excavations found a nearly complete skeleton that is the largest dinosaur skeleton ever found in Japan. It’s been known as “Mukawaryu,” nicknamed after the excavation site.
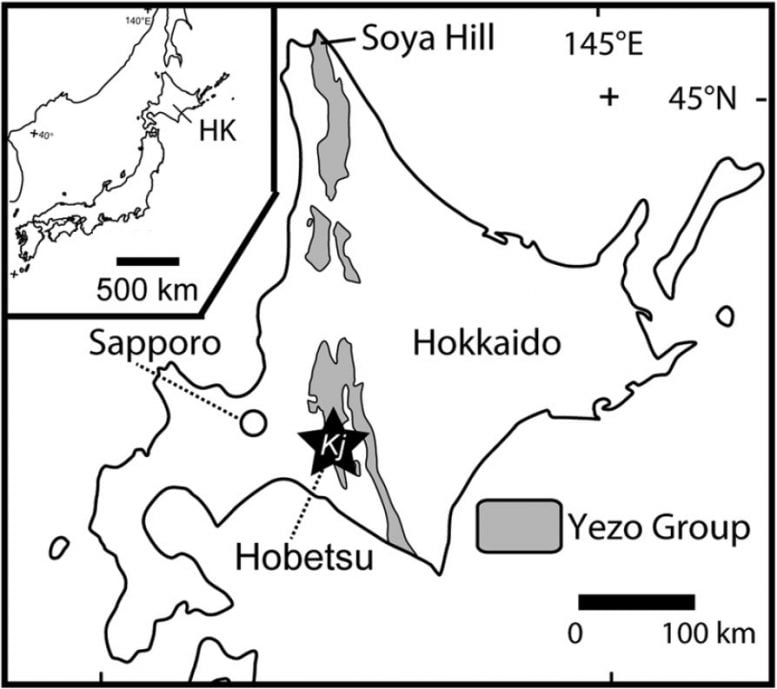
Map of Hokkaido showing the location of Hobetsu district where Kamuysaurus (black star labeled “Kj”) was excavated. Credit: Kobayashi Y., et al, Scientific Reports, September 5, 2019
In the current study, a group of researchers led by Professor Yoshitsugu Kobayashi of the Hokkaido University Museum conducted comparative and phylogenetic analyses on 350 bones and 70 taxa of hadrosaurids, which led to the discovery that the dinosaur belongs to the Edmontosaurini clade, and is closely related to Kerberosaurus unearthed in Russia and Laiyangosaurus found in China.

A fossilized skeleton of Kamuysaurus japonicus was first discovered in the Hobetsu district of Mukawa Town, Hokkaido, in 2013. Ensuing excavations found a nearly complete skeleton (above), currently the largest dinosaur skeleton ever found in Japan. Credit: Kobayashi Y., et al, Scientific Reports, September 5, 2019
The research team also found that Kamuysaurus japonicus, or the deity of Japanese dinosaurs, has three unique characteristics that are not shared by other dinosaurs in the Edmontosaurini clade: the low position of the cranial bone notch, the short ascending process of the jaw bone, and the anterior inclination of the neural spines of the sixth to twelfth dorsal vertebrae.
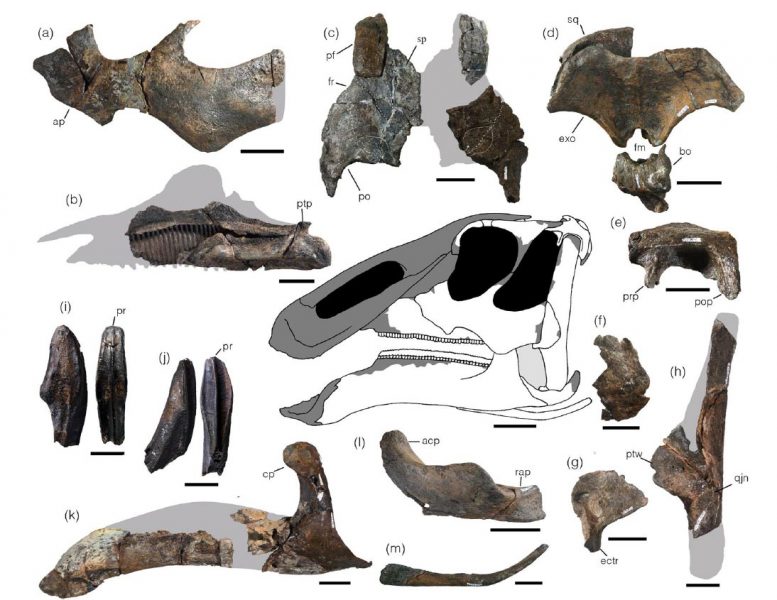
Selected skull elements of Kamuysaurus japonicus. Its unique characteristics include the low position of the cranial bone notch (quadratojugal notch, qjn) and the short ascending process of the jaw bone (surangular, acp). Credit: Kobayashi Y., et al, Scientific Reports, September 5, 2019
According to the team’s histological study, the dinosaur was an adult aged 9 or older, measured 8 meters (26 feet) long and weighed 4 tons or 5.3 tons (depending on whether it was walking on two or four legs respectively) when it was alive. The frontal bone, a part of its skull, has a big articular facet connecting to the nasal bone, suggesting the dinosaur may have had a crest. The crest, if it existed, is believed to resemble the thin, flat crest of Brachylophosaurus subadults, whose fossils have been unearthed in North America.
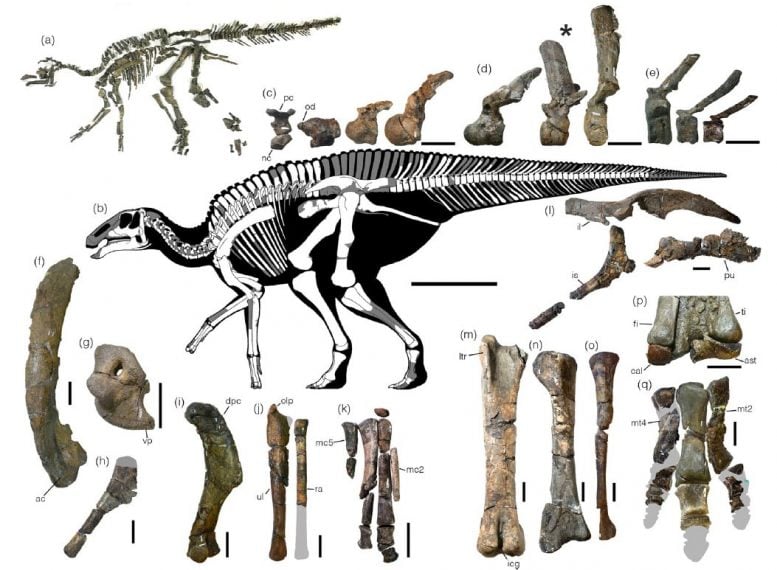
Holotype skeleton of Kamuysaurus japonicus (a). Reconstructed skeleton showing recovered elements in white (b). Its unique characteristics include the anterior inclination of neural spines of the sixth to twelfth dorsal vertebrae (*). Credit: Kobayashi Y., et al, Scientific Reports, September 5, 2019
The study also shed light on the origin of the Edmontosaurini clade and how it might have migrated. Its latest common ancestors spread widely across Asia and North America, which were connected by what is now Alaska, allowing them to travel between the two continents. Among them, the clade of Kamuysaurus, Kerberosaurus, and Laiyangosaurus inhabited the Far East during the Campanian, the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous epoch, before evolving independently.
The research team’s analyses pointed to the possibility that ancestors of hadrosaurids and its subfamilies, Hadrosaurinae and Lambeosaurinae, preferred to inhabit areas near the ocean, suggesting the coastline environment was an important factor in the diversification of the hadrosaurids in its early evolution, especially in North America.
###
Reference: “A New Hadrosaurine (Dinosauria: Hadrosauridae) from the Marine Deposits of the Late Cretaceous Hakobuchi Formation, Yezo Group, Japan” by Yoshitsugu Kobayashi, Tomohiro Nishimura, Ryuji Takasaki, Kentaro Chiba, Anthony R. Fiorillo, Kohei Tanaka, Tsogtbaatar Chinzorig, Tamaki Sato and Kazuhiko Sakurai, 5 September 2019, Scientific Reports.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-48607-1








Be the first to comment on "New Genus and Species of Dinosaur Identified From the Largest Dinosaur Skeleton Ever Found in Japan"