A new quantum theory developed by scientists at the City University of Hong Kong provides unprecedented insights into the ‘light-induced phase’ of matter, offering potential to revolutionize quantum photonics and control at room temperature. The theory significantly advances our understanding of the excited state dynamics and optical properties of molecules, improving light-harvesting technologies and paving the way for breakthroughs in optical communications, biological imaging, and quantum metrology.
A team led by a physicist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently developed a new quantum theory that explains the “light-induced phase” of matter and predicts its novel functionalities. The new theory has the potential to revolutionize the field of quantum photonics and quantum control at room temperature. It also opens the door to a variety of next-generation light-based applications, such as optical communications, quantum computing and light-harvesting technologies.
Scientists have found exotic phases in matter, in addition to the usual ones, known as the solid, liquid, and gas phases. And in different phases in which the atoms undergo certain arrangements in space, the matter may have different properties. As one category of the newly discovered phases, light-induced phases have drawn a lot of attention from scientists in the past decade, as they have been regarded as a promising platform for new photovoltaic panels and new chemical platforms, as well as a new avenue for modern quantum technology.

A Novel Quantum Theory to Overcome Limitations
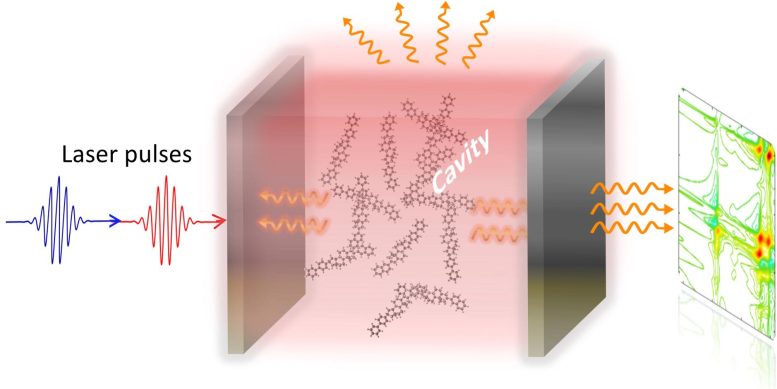
“The ultrafast processes of photoactive molecules, such as electron transfer and energy redistribution, which are typically at the femtosecond scale (10-15s), are of extensive importance for light-harvesting devices, energy conversion, and quantum computing,” explained Dr. Zhang Zhedong, Assistant Professor of Physics at CityU, who led the study. “However, the research on these processes is full of obscurities. Most of the existing theories related to light-induced phases are bottlenecked by time and energy scales and therefore cannot explain the transient properties and ultrafast processes of molecules when short laser pulses come into play. These impose a fundamental limit for exploring the light-induced phases of matter.”
To tackle these difficulties, Dr. Zhang and his collaborators developed a novel quantum theory for the optical signals of the light-induced phases of molecules, which is the first in the world. The new theory, through mathematical analysis in conjunction with numerical simulations, explains the excited state dynamics and optical properties of molecules in real time, overcoming the bottlenecks resulting from existing theories and techniques.
The new theory integrates advanced quantum electrodynamics into ultrafast spectroscopy. It uses modern algebra to explain the nonlinear dynamics of molecules, which lays the foundation for developing state-of-the-art technological applications for lasers and material characterization. It thus offers new principles for optical detection and quantum metrology.
Unlocking Room-Temperature Molecular Cooperativity
“What is particularly fascinating about our new theory is that the cooperative motion of a cluster of molecules shows a wave-like behavior, which spreads over a distance. This was not achievable in conventional studies. And this collective motion can exist at room temperature, instead of only in an ultralow, cryogenic temperature previously. This means that precise control and sensing of particle motion may be feasible at room temperature. This may open new frontiers of research, such as collective-driven chemistry that could potentially revolutionize the study of photochemistry,” said Dr. Zhang.
The new quantum theory facilitates the design of next-generation light-harvesting and emitting devices, as well as laser operation and detection. The coherence emerging from the light-induced molecular cooperativity may lead to bright emission of light. The spectroscopic probes of the light-induced phase of matter in the research can help to exploit next-generation optical sensing techniques and quantum metrology.
At a larger scale, the light-induced phases may enable a variety of novel light-based interdisciplinary applications, such as optical communications, biological imaging, control of chemical catalysis, and designating light-harvesting devices in an energy-efficient manner.
In the near future, the researchers plan to explore the light-induced phases and their effect on quantum materials, and develop new spectroscopic techniques and detection in the context of quantum entanglement.
The findings were published in the scientific journal Physical Review Letters under the title “Multidimensional coherent spectroscopy for molecular polaritons: Langevin approach.”
Reference: “Multidimensional Coherent Spectroscopy of Molecular Polaritons: Langevin Approach” by Zhedong Zhang, Xiaoyu Nie, Dangyuan Lei and Shaul Mukamel, 10 March 2023, Physical Review Letters.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.103001
Dr. Zhang is the first author of the paper. He and Professor Shaul Mukamel, of the University of California Irvine, are the corresponding authors. Their collaborators include Dr. Lei Dangyuan, from the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering at CityU, and Mr. Nie Xiaoyu, currently studying in the Centre of Quantum Technologies in the National University of Singapore. Key funding sources for the research include the Research Grants Council in Hong Kong and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
1 Comment
According to the topological vortex gravitational field theory, it is not impossible to manipulate microscopic particles through light waves, rays, and even acoustic waves. This research method has the potential to become the normal state of Particle physics research in the future. Just like light can manipulate plant growth, sunlight can generate electricity from solar panels.