
Researchers developed a technique to embed fairness into the machine-learning internal representation, ensuring fair outputs from biased training data and improving performance in tasks like facial recognition and animal species classification.
A new technique boosts models’ ability to reduce bias, even if the dataset used to train the model is unbalanced.
If a machine-learning model is trained using an unbalanced dataset, such as one that contains far more images of people with lighter skin than people with darker skin, there is serious risk the model’s predictions will be unfair when it is deployed in the real world.
But this is only one part of the problem. MIT scientists have found that machine-learning models that are popular for image recognition tasks actually encode bias when trained on unbalanced data. This bias within the model is impossible to fix later on, even with state-of-the-art fairness-boosting techniques, and even when retraining the model with a balanced dataset.
So, the researchers came up with a technique to introduce fairness directly into the model’s internal representation itself. This enables the model to produce fair outputs even if it is trained on unfair data, which is especially important because there are very few well-balanced datasets for machine learning.
The solution they developed not only leads to models that make more balanced predictions, but also improves their performance on downstream tasks like facial recognition and animal species classification.

MIT researchers have found that, if a certain type of machine learning model is trained using an unbalanced dataset, the bias that it learns is impossible to fix after the fact. They developed a technique that induces fairness directly into the model, no matter how unbalanced the training dataset was, which can boost the model’s performance on downstream tasks. Credit: Jose-Luis Olivares, MIT
“In machine learning, it is common to blame the data for bias in models. But we don’t always have balanced data. So, we need to come up with methods that actually fix the problem with imbalanced data,” says lead author Natalie Dullerud, a graduate student in the Healthy ML Group of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) at MIT.
Dullerud’s co-authors include Kimia Hamidieh, a graduate student in the Healthy ML Group; Karsten Roth, a former visiting researcher who is now a graduate student at the University of Tubingen; Nicolas Papernot, an assistant professor in the University of Toronto’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science; and senior author Marzyeh Ghassemi, an assistant professor and head of the Healthy ML Group. The research will be presented at the International Conference on Learning Representations.
Defining fairness
The machine-learning technique the researchers studied is known as deep metric learning, which is a broad form of representation learning. In deep metric learning, a neural network learns the similarity between objects by mapping similar photos close together and dissimilar photos far apart. During training, this neural network maps images in an “embedding space” where a similarity metric between photos corresponds to the distance between them.
For example, if a deep metric learning model is being used to classify bird species, it will map photos of golden finches together in one part of the embedding space and cardinals together in another part of the embedding space. Once trained, the model can effectively measure the similarity of new images it hasn’t seen before. It would learn to cluster images of an unseen bird species close together, but farther from cardinals or golden finches within the embedding space.
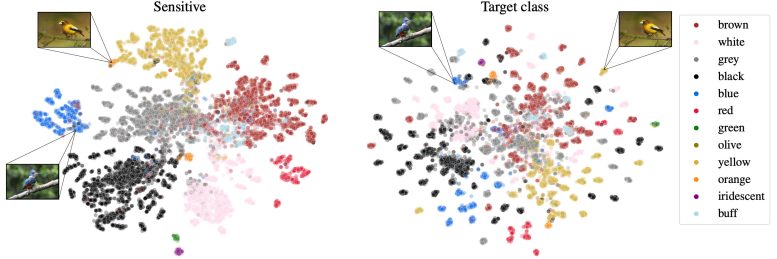
This image shows two distinct PARADE embeddings for bird color. On the left, both example images are mapped to clusters with birds of the same plumage. On the right in the class label embedding, due to de-correlation, the images are separated from the region of space with other birds of the same plumage, but are still well-clustered, indicating that PARADE can find other attributes to distinguish these species clusters. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
The similarity metrics the model learns are very robust, which is why deep metric learning is so often employed for facial recognition, Dullerud says. But she and her colleagues wondered how to determine if a similarity metric is biased.
“We know that data reflect the biases of processes in society. This means we have to shift our focus to designing methods that are better suited to reality,” says Ghassemi.
The researchers defined two ways that a similarity metric can be unfair. Using the example of facial recognition, the metric will be unfair if it is more likely to embed individuals with darker-skinned faces closer to each other, even if they are not the same person, than it would if those images were people with lighter-skinned faces. Second, it will be unfair if the features it learns for measuring similarity are better for the majority group than for the minority group.
The researchers ran a number of experiments on models with unfair similarity metrics and were unable to overcome the bias the model had learned in its embedding space.
“This is quite scary because it is a very common practice for companies to release these embedding models and then people finetune them for some downstream classification task. But no matter what you do downstream, you simply can’t fix the fairness problems that were induced in the embedding space,” Dullerud says.
Even if a user retrains the model on a balanced dataset for the downstream task, which is the best-case scenario for fixing the fairness problem, there are still performance gaps of at least 20 percent, she says.
The only way to solve this problem is to ensure the embedding space is fair to begin with.
Learning separate metrics
The researchers’ solution, called Partial Attribute Decorrelation (PARADE), involves training the model to learn a separate similarity metric for a sensitive attribute, like skin tone, and then decorrelating the skin tone similarity metric from the targeted similarity metric. If the model is learning the similarity metrics of different human faces, it will learn to map similar faces close together and dissimilar faces far apart using features other than skin tone.
Any number of sensitive attributes can be decorrelated from the targeted similarity metric in this way. And because the similarity metric for the sensitive attribute is learned in a separate embedding space, it is discarded after training so only the targeted similarity metric remains in the model.
Their method is applicable to many situations because the user can control the amount of decorrelation between similarity metrics. For instance, if the model will be diagnosing breast cancer from mammogram images, a clinician likely wants some information about biological sex to remain in the final embedding space because it is much more likely that women will have breast cancer than men, Dullerud explains.
They tested their method on two tasks, facial recognition and classifying bird species, and found that it reduced performance gaps caused by bias, both in the embedding space and in the downstream task, regardless of the dataset they used.
Moving forward, Dullerud is interested in studying how to force a deep metric learning model to learn good features in the first place.
“How do you properly audit fairness? That is an open question right now. How can you tell that a model is going to be fair, or that it is only going to be fair in certain situations, and what are those situations? Those are questions I am really interested in moving forward,” she says.
Reference: “Is Fairness Only Metric Deep? Evaluating and Addressing Subgroup Gaps in DML” by Natalie Dullerud, Karsten Roth, Kimia Hamidieh, Nicolas Papernot and Marzyeh Ghassemi, 23 March 2022, Computer Science > Machine Learning.
arXiv:2203.12748
PDF







Be the first to comment on "Injecting Fairness Into AI: Machine-Learning Models That Produce Fair Outputs Even When Trained on Unfair Data"