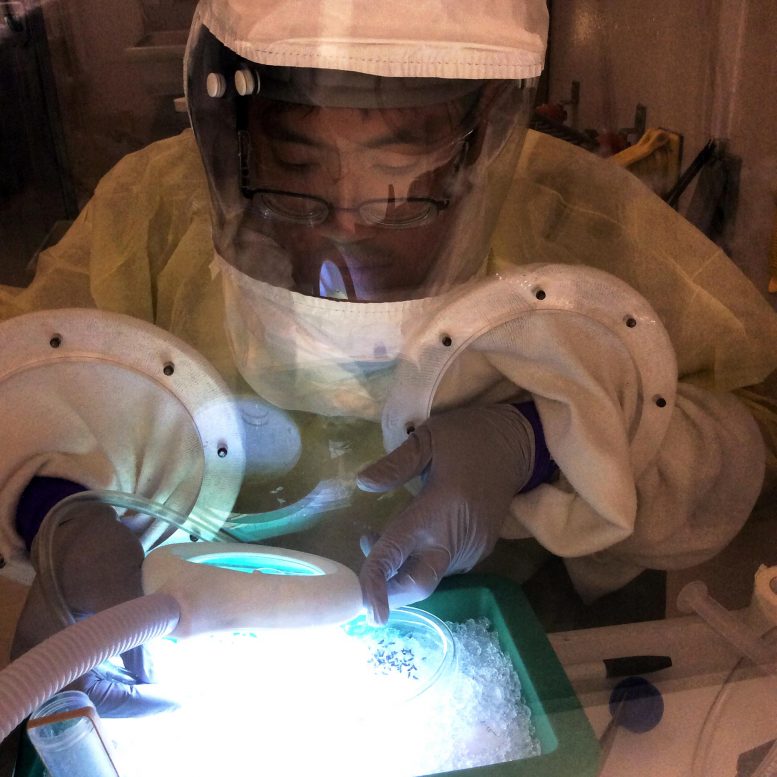

A study at the Kansas State University Biosecurity Research Institute is the first to confirm that SARS-CoV-2 cannot be transmitted to people by mosquitoes. The study has been published by Nature Scientific Reports. Credit: Kansas State University
A new study by Kansas State University researchers is the first to confirm that SARS-CoV-2 cannot be transmitted to people by mosquitoes.
Stephen Higgs, associate vice president for research and director of the university’s Biosecurity Research Institute, or BRI, together with colleagues from the BRI and the College of Veterinary Medicine had the findings published July 17 by Nature Scientific Reports.
The article, “SARS-CoV-2 failure to infect or replicate in mosquitoes: an extreme challenge,” details the study’s findings, which provide the first experimental investigation on the capacity of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 disease, to infect and be transmitted by mosquitoes.
“While the World Health Organization has definitively stated that mosquitoes cannot transmit the virus, our study is the first to provide conclusive data supporting the theory,” said Higgs, Peine professor of biosecurity and university distinguished professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology.
The study, which was done at the BRI, a biosafety level-3 facility, ultimately found that the virus is unable to replicate in three common and widely distributed species of mosquitoes — Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus — and therefore cannot be transmitted to humans.
“I am proud of the work we are doing at K-State to learn as much as we can about this and other dangerous pathogens,” said Higgs. “This work was possible because of the unique capabilities of the BRI and the dedicated BRI and institutional staff.”
Colleagues involved with the study include Yan-Jang Huang, research assistant professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology; Dana Vanlandingham, professor of diagnostic medicine and pathobiology; Ashley Bilyeu and Haelea Sharp, research assistants in diagnostic medicine and pathobiology; and Susan Hettenbach, research assistant at the BRI.
Researchers at the BRI have completed four additional studies on COVID-19 since March and this is the first peer-reviewed publication based on SARS-CoV-2 experiments wholly conducted at K-State.
Research at the Biosecurity Research Institute has been ongoing with other animal pathogens that can be transmitted from animals to people, including Rift Valley fever and Japanese encephalitis, as well as diseases that could devastate America’s food supply, such as African swine fever and classical swine fever. The research was in part supported by the National Bio and Agro-Defense Facility Transition Fund provided by the state of Kansas.
“We have remarkable talent and capabilities working within our research and training facility at the BRI,” said Peter Dorhout, K-State vice president for research. “The BRI is one of the critical anchor facilities in the North Campus Corridor, which serves as our growing research and development space for private sector and government agency partnerships with K-State.”
Reference: “SARS-CoV-2 failure to infect or replicate in mosquitoes: an extreme challenge” by Yan-Jang S. Huang, Dana L. Vanlandingham, Ashley N. Bilyeu, Haelea M. Sharp, Susan M. Hettenbach and Stephen Higgs, 17 July 2020, Scientific Reports.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-68882-7








This story presupposes the SARS-CoV-2 virus has been isolated and proven to cause the COVID19 disease. A concordance with Koch’s postulates that has not yet occured.
Presently it is so. But the very typical nature of the virus is with an adaptive potential to survive as the fittest. I do mean that the virus may become able to replicate in mosquitoes, in future.
277 mosquitoes were inoculated with the virus, then 48 of those tested positive for the virus before the 24hr mark, and 1 mosquitoe tested positive for the virus after the 24hr mark.
This is a lab setting and I’m not sure they are configuring in the natural behavior of mosquitoes in the research.
How did they then use the primate in the study?
Does Audible Function?
To begin with, you receive a free audiobook
and take a free trial of Audible. This really is among even an Audible originals or the classics.
At the conclusion of the trial, you can purchase a monthly subscription of Audible.
You will need to register to your membership using your Amazon account.
Audible awards each month. It is possible to use this credit to buy Audible audio books in various categories including technology, style,
love, social networking, advertisements, etc..
If you would like to buy books, you can buy Audible credits
or pay per sound publication.
Interestingly, a member can download a couple of six star Originals on the first Friday of each month.
They do not cost any credits. These Audible Originals can be kept
by you .
You have Audible audio books on your library even in case you cancel your
subscription.
It is possible to listen to Audible audio books anywhere using apps on Windows,
your telephone or Mac computer or Alexa device.|
With over 300,000 names to its name, Audible is the world’s biggest seller and manufacturer of audiobooks. http://draftprosystemsfl.com/forums/users/kensievwright0/