For Experimental Physicists, Quantum Frustration Leads to Fundamental Discovery
“Chiral bose-liquid state” is a new phase of matter, according to UMass Amherst professor.
A team of physicists, including University of Massachusetts assistant professor Tigran Sedrakyan, recently announced in the journal Nature that they have discovered a new phase of matter. Called the “chiral bose-liquid state,” the discovery opens a new path in the age-old effort to understand the nature of the physical world.
Under everyday conditions, matter can be a solid, liquid, or gas. But once you venture beyond the everyday—into temperatures approaching absolute zero, things smaller than a fraction of an atom or which have extremely low states of energy—the world looks very different. “You find quantum states of matter way out on these fringes,” says Sedrakyan, “and they are much wilder than the three classical states we encounter in our everyday lives.”
Sedrakyan has spent years exploring these wild quantum states, and he is particularly interested in the possibility of what physicists call “band degeneracy,” “moat bands” or “kinetic frustration” in strongly interacting quantum matter.
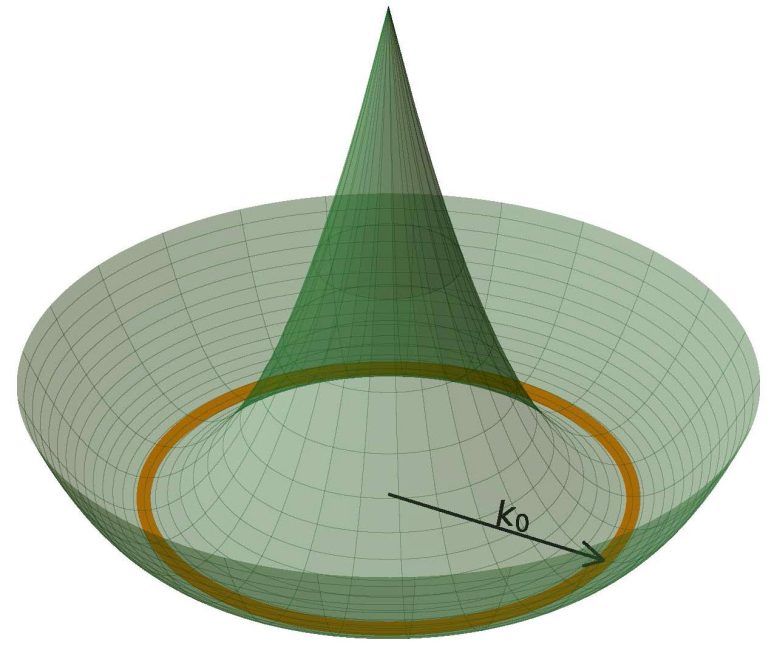
Typically, particles in any system bump into each other, and in so doing they cause predictable effects, like billiard balls knocking into each other and then reacting in a predictable pattern. In other words, the effects and the particles are correlated. But in a frustrated quantum system, there are infinite possibilities that stem from the interaction of particles—perhaps the billiard ball levitates or zooms off at an impossible angle—and some of these infinite possibilities can lead to novel quantum states.
Engineering a Frustration Machine
What Sedrakyan and his colleagues have done is to engineer a frustration machine: a bilayer semiconducting device. The top layer is electron-rich, and these electrons can move freely. The bottom layer is filled with “holes,” or places that a roving electron can occupy. Then the two layers are brought extremely close together—interatomic close.
If the number of electrons in the top layer and holes in the bottom layer were equal, then you would expect to see the particles acting in a correlated manner, but Sedrakyan and his colleagues designed the bottom layer so that there is a local imbalance between the number of electrons and holes in the bottom layer. “It’s like a game of musical chairs,” Sedrakyan says, “designed to frustrate the electrons. Instead of each electron having one chair to go to, they must now scramble and have many possibilities in where they ‘sit’”.
Unique Characteristics of the Chiral Bose-Liquid
This frustration kicks off the novel chiral edge state, which has a number of surprising characteristics. For instance, if you cool quantum matter in a chiral state down to absolute zero, the electrons freeze into a predictable pattern, and the emergent charge-neutral particles in this state will all either spin clockwise or counterclockwise. Even if you smash another particle into one of these electrons, or you introduce a magnetic field, you can’t alter its spin—it’s surprisingly robust and can even be used to encode digital data in a fault-tolerant way.
Even more surprising is what happens when an outside particle does smash into one of the particles in the chiral edge state. To return to the billiard-ball metaphor, you would expect to send the eight-ball flying when the cue ball smacks into it. But if the pool balls were in a chiral bose-liquid state, all 15 of them would react in exactly the same way when the eight-ball was struck. This effect is due to the long-range entanglement present in this quantum system.
Experimental Evidence for Chiral Bose-Liquid
It is difficult to observe the chiral bose-liquid state, which is why it has remained hidden for so long. To do so, the team of scientists, including theoretical physicists Rui Wang and Baigeng Wang (both of Nanjing University) as well as experimental physicists Lingjie Du (Nanjing University) and Rui-Rui Du (Peking University) designed a theory and an experiment that used an extremely strong magnetic field that is capable of measuring the movements of the electrons as they race for chairs.
“On the edge of the semiconductor bilayer, electrons and holes move with the same velocities,” says Lingjie Du. “This leads to helical-like transport, which can be further modulated by external magnetic fields as the electron and hole channels are gradually separated under higher fields.” The magneto-transport experiments therefore successfully reveal the first piece of evidence of the chiral bose-liquid, which the authors also call the “excitonic topological order” in the published paper.
Reference: “Excitonic topological order in imbalanced electron–hole bilayers” by Rui Wang, Tigran A. Sedrakyan, Baigeng Wang, Lingjie Du and Rui-Rui Du, 14 June 2023, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06065-w
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Program for Innovative Talents and Entrepreneurs in Jiangsu, the Xiaomi Foundation, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the National Science Foundation.
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
5 Comments
“For every fact there is an infinity of hypotheses. ”
― Robert M. Pirsig (1928-2016)
According to the topological vortex gravitational field theory, all quantum behaviors can be explained by the interaction of topological vortex gravitational field, that is, mathematics, rather than God, cat, moat bands, and billiard-ball.
What is the relevance with the article matter?
Good article. However, you must address a few things.
1) The first phase state of matter is plasma. Which, for some reason, is not mentioned in this article.
2) Zero Kevin, absolute zero or Stasis, cannot be achieved.
3) “Quantum” or annealing computers, produced by D-Wave systems Inc use this technology, also used in many worldwide corporations and in the crypto space.
4) Chirality is nothing new, neither is the ability to control “Natural” phenomenon by using a combination magnetism and dielectricity (implosion, compression and explosion).
1. The usual states are in order solid, liquid, gas and plasma. Plasma is not relevant to these solid state physics phenomena.
2. That is why the article says “approaches” zero kelvin (not “Kevin” or “Kelvin”, but the SI unit kelvin).
3. Not relevant here.
4. Chirality was not the topic of the article, which was new (a new phase).