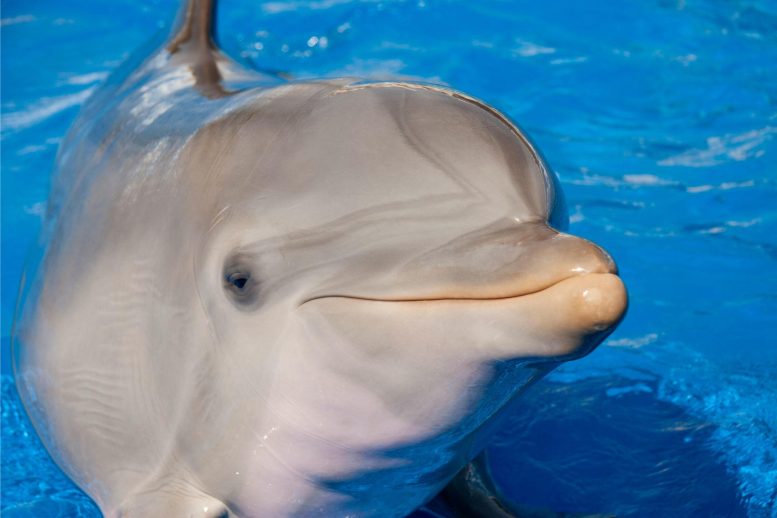

Scientists have discovered that bottlenose dolphins can sense weak electric fields using vibrissal pits on their snouts, a trait previously believed to be a vestigial feature. In experiments with dolphins Donna and Dolly, they found that these mammals could detect electric fields as weak as 2.4μV/cm and pulsating fields produced by fish gills. This ability is thought to help dolphins locate prey and navigate using the Earth’s magnetic field, similar to the electrosensitivity found in sharks.
Bottlenose dolphins might use their electric sense to navigate around the world.
Born tail first, bottlenose dolphin calves are initially adorned with two delicate rows of whiskers along their snout, resembling the tactile whiskers of seals. However, these whiskers are shed shortly after birth, leaving behind a pattern of indentations called vibrissal pits. Recently, Tim Hüttner and Guido Dehnhardt, researchers from the University of Rostock in Germany, began to suspect that these pits might serve a purpose beyond being mere remnants.
Could they allow adult bottlenose dolphins to sense weak electric fields? Taking an initial close look, they realized that the remnant pits resemble the structures that allow sharks to detect electric fields, and when they checked whether captive bottlenose dolphins could sense an electric field in water, all of the animals felt the field.
“It was very impressive to see,” says Dehnhardt, who recently published the extraordinary discovery and how the animals could use their electric sense in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
Sensitivity Testing
To find out how sensitive bottlenose dolphins are to the electric fields produced by lifeforms in water Dehnhardt and Hüttner teamed up with Lorenzo von Fersen at Nuremberg Zoo and Lars Miersch at the University of Rostock. First, they tested the sensitivity of two bottlenose dolphins, Donna and Dolly, to different electric fields to find out whether the dolphins could detect a fish buried in the sandy sea floor.
After training each animal to rest its jaw on a submerged metal bar, Hüttner, Armin Fritz (Nuremberg Zoo) and an army of colleagues taught the dolphins to swim away within 5 seconds of feeling an electric field produced by electrodes immediately above the dolphin’s snout.
Gradually decreasing the electric field from 500 to 2μV/cm, the team kept track of how many times the dolphins departed on cue and were impressed; Donna and Dolly were equally sensitive to the strongest fields, exiting correctly almost every time. It was only when the electric fields became weaker that it became evident that Donna was slightly more sensitive, sensing fields that were 2.4μV/cm, while Dolly became aware of fields of 5.5μV/cm.
However, the electric fields produced by living animals aren’t just static. The pulsing movements of fish gills cause their electric fields to fluctuate, so could Donna and Dolly sense pulsing fields as well? This time the team pulsed the electric fields 1, 5, and 25 times per second while reducing the field strength, and sure enough, the dolphins could sense the fields.
However, neither of the animals were as sensitive to the alternating fields as they were to the unvarying electric fields. Dolly could only pick up the slowest field at 28.9μV/cm, while Donna picked up all three of the oscillating fields, sensing the slowest at 11.7μV/cm.
Practical Implications of Electric Sense in Dolphins
So what does this new super sense mean for dolphins in practice? Dehnhardt says, “The sensitivity to weak electric fields helps a dolphin search for fish hidden in sediment over the last few centimeters before snapping them up,” in contrast to sharks, the electrosensitive superstars, which are capable of sensing the electric fields of fish within 30–70cm.
Hüttner and Dehnhardt also suspect that the dolphin’s ability to feel electricity could help them on a larger scale.
“This sensory ability can also be used to explain the orientation of toothed whales to the earth’s magnetic field,” says Dehnhardt, explaining that dolphins swimming through weak areas of the earth’s magnetic field at a normal speed of 10m/s could generate a detectable electric field of 2.5μV/cm across their body. And, if the animals swim faster, they are even more likely to sense the planet’s magnetic field, allowing them to use their electric sense to navigate the globe by magnetic map.
Reference: “Bottlenose dolphins’ electric super sense could help them navigate the globe” by Kathryn Knight, 30 November 2023, Journal of Experimental Biology.
DOI: 10.1242/jeb.246907








Be the first to comment on "Scientists Discover New Sense of Bottlenose Dolphins: They Feel Electricity"