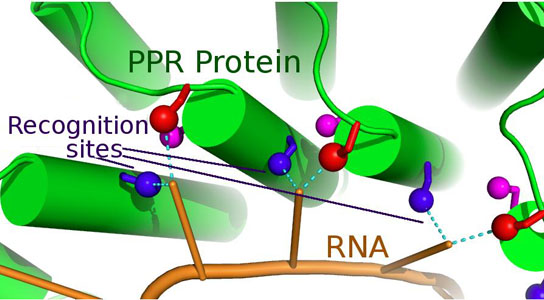
A molecular model of a PPR protein recognizing a specific RNA molecule. The identity of specific amino acid residues in the protein (colored sticks) determines the sequence of the RNA molecule it can bind. Credit: Charlie Bond
A team of scientists has cracked a code underlying recognition of RNA molecules by a superfamily of RNA-binding proteins called pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins, providing a significant step toward the prediction of native binding sites of the enormous number of PPR proteins found in nature.
Scientists have cracked a molecular code that may open the way to destroying or correcting defective gene products, such as those that cause genetic disorders in humans.
The code determines the recognition of RNA molecules by a superfamily of RNA-binding proteins called pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins.
When a gene is switched on, it is copied into RNA. This RNA is then used to make proteins that are required by the organism for all of its vital functions. If a gene is defective, its RNA copy and the proteins made from this will also be defective. This forms the basis of many terrible genetic disorders in humans.
RNA-binding PPR proteins could revolutionize the way we treat disease. Their secret is their versatility — they can find and bind a specific RNA molecule, and have the capacity to correct it if it is defective, or destroy it if it is detrimental. They can also help ramp up production of proteins required for growth and development.
The new paper in PLOS Genetics describes for the first time how PPR proteins recognize their RNA targets via an easy-to-understand code. This mechanism mimics the simplicity and predictability of the pairing between DNA strands described by Watson and Crick 60 years ago, but at a protein/RNA interface.
This exceptional breakthrough comes from an international, interdisciplinary research team including UWA researchers Professor Ian Small and Aaron Yap from the ARC Center for Excellence in Plant Energy Biology and Professor Charlie Bond and Yee Seng Chong from UWA’s School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, along with Professor Alice Barkan’s team at the University of Oregon. This research was publicly funded by the ARC and the WA State Government in Australia and the NSF in the USA.
“Many PPR proteins are vitally important, but we don’t know what they do. Now we’ve cracked the code, we can find out,” said ARC Plant Energy Biology Director Ian Small.
“What’s more, we can now design our own synthetic proteins to target any RNA sequence we choose – this should allow us to control the expression of genes in new ways that just weren’t available before. The potential is really exciting.”
“This discovery was made in plants but is applicable across many species as PPR proteins are found in humans and animals too,” says Professor Bond.
Reference: “A Combinatorial Amino Acid Code for RNA Recognition by Pentatricopeptide Repeat Proteins” by Alice Barkan, Margarita Rojas, Sota Fujii, Aaron Yap, Yee Seng Chong, Charles S. Bond and Ian Small, 16 August 2012, PLOS Genetics.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002910








Be the first to comment on "Molecular Code for How PPR Proteins Recognize their RNA Targets Discovered"