A newly published study reveals how HZB and TU Delft scientists used a solar cell and a photo anode made of a metal oxide to achieve a solar hydrogen production breakthrough.
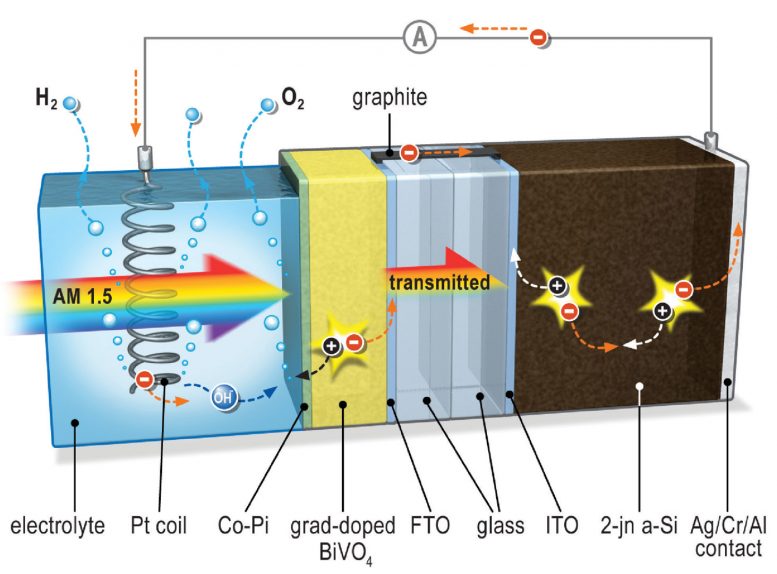
Using a simple solar cell and a photo anode made of a metal oxide, HZB and TU Delft scientists have successfully stored nearly five percent of solar energy chemically in the form of hydrogen. This is a major feat as the design of the solar cell is much simpler than that of the high-efficiency triple-junction cells based on amorphous silicon or expensive III-V semiconductors that are traditionally used for this purpose. The photo anode, which is made from the metal oxide bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) to which a small amount of tungsten atoms was added, was sprayed onto a piece of conducting glass and coated with an inexpensive cobalt phosphate catalyst. “Basically, we combined the best of both worlds,” explains Prof. Dr. Roel van de Krol, head of the HZB Institute for Solar Fuels: “We start with a chemically stable, low-cost metal oxide, add a really good but simple silicon-based thin film solar cell, and – voilà – we’ve just created a cost-effective, highly stable, and highly efficient solar fuel device.”
Thus the experts were able to develop a rather elegant and simple system for using sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process, called artificial photosynthesis, allows solar energy to be stored in the form of hydrogen. The hydrogen can then be used as a fuel either directly or in the form of methane, or it can generate electricity in a fuel cell. One rough estimate shows the potential inherent in this technology: At a solar performance in Germany of roughly 600 Watts per square meter, 100 square meters of this type of system is theoretically capable of storing 3 kilowatt hours of energy in the form of hydrogen in just one single hour of sunshine. This energy could then be available at night or on cloudy days.
Metal oxide as photo anode prevents corrosion of the solar cell
Van de Krol and his team essentially started with a relatively simple silicon-based thin film cell to which a metal oxide layer was added. This layer is the only part of the cell that is in contact with the water, and acts as a photo anode for oxygen formation. At the same time, it helps to prevent corrosion of the sensitive silicon cell. The researchers systematically examined and optimized processes such as light absorption, separation of charges, and splitting of water molecules. Theoretically, a solar-to-chemical efficiency of up to nine percent is possible when you use a photo anode made from bismuth vanadate, says van de Krol. Already, they were able to solve one problem: Using an inexpensive cobalt phosphate catalyst, they managed to substantially accelerate the process of oxygen formation at the photo anode.
A new record: More than 80 percent of the incident photons contribute to the current!
The biggest challenge, however, was the efficient separation of electrical charges within the bismuth vanadate film. Metal oxides may be stable and cheap, but the charge carriers have a tendency to quickly recombine. This means they are no longer available for the water splitting reaction. Now, Van de Krol and his team have figured out that it helps to add wolfram atoms to the bismuth vanadate film. “What’s important is that we distribute these wolfram atoms in a very specific way so that they can set up an internal electric field, which helps to prevent recombination,” explains van de Krol. For this to work, the scientists took a bismuth vanadium wolfram solution and sprayed it onto a heated glass substrate. This caused the solution to evaporate. By repeatedly spraying different wolfram concentrations onto the glass, a highly efficient photo-active metal oxide film some 300 nanometers thick was created. ”We don’t really understand quite yet why bismuth vanadate works so much better than other metal oxides. We found that more than 80 percent of the incident photons contribute to the current, an unexpectedly high value that sets a new record for metal oxides” says van de Krol. The next challenge is scaling these kinds of systems to several square meters so they can yield relevant amounts of hydrogen.
Reference: “Efficient solar water splitting by enhanced charge separation in a bismuth vanadate-silicon tandem photoelectrode” by Fatwa F. Abdi, Lihao Han, Arno H. M. Smets, Miro Zeman, Bernard Dam and Roel van de Krol, 29 July 2013, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3195
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
1 Comment
The math is seriously falty in ghis article. If the cel generates 600 watts off energy per m2, then 100 m2 wouldd generate SIXTY KILLOWATS, which is 60 KWh per hr. BTW, saying KWh per hr is superfflouous as its merely KW muliplied by hrs, on both sides off the equation.
J F Notman. ( Brit in Holland)