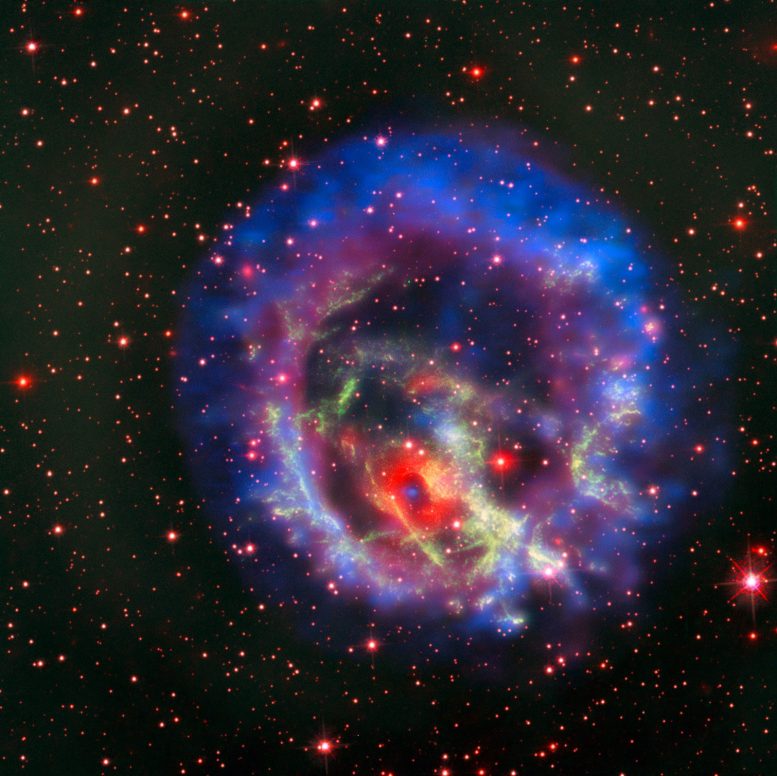

This new picture created from images from telescopes on the ground and in space tells the story of the hunt for an elusive missing object hidden amid a complex tangle of gaseous filaments in one of our nearest neighboring galaxies, the Small Magellanic Cloud. The reddish background image comes from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and reveals the wisps of gas forming the supernova remnant 1E 0102.2-7219 in green. The red ring with a dark center is from the MUSE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope and the blue and purple images are from the NASA Chandra X-Ray Observatory. The blue spot at the center of the red ring is an isolated neutron star with a weak magnetic field, the first identified outside the Milky Way. Credit: ESO/NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)/F. Vogt et al.
New images from ESO’s Very Large Telescope in Chile and other telescopes reveal a rich landscape of stars and glowing clouds of gas in one of our closest neighboring galaxies, the Small Magellanic Cloud. The pictures have allowed astronomers to identify an elusive stellar corpse buried among filaments of gas left behind by a 2000-year-old supernova explosion. The MUSE instrument was used to establish where this elusive object is hiding, and existing Chandra X-ray Observatory data confirmed its identity as an isolated neutron star.
Spectacular new pictures, created from images from both ground- and space-based telescopes, tell the story of the hunt for an elusive missing object hidden amid a complex tangle of gaseous filaments in the Small Magellanic Cloud, about 200,000 light-years from Earth.
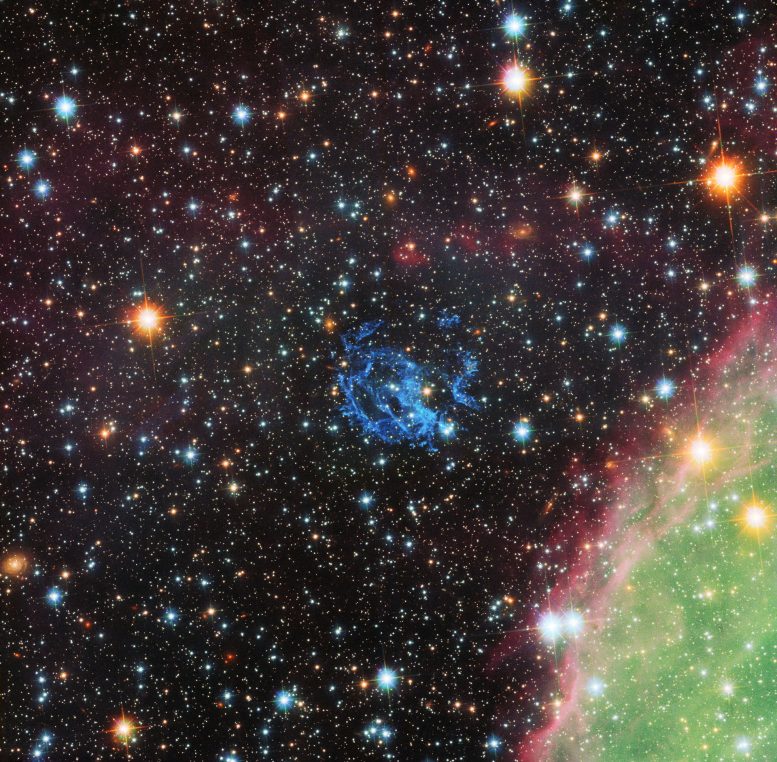

This picture from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope sets the scene for the story of the hunt for an elusive missing object hidden amid a complex tangle of gaseous filaments in one of our nearest neighboring galaxies, the Small Magellanic Cloud. The wisps of gas forming the supernova remnant 1E 0102.2-7219 show up in blue near the center of the picture. Part of the massive star-forming region, N 76, also known as Henize 1956, appears at the lower right in green and pink. Credit: NASA, ESA and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
New data from the MUSE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope in Chile has revealed a remarkable ring of gas in a system called 1E 0102.2-7219, expanding slowly within the depths of numerous other fast-moving filaments of gas and dust left behind after a supernova explosion. This discovery allowed a team led by Frédéric Vogt, an ESO Fellow in Chile, to track down the first-ever isolated neutron star with low magnetic field located beyond our own Milky Way galaxy.
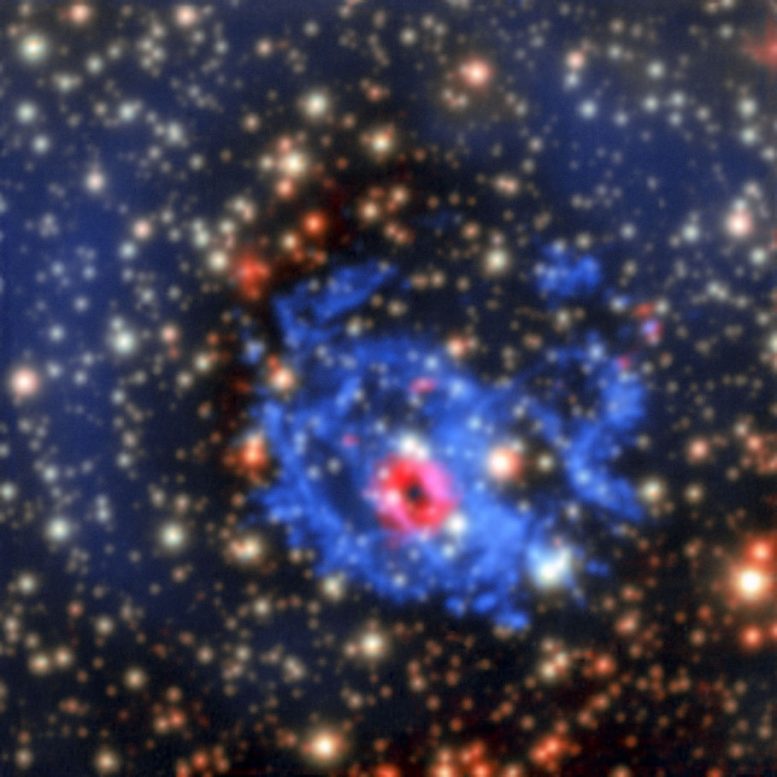

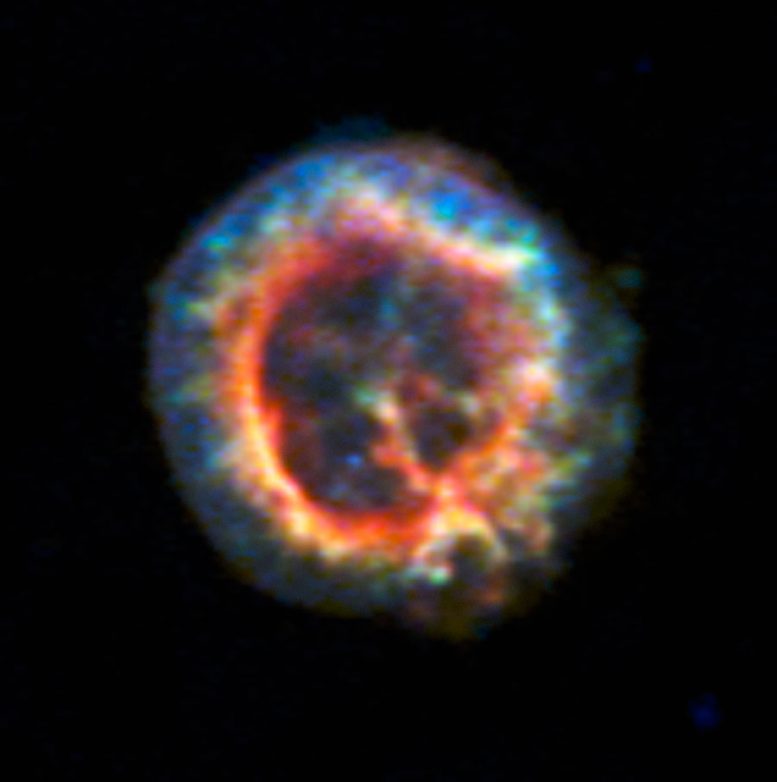
This new picture from the MUSE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope in Chile shows how an elusive missing object was found amid a complex tangle of gaseous filaments in one of our nearest neighboring galaxies, the Small Magellanic Cloud. The wisps of gas forming the supernova remnant 1E 0102.2-7219 show up in blue, but the red ring in the MUSE data, revealing glowing neon and oxygen forms, is perfectly centered on an X-ray source — an isolated neutron star with a weak magnetic field, the first identified outside the Milky Way. Credit: ESO/F. Vogt et al.
The team noticed that the ring was centered on an X-ray source that had been noted years before and designated p1. The nature of this source had remained a mystery. In particular, it was not clear whether p1 actually lies inside the remnant or behind it. It was only when the ring of gas — which includes both neon and oxygen — was observed with MUSE that the science team noticed it perfectly circled p1. The coincidence was too great, and they realized that p1 must lie within the supernova remnant itself. Once p1’s location was known, the team used existing X-ray observations of this target from the Chandra X-ray Observatory to determine that it must be an isolated neutron star, with a low magnetic field.
In the words of Frédéric Vogt: “If you look for a point source, it doesn’t get much better than when the Universe quite literally draws a circle around it to show you where to look.”
This archival image from the NASA Chandra X-Ray Observatory shows how an elusive missing object was found amid a complex tangle of gaseous filaments in one of our nearest neighboring galaxies, the Small Magellanic Cloud. The supernova remnant 1E 0102.2-7219 shows up dramatically, but when combined with MUSE data, the blue dot just below center proves to be an isolated neutron star with a weak magnetic field, the first identified outside the Milky Way. Credit: ESO/NASA
When massive stars explode as supernovae, they leave behind a curdled web of hot gas and dust, known as a supernova remnant. These turbulent structures are key to the redistribution of the heavier elements — which are cooked up by massive stars as they live and die — into the interstellar medium, where they eventually form new stars and planets.
Typically barely ten kilometers across, yet weighing more than our Sun, isolated neutron stars with low magnetic fields are thought to be abundant across the Universe, but they are very hard to find because they only shine at X-ray wavelengths. The fact that the confirmation of p1 as an isolated neutron star was enabled by optical observations is thus particularly exciting.
ESOcast 155 Light: Dead Star Circled by Light (4K UHD)
Co-author Liz Bartlett, another ESO Fellow in Chile, sums up this discovery: “This is the first object of its kind to be confirmed beyond the Milky Way, made possible using MUSE as a guidance tool. We think that this could open up new channels of discovery and study for these elusive stellar remains.”
Zooming in on a neutron star in the Small Magellanic Cloud
Reference: “Identification of the central compact object in the young supernova remnant 1E 0102.2-7219” by Frédéric P. A. Vogt, Elizabeth S. Bartlett, Ivo R. Seitenzahl, Michael A. Dopita, Parviz Ghavamian, Ashley J. Ruiter and Jason P. Terry, 2 April 2018, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-018-0433-0








It never ceases to amaze me that, through science, we can discover the wonders of the universe and the immense amount of knowledge we still have to obtain about it. There are no words that can do these discoveries the justice they deserve or tell us about our part in all of this. Many thanks for giving us the opportunity to view and to read about them.