
Scientists propose the likely reason for the scarcity of exoplanets measuring between 1.5 and two times Earth’s radius is the planetary shrinkage over billions of years.
Studying data from the Kepler space telescope, Flatiron Institute researchers found that planetary shrinkage over billions of years likely explains a yearslong mystery: The scarcity of planets roughly double Earth’s size.
There’s been a breakthrough in the case of the missing planets.
While planet-hunting missions have discovered thousands of worlds orbiting distant stars, there’s a severe scarcity of exoplanets that measure between 1.5 and two times Earth’s radius. That’s the middle ground between rocky super-Earths and larger, gas-shrouded planets called mini-Neptunes. Since discovering this ‘radius gap’ in 2017, scientists have been sleuthing out why there are so few midsize heavenly bodies.
The new clue arose from a fresh way of looking at the data. A team of researchers led by the Flatiron Institute’s Trevor David investigated whether the radius gap changes as planets age. They divvied up exoplanets into two groups — young and old — and reassessed the gap. The least common planet radii from the younger set were smaller on average than the least common ones from the older set, they found. While the scarcest size for younger planets was about 1.6 times Earth’s radius, it’s about 1.8 times Earth’s radius at older ages.
The implication, the researchers propose, is that some mini-Neptunes shrink drastically over billions of years as their atmospheres leak away, leaving behind only a solid core. By losing their gas, the mini-Neptunes “jump” the planet radius gap and become super-Earths. As time goes on, the radius gap shifts as larger and larger mini-Neptunes make the jump, transforming into larger and larger super-Earths. The gap, in other words, is the chasm between the largest-size super-Earths and the smallest-size mini-Neptunes that can still retain their atmospheres. The researchers reported their findings May 14, 2021, in The Astronomical Journal.
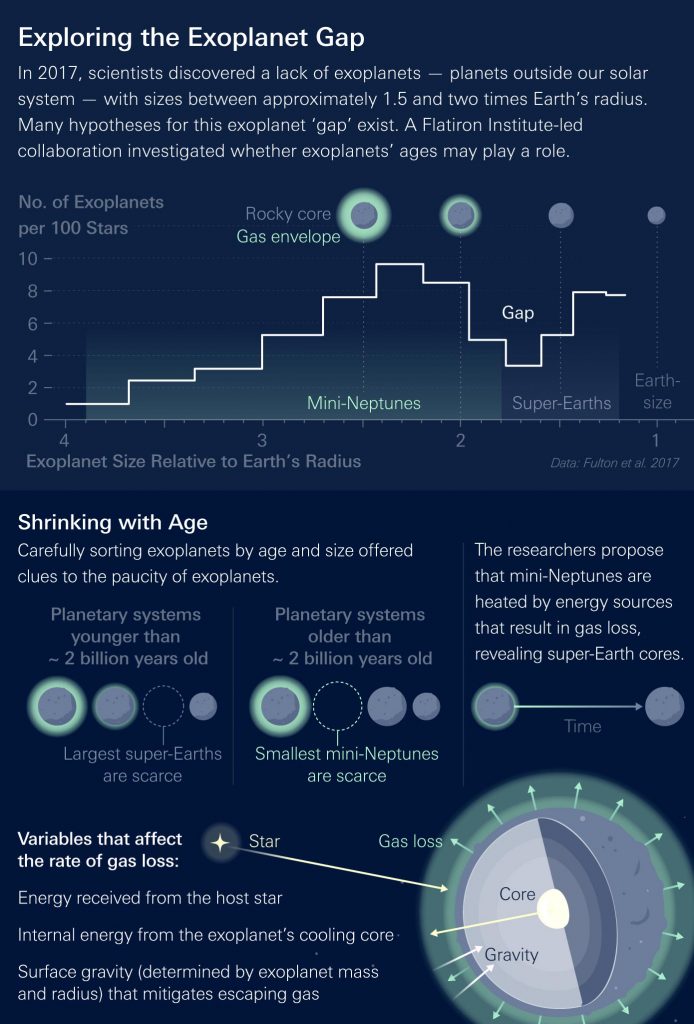
An infographic describing the exoplanet radius gap. Credit: Simons Foundation
“The overarching point is that planets are not the static spheres of rocks and gas we sometimes tend to think of them as,” says David, a research fellow at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics (CCA) in New York City. In some previously proposed models of atmosphere loss, “some of these planets were 10 times larger at the starts of their lives.”
The findings lend credence to two previously proposed suspects in the case: leftover heat from planetary formation and intense radiation from the host stars. Both phenomena add energy into a planet’s atmosphere, causing gas to escape into space. “Probably both effects are important,” says David, “but we’ll need more sophisticated models to tell how much each of them contributes and when” in the planet’s life cycle.
The paper’s co-authors include CCA research fellow Gabriella Contardo, CCA associate research scientist Ruth Angus, CCA associate research scientist Megan Bedell, CCA associate research scientist Daniel Foreman-Mackey and CCA guest researcher Samuel Grunblatt.
The new study used data collected by the Kepler spacecraft, which measured the light from distant stars. When an exoplanet moves between a star and Earth, the observed light from the star dims. By analyzing how quickly the planet orbits its star, the star’s size, and the extent of the dimming, astronomers can estimate the exoplanet’s size. These analyses ultimately led to the discovery of the radius gap.
A computer simulation of how the distribution of planet sizes changes as planetary systems age. The radius gap is evident at around double Earth’s radius — though it depends on the orbital periods of the planets. Evidence suggests that the gap shifts over time as gas-enveloped mini-Neptune planets lose their atmospheres, leaving behind a solid super-Earth. One planet undergoing this process is highlighted (depicted as a core with an atmosphere), with its change in size plotted on the right. Credit: Animation by Erik Petigura (UCLA); Simulation by James Owen (Imperial College London)
Scientists have previously proposed a few potential mechanisms for the gap’s creation, with each process taking place over a different timescale. Some believed that the gap occurs during planetary formation when some planets form without enough nearby gas to puff up their size. In this scenario, the planet’s radius, and therefore the radius gap, would be imprinted at birth. Another hypothesis was that collisions with space rocks could blast away a planet’s thick atmosphere, preventing tinier planets from accumulating lots of gas. This impact mechanism would take roughly 10 million to 100 million years.
Other potential mechanisms require more time. One proposal is that intense X-rays and ultraviolet radiation from a planet’s host star strips gas away over time. This process, called photoevaporation, would take less than 100 million years for most planets but could take billions of years for some. Another suggestion is that remnant heat from a planet’s formation slowly adds energy to the planet’s atmosphere, causing gas to escape into space over billions of years.
David and his colleagues started their investigation by taking a closer look at the gap itself. Gauging the sizes of stars and exoplanets can be tricky, so they cleaned up the data to only include planets whose diameters were confidently known. This data processing revealed an emptier gap than previously thought.
The researchers then sorted the planets based on whether they were younger or older than 2 billion years. (Earth, for comparison, is 4.5 billion years old.) Since a star and its planets form simultaneously, they determined each planet’s age based on its star’s age.
The results suggest that smaller mini-Neptunes are unable to hold on to their gas. Over billions of years, the gas is stripped away, leaving behind a mostly solid super-Earth. That process takes longer for larger mini-Neptunes — which become the largest super-Earths — but won’t impact the most gargantuan gas planets, whose gravity is strong enough to hold their atmospheres.
The fact that the radius gap evolves over billions of years suggests that the culprit isn’t planetary collisions or an inherent quirk of planetary formation. Remnant heat from inside the planets gradually stripping away the atmosphere is a good fit, David says, but intense radiation from the parent stars could also contribute, especially early on. The next step is for scientists to better model how planets evolve to suss out which explanation plays a bigger role. That could mean considering additional complexities such as the interactions between fledgling atmospheres and planetary magnetic fields or magma oceans.
Reference: “Evolution of the Exoplanet Size Distribution: Forming Large Super-Earths Over Billions of Years” by Trevor J. David, Gabriella Contardo, Angeli Sandoval, Ruth Angus, Yuxi (Lucy) Lu, Megan Bedell, Jason L. Curtis, Daniel Foreman-Mackey, Benjamin J. Fulton, Samuel K. Grunblatt and Erik A. Petigura, 14 May 2021, The Astronomical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/abf439








Very interesting article, however, a lot more data is needed to validate the theory behind it. It will be interesting to see what the future holds when a much larger sample size of planets and more examples of these small ice giants are found. Will theory and observation still take the same tack or will they go separate ways.
Babu G. Ranganathan*
(B.A. Bible/Biology)
JUST BECAUSE SCIENCE CAN EXPLAIN how an airplane works doesn’t mean that no one designed or made the airplane. And just because science can explain how life or the universe works doesn’t mean there was no Designer and Maker behind them.
Natural laws may explain how the order in the universe works and operates, but mere undirected natural laws cannot explain the origin of that order. Once you have a complete and living cell then the genetic code and biological machinery exist to direct the formation of more cells from raw materials such as amino acids and other chemicals, but how could life or the cell have naturally originated when no directing code and mechanisms existed in nature? Read my Internet article: HOW FORENSIC SCIENCE REFUTES ATHEISM.
WHAT IS SCIENCE? Science simply is knowledge based on observation. No human observed the universe coming by chance or by design, by creation or by evolution. These are positions of faith. The issue is which faith the scientific evidence best supports.
SCIENCE SHOWS THAT THE UNIVERSE CANNOT BE ETERNAL because it could not have sustained itself eternally due to the law of entropy (increasing and irreversible net energy decay, even in an open system). Even a hypothetical oscillating universe could not continue to oscillate eternally! Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity shows that space, matter, and time all are physical and all had a beginning. Space even produces particles because it’s actually something, not nothing. What about the Higgs boson (the so-called “God Particle”)? The Higgs boson, even if it existed, would not have created mass from nothing, but rather it would have converted energy into mass. Einstein showed that all matter is some form of energy. Even time had a beginning! Time is not eternal.
The law of entropy doesn’t allow the universe to be eternal. If the universe were eternal, everything, including time (which modern science has shown is as physical as mass and space), would have become totally entropied by now and the entire universe would have ended in a uniform heat death a long, long time ago. The fact that this hasn’t happened already is powerful evidence for a beginning to the universe.
Popular atheistic scientist Stephen Hawking admits that the universe had a beginning and came from nothing but he believes that nothing became something by a natural process yet to be discovered. That’s not rational thinking at all, and it also would be making the effect greater than its cause to say that nothing created something. The beginning had to be of supernatural origin because science teaches us from the First Law of Thermodynamics that natural laws and processes do not have the ability to bring something into existence from nothing.
The supernatural origin of the universe cannot be proved by science but science points to a supernatural intelligence and power for the origin and order of the universe. Where did God come from? Obviously, unlike the universe, God’s nature doesn’t require a beginning.
The disorder in the universe can be explained because of chance and random processes, but the order can be explained only because of intelligence and design.
Gravity may explain how the order found in the precise and orderly courses of thousands of billions of stars is maintained, but gravity cannot explain the origin of that order.
Some evolutionary astronomers believe that trillions of stars crashed into each other leaving surviving stars to find precise orderly orbits in space. Not only is this irrational, but if there was such a mass collision of stars then there would be a super mass residue of gas clouds in space to support this hypothesis. The present level of residue of gas clouds in space doesn’t support the magnitude of star deaths required for such a hypothesis. And, as already stated, the origin of stars cannot be explained by the Big Bang because of the reasons mentioned above. It’s one thing to say that stars may decay and die into random gas clouds, but it is totally different to say that gas clouds form into stars.
Even the father of Chaos theory admitted that the “mechanisms” existing in the non-living world allow for only very rudimentary levels of order to arise spontaneously (by chance), but not the kind or level of order we find in the structures of DNA, RNA, and proteins. Yes, individual amino acids have been shown to come into existence by chance but not protein molecules which require that the various amino acids be in a precise sequence just like the letters found in a sentence.
Some things don’t need experiment or scientific proof. In law there is a dictum called prima facie evidence. It means “evidence that speaks for itself.”
An example of a true prima facie would be if you discovered an elaborate sand castle on the beach. You don’t have to experiment to know that it came by design and not by the chance forces of wind and water.
If you discovered a romantic letter or message written in the sand, you don’t have to experiment to know that it was by design and not because a stick randomly carried by wind put it there. You naturally assume that an intelligent and rational being was responsible.
It’s interesting that Carl Sagan would have acknowledged sequential radio signals in space as evidence of intelligent life sending them, but he wouldn’t acknowledge the sequential structure of molecules in DNA (the genetic code) as evidence of an intelligent Cause. Read my popular Internet article, HOW DID MY DNA MAKE ME.
I encourage all to read my popular Internet articles:
NATURAL LIMITS TO EVOLUTION
HOW FORENSIC SCIENCE REFUTES ATHEISM
Visit my latest Internet site: THE SCIENCE SUPPORTING CREATION (This site answers many arguments, both old and new, that have been used by evolutionists to support their theory)
Author of popular Internet article, TRADITIONAL DOCTRINE OF HELL EVOLVED FROM GREEK ROOTS
*I have given successful lectures (with question and answer period afterwards) defending creation before evolutionist science faculty and students at various colleges and universities. I’ve been privileged to be recognized in the 24th edition of Marquis “Who’s Who in The East” for my writings on religion and science.
A mix of superstition and pseudoscience, full of sound and fury, signifying nothing.
Shrinking planets are nothing more then the crushing weight of the universe around it. The further the universe expands the less mass it has surrounding it, ultimately crushing it to through expansion. Existence can only reach so far. Beyond existence is only possible through expansion. Eventually expansion stops as well as existence.
What is your evidence?
The work described in the article has lots of evidence.
Earth (and others like her) isn’t shrinking. She’s growing. And the core isn’t cooling. It maintains a constant temperature because it’s constantly feeding energy into itself from the sun. Not just solar radiance, but all that harmful radiation as well… How you ask? The magnetic field. It’s center is not just some random point where nothing happens. It’s intricately tied to the planets condition, it’s weather, it’s internal temperature… Everything about our planet is influenced by our magnetic field. The center of the magnetic field is a toroidal vortex, and tremendous amounts of solar and cosmic energy are funneled into it, where it then focuses all that energy into a laser like beam, which then exits the Earth directly out the South magnetic pole and safely into space.
What is your evidence?
The work described in the article has lots of evidence.
I don’t think anymore data is needed, so every 50 million years we would need to create an artificial planet by the stimates and calculations of this scientists. It would be a hefty price to pay by humanity scale but if we would want to we would need to also calculate the amount of debrees orbiting near stars and close proximity exoplanets and planets.
First, @babu: I would love to have a debate with someone over creationism vs evolution, but it would appear you are mistaken on several parts of understanding what science is.
Most scientists easily admit nothing is actually known and is all just highly possible. We do not know for sure the sun will rise tomorrow, even though it has been all our life. We also never would say we know for sure the universe is finite, one of the greatest scientists to ever live actually believed it was infinite.
Albert Einstein only “gave in” to a finite universe based off red shift and other observations being made at the time. He wanted to believe it was infinite because he “discovered” matter and energy can not be created or destroyed, instead they bounce between forms. If you can’t create or destroy energy, just transfer it, then scientifically speaking it’s impossible the universe isn’t infinite. There is still debate to this day over if it’s finite or infinite. This has nothing to do with general relativity theory, or the theory that time flows relative to the person recording it.
Go look up some of your uses of things like god particle, as you don’t understand what a god particle is. It is not creating anything, it is simply the part of something that gives it mass. An example would be if we didn’t know why coffee made people alert, so we theorized there might be something in coffee that does this. Then we take coffee apart piece by piece looking for this thing, and you end up with caffeine. Nothing is being created or destroyed here, just discovered. The god particle is simply the part of something that gives it mass. Ever wonder why light can go light speed but you can’t? That particle is the reason, and knowing why it’s in almost everything but not in certain energy forms would help us greatly.
There is so much in your post that is cringe worthy I will stop here so I may make my comments on the article. I suggest you do what we scientists do and try to put your beliefs aside for a while and be open to change as you retake physics 101 and research more about Albert Einstein. You can download his original publication of the general theory of relativity online, and it’s even been translated to English (mostly). I have it on my phone at all times just for a fun read. Then you can get back to me on the law of entropy being the nail in the coffin for infinity vs finite.
This is not to say I don’t believe in a god, this is to try to explain to you what god is. If there is a creator who is everywhere at every moment, can change anything they want (ex. pray to God and things change for you), and knows everything then there is only one answer for what god could be. Energy, put simply. The only thing that’s everywhere in the universe constantly and “has always been and will always be” is energy. Energy, if it where somehow controlled, could discreetly change things without our knowledge. You are made of energy, as am I, so thus energy would know everything we do and think, because our thoughts are simply electricity in the brain, a form of energy. I am done with that, and I could be wrong. We came here for the scientific article, not a debate about who is right and who is wrong on what belief system.
I guess my main concern with shrinking planets is that if this where true, then there should be more middle sized planets then we find. If ice giants are really slowly shrinking, it would only make sense that some would be found in this gap. They do not suddenly change from a Neptune sized object to a super earth overnight, so where are the planets that are in the middle of the transition?
The huge problem behind pointing to one reason Neptune’s might loose mass is it depends on the star they are by. The article implies the loss of mass due to the parent star would mostly happen at the beginning of the planet’s life, but stars like our own sun do not start out fully “turned on”.
The leading theory is that our sun was actually smaller and less volatile earlier, so much so that Venus would have been in the goldy locks zone and thus supported liquid water. This would stand to reason then that as our sun ages it will start eating more of Neptune’s atmosphere, not less. However, this depends on the type of star the planet is orbiting. This information has been left out of the article sadly.
A good way to prove this would be to find multiple stars of a same type in the middle of their life that have these ice giants and check their sizes. This is where you would find your missing middle sized planets. If they are not there, then the only way this could be possible is if it is a sudden event that happens in millions of years or less.
By the way, just to mention, our sun is in about the middle of it’s life cycle. So we are now basing a Neptune sized planet off of a middle aged Neptune. A gold star to anyone who can explain why they are using Neptune instead of the other giants. I already gave a hint by specifying what kind of giant it was.
I don’t think the answer to superstition is more superstition. Science is based on evidence, and we now know the universe is 100 % natural system – no room for “puny gods” as Marvel movies has it.
That planets orbit a larger massed star for many orbits is a consequence of physical laws, who in turn are consequences of symmetries [ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noether%27s_theorem ]. There is no principle problem in natural systems having robust, trustworthy, properties.
Dark matter-plasma-gas-particles-suns-planets-magnatars-blackholes-repeat lmao. Simple version☝️
?
The planet classification is of a mass that is large enough to be hyrostatic rounded and dominates its orbit and has no fusion (as a star would). The cores of gas giants are under study.
“Gas giants also have cores, though the composition of these are still a matter of debate and range in possible composition from traditional stony/iron, to ice or to fluid metallic hydrogen.”
[ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Planetary_core ]
P. S. HOW COULD A BALL OF GAS BE CLASSIFIED AS A PLANET , THAT HAS NOTHING SOLID ABOUT IT ? I WOULD RATHER ponder BALLS OF GAS WE CALL PLANETS JUST FORMATIONS OF MATTER NOT SURE YET WHAT TO BECOME. WHY WOULD THIS BE WRONG OR CORRECT.?
Beam me up Scotty!