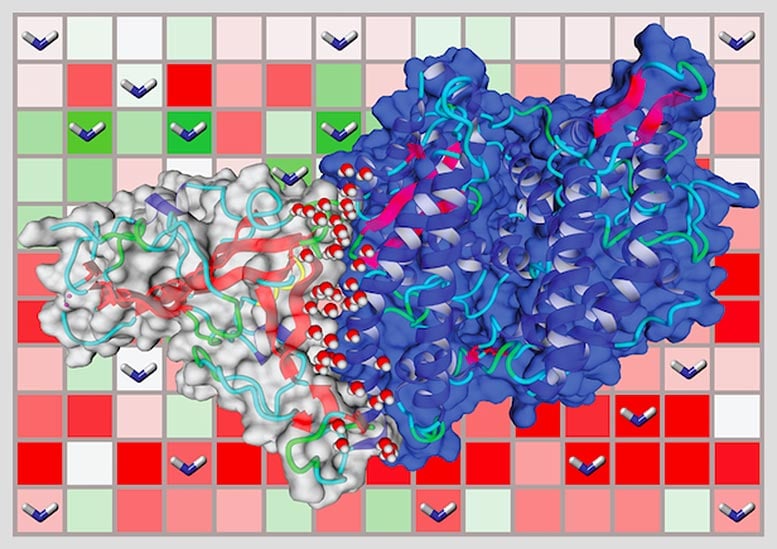
In blue, the human ACE2 protein and in grey, the coronavirus spike protein. Pictured are how the two proteins interact in a lock-and-key mechanism, which allows the virus to enter the cell and hijack its protein-making machinery to replicate itself. Credit: Javier Delgado
Ducks, rats, mice, pigs, and chickens had lower or no susceptibility to infection.
Humans, followed by ferrets and to a lesser extent cats, civets, and dogs are the most susceptible animals to SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to an analysis of ten different species carried out by researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), based in Barcelona.
The findings, published in PLOS Computational Biology, found that ducks, rats, mice, pigs, and chickens had lower or no susceptibility to infection compared to humans.
“Knowing which animals are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 helps us prevent building up animal reservoirs from which the coronavirus can re-emerge at a later date,” says Luis Serrano, ICREA Research Professor, Director of the CRG and senior author of the study. “Our findings offer a clue for why minks – which are closely related to the ferret – are being infected by the disease, which is probably made worse by their packed living conditions and close contact with human workers.”
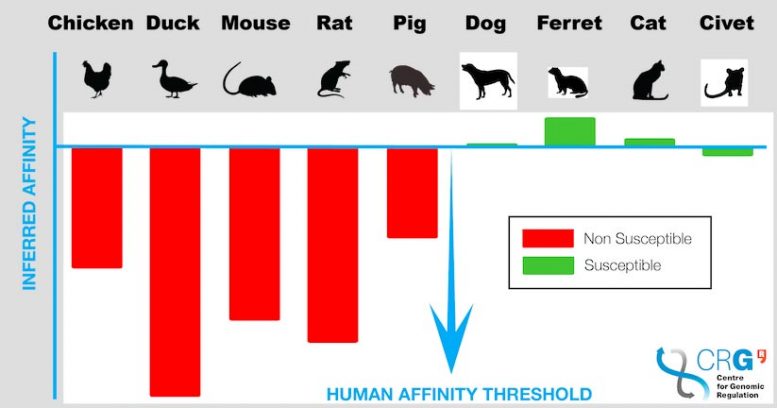
The binding affinity for the ACE2 receptors with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 across eight different species compared to humans (the blue baseline). Species above the threshold are vulnerable to letting the coronavirus enter the cell while those below have significantly lower or no risk for infection. Credit: Javier Delgado
“Though we also find a potential susceptibility to infection by cats, they don’t co-exist with humans in the same conditions as other animals, which may explain why so far there are no known cases of people being infected by their pets,” adds Dr. Serrano.
Ten species were studied in this paper. Five species – humans, cats, ferrets, civets, and dogs – have had documented cases of infection by SARS-CoV-2. There are no reports of infection in the other five species – mice, rats, pigs, chickens, and ducks.
The researchers used computer modeling to test how the coronavirus uses its spike proteins, which protrude from the surface of the virus, to infiltrate the cells of different animals. The main point of entry on a cell’s surface is the ACE2 receptor, which binds with the spike protein through a lock-and-key mechanism. There are many different variants of ACE2 within human populations and across different species.
Variants of the ACE2 receptor in humans followed by ferrets, cats, dogs, and civets have the highest binding affinities to the viral spike protein, while mice, rats, chickens, and ducks have poor binding energy.
However, binding affinity is not enough on its own to gauge a cell’s susceptibility to infection. The researchers also tested the different species ‘codon adaptation index’ – which is how efficient the coronavirus is at commandeering a cell’s machinery once it has entered. The more efficient the process, the better the coronavirus can create the proteins it needs to replicate.
Humans, chickens, and ducks have the highest codon adaptation index, while the other species are worse adapted.
Considering both binding affinity and the codon adaptation index, the researchers conclude that humans, followed by ferrets, cats, civets, and dogs are the most susceptible animals to infection by coronavirus.
They also found that different human variants of ACE2 showed differences in stability and binding to the spike protein, a sensitivity that may underlie why some people suffer from severe COVID-19 symptoms.
“We have identified mutations on the S-protein that dramatically reduce the capacity of SARS-CoV-2 to enter into the cell, protecting the host from catching COVID-19,” says Javier Delgado, researcher at the CRG and first author of the study. “We are now engineering mini-proteins from the human ACE2 protein to ‘distract’ the attention of the virus from entering cells and block infection. Should new mutations of the viral spike protein arise, we could engineer new variants to block them.”
Understanding SARS-CoV-2 infectivity across different species can better inform public health measures, helping reduce human contact with other susceptible animals and avoiding the potential prolongation of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the WHO, since June 2020, 214 human cases of COVID-19 have been identified in Denmark with SARS-CoV-2 variants associated with farmed minks, including 12 cases with a unique variant, reported on November 5. Preliminary findings indicate that this particular mink-associated variant has moderately decreased sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies – though this has not been demonstrated.
Reference: “In silico mutagenesis of human ACE2 with S protein and translational efficiency explain SARS-CoV-2 infectivity in different species” by Javier Delgado Blanco, Xavier Hernandez-Alias, Damiano Cianferoni and Luis Serrano, 7 December 2020, PLOS Computational Biology.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008450
Funding: Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, the Government of Catalonia, “la Caixa” foundation, CERCA centers, the Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology and the Severo Ochoa Centre of Excellence.








So if pet cats and dogs are in an environment contaminated by covid 19 do they become ill with the virus. Can they infect humans can they be carriers. Are the same precautions one takes now extended to our pets. How does one care for an infected pet or are they only carriers.
I hope this doesn’t mean we’ll be restricted from having any of these animals.