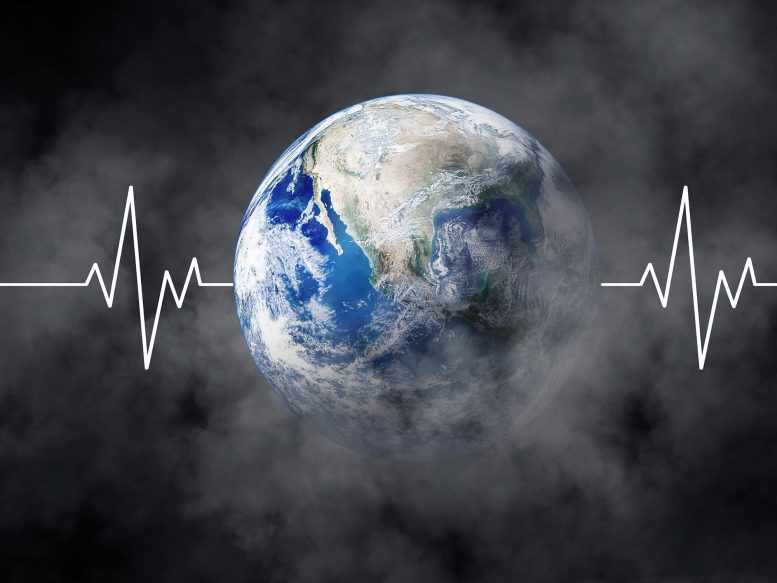

Research on the Quaternary period reveals rapid climate changes, known as Dansgaard-Oeschger events, in the last and penultimate glacial periods through Greenland ice cores and Turkish stalagmites. These findings, highlighting the North Atlantic’s influence, aim to improve climate models and extend understanding of climate variability up to 700,000 years.
Throughout the Quaternary period of recent geological history, there have been alternating cycles of ice ages and warm intervals. Scientists can understand past climate changes by analyzing the composition of climate records. Specifically, for the last ice age that occurred about 100,000 years ago, ice core samples from Greenland have been particularly valuable, offering detailed insights into the climate data of that time.
For example, Greenland ice cores show that there were repeated rapid increases in temperature. “We are talking about increases of 5 to 10 degrees within 30 to 40 years on average in the case of Europe. A Neanderthal would have experienced increases in the average temperature of several degrees over the course of their life,” explains Prof. Dominik Fleitmann, Professor of Quaternary Geology at the University of Basel. He calls the phenomena “climate hiccups”.
These Dansgaard-Oeschger events are well-documented for the last glacial period, but the climate records from Greenland only cover the last 120,000 years. It was therefore previously unknown whether these Dansgaard-Oeschger events also occurred during the penultimate glacial period 135,000 to 190,000 years ago. Frederick Held, a PhD candidate in Fleitmann’s research group, was able to show that Dansgaard-Oeschger events also occurred during the penultimate glacial period using isotopic measurements on stalagmites. He is the lead author of the study which was published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
The North Atlantic as the source of change
The stalagmites examined originate from the Sofular Cave in Turkey, which is located in a region that is very sensitive to climate change. The researchers therefore refer to it as a key region, as it is influenced by the winds of the North Atlantic and the Black Sea is just a few kilometers away. “We used the isotopic composition in the stalagmites to determine the moisture sources from which they are formed – the Black Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, and the North Atlantic,” explains Frederick Held.
For the first time, the evaluations carried out on the stalagmites from the Sofular Cave have proven that Dansgaard-Oeschger events also occurred during the penultimate glacial period. “It was previously unknown whether these relatively brief temperature events actually happened in earlier glacial periods,” states Held. However, they occurred less frequently in the penultimate glacial period than in the last one: “The temperature peaks are twice as far apart from one another, meaning there were longer cold phases between them.”
These temperature fluctuations originate in the North Atlantic, as the circulation of the ocean is a global conveyor belt for heat and can sometimes be stronger and sometimes weaker. “For example, the circulation affects the exchange of heat between the atmosphere and the ocean, which, in turn, impacts the balance of heat in the Northern Hemisphere and air flows and rainfall,” explains Held. He states that weakened circulation also reduces the quantity of CO2 which the ocean absorbs from the atmosphere.
These ocean currents were different in the penultimate glacial period than in the last one, which explains the different intervals between the Dansgaard-Oeschger events. This shows that not all glacial periods are the same and not all warm periods are the same.
The researchers compared the data from the stalagmites with marine sediment cores, which also act as natural climate archive. The more pieces there are in the puzzle, the more accurate the picture of what happened, and feedback mechanisms can be captured more precisely.
Better understanding the mechanisms
Taking a look at the last two glacial periods, it becomes clear how fast climate can change. “Climate change drives forward new ecosystems,” says Dominik Fleitmann. “Our dream is to create a continuous dataset for the last 600,000 to 700,000 years and close any gaps in our knowledge.”
The evaluations help us to better understand the Earth in terms of which factors result in abrupt fluctuations in climate, what trends can be observed, and how and under what conditions the oceans’ circulation patterns change.
Current climate models can be tested using data from the past. “Patterns that are established can help climate researchers to further improve their models and therefore refine assumptions for future trends,” explains Fleitmann.
The geologist also hopes to clarify any outstanding questions by means of additional analyses. “For example, we do not yet know whether the increases in temperature were periodic or stochastic, in other words random.” PhD candidate Frederick Held adds: “Until now, we have been able to describe the trends, but it would be great if we were able to establish an absolute temperature value.”
Reference: “Dansgaard-Oeschger cycles of the penultimate and last glacial period recorded in stalagmites from Türkiye” by F. Held, H. Cheng, R. L. Edwards, O. Tüysüz, K. Koç and D. Fleitmann, 8 February 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45507-5






We are commonly told that today’s warming is “unprecedented,” which I question, and is the result of the burning of fossil fuels. Then we are presented with this article, which says, “We are talking about increases of 5 to 10 degrees within 30 to 40 years on average in the case of Europe.” If that is true, then what is happening today certainly doesn’t look “unprecedented” with 1 deg C in a century.
As to the warming being from anthropogenic sources resulting from industrialization, that couldn’t have been possible during the time of Neanderthals.
Occam’s Razor essentially states “Entities must not be multiplied beyond necessity.” Or, in more modern parlance, “The simplest explanation is usually the best one.” The corollary to that, as expressed by the Sagan Standard, “Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence,” also bears on the controversy about Earth’s recent warming, and its cause(s). It would seem to me that the simplest explanation is natural variation, with no need to appeal to ‘multiplied entities.’
We have a situation where it seems that the consensus paradigm about global warming violates both Occam’s Razor and the Sagan Standard because we have examples of rapid warming, many times in the past, when anthropogenic influences didn’t exist. Yet, based largely on taking the singular behavior of CO2 out of the context of its participation in a seemingly chaotic, complex, dynamic-system of numerous feedback loops, climatologists have decided to build digital edifices to prove their beliefs. Unfortunately, even our supercomputers aren’t up to handling the job adequately and the programmers have had to make a lot of assumptions that they embellish with the name “parameterizations.”
There are many reasons to question the extant paradigm, which should call up Sagan’s Standard. Instead, the skeptical questioners are likely to suffer ad hominem attacks of the form of “climate denial” or “science denier.” I do not claim to know the answer to the controversial problem. However, I think that it is imprudent to advocate for economic and social changes that are revolutionary, when many simple questions are being ignored, such as why the ice cores from Law Dome (Antarctica) appear to show temperatures changing 800 years before the atmospheric CO2 concentrations change, or why when anthropogenic CO2 emissions declined 14-18% in April 2020, the seasonal ramp-up phase of CO2 is indistinguishable from the preceding or following year.