According to the research, the medicinal usage of ketamine has a low risk of addiction.
Scientists have demonstrated that ketamine causes just a brief increase in dopamine and has no effect on neuronal communication.
Ketamine is a common anesthetic in medicine which is also increasingly prescribed to treat depressive symptoms. This very fast-acting psychotropic drug is particularly suitable for the treatment of individuals who have become resistant to standard antidepressants.
However, there has been disagreement about its prescription since some people believe there is a significant danger of addiction. A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) has investigated this by administering the drug to mice. Like other drugs, it causes an increase in dopamine in their brains, but it also inhibits a specific receptor that precludes the progression to addiction. The findings were recently published in the prestigious journal Nature.
Ketamine, discovered by American scientist Calvin Lee Stevens in 1962, is a synthetic drug produced from phencyclidine with strong anaesthetic effects. It is widely utilized in both human and animal medicine, most notably for pain relief and brief sedation. It is also illegally used for recreational reasons, with the dissociative effect causing a distorted perception of reality.
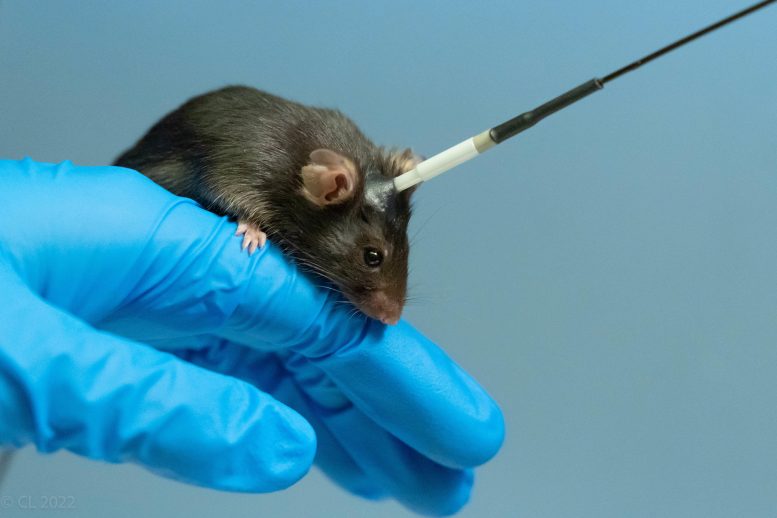
The research team used a device that allowed mice to self-administer doses of ketamine via a catheter. Credit: Christian Lüscher
Ketamine has also been used to treat depressive symptoms in individuals who have failed to respond to conventional treatments for the past ten years or so. Its impact is very rapid: its effect is noticed a few hours after the first dosage, while traditional antidepressants take several weeks to act. Despite the fact that it is increasingly being prescribed for this type of treatment, this drug is still hotly contested within the scientific community.
‘‘Some people believe that ketamine presents a strong addictive risk if taken for a long time, while others do not. The whole point of our research was to try to provide some answers,’’ explains Christian Lüscher, a Full Professor in the Department of Basic Neurosciences at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine and a specialist in the mechanisms underlying addiction.
Addiction vs. Dependence
Addiction is defined as the compulsive use of a substance despite its negative consequences (behavioral disorder). Dependence, on the other hand, is characterized by the appearance of one or more withdrawal symptoms on abrupt cessation of use (physiological disorder). Dependence – the physical manifestations of which vary greatly depending on the drug – affects everyone. Addiction, on the other hand, affects only a minority of people and is not caused by all drugs.
In the case of cocaine, for example, only 20% of users become addicted, even after prolonged exposure. For opiates, the rate is 30%. In its recent work, Christian Lüscher’s team sought to assess the risk of addiction to ketamine.
Short stimulation of the reward system
The UNIGE researchers used a device that allowed mice to self-administer doses of ketamine. ‘‘The drugs intensely stimulate the reward system in the brain, which leads to an increase in dopamine levels. The first step was to observe whether this mechanism was also at work when taking ketamine,’’ explains Yue Li, a Postdoctoral Scholar in the Department of Basic Neuroscience at the UNIGE Faculty of Medicine.
The scientists found that the level of dopamine – also known as the ‘‘pleasure molecule’’ – increased with each dose and induced a positive reinforcement in the mice, which motivated them to repeat the self-administration. ‘‘However, unlike cocaine, for example, we found that the dopamine level fell very quickly after taking the drug,’’ says Yue Li.
A drug that does not leave its “mark”
The research team wanted to understand this phenomenon. They discovered that ketamine triggered an increase in dopamine by inhibiting a molecule called the NMDA receptor in the reward center of the rodent brain. Dopamine then binds to another receptor (called the D2 receptor), which acts as a rapid brake on the increase in dopamine. The researchers also confirmed that the action of the NMDA receptor is necessary to modify the communication between the nerve cells that underlie the behavioral change leading to addiction. Ketamine’s inhibition of the NMDA receptor makes this modification impossible.
‘‘The consequence of this dual action of ketamine is that it does not induce the synaptic plasticity that addictive drugs do and that persists in the brain after the substance has worn off. It is this memorization of the product in the reward system – absent in the case of ketamine – that drives the repetition of consumption, explains Christian Lüscher. Therefore, the addictive risk of ketamine appears to be zero in rodents. Is this also the case in humans? Could this risk vary according to the individual? Our study provides a solid framework for debating access to its therapeutic use,’’ concludes Christian Lüscher.
Reference: “Dual action of ketamine confines addiction liability” by Linda D. Simmler, Yue Li, Lotfi C. Hadjas, Agnès Hiver, Ruud van Zessen, and Christian Lüscher, 27 July 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04993-7





Be the first to comment on "Ketamine May Be Safe for Medical Use"