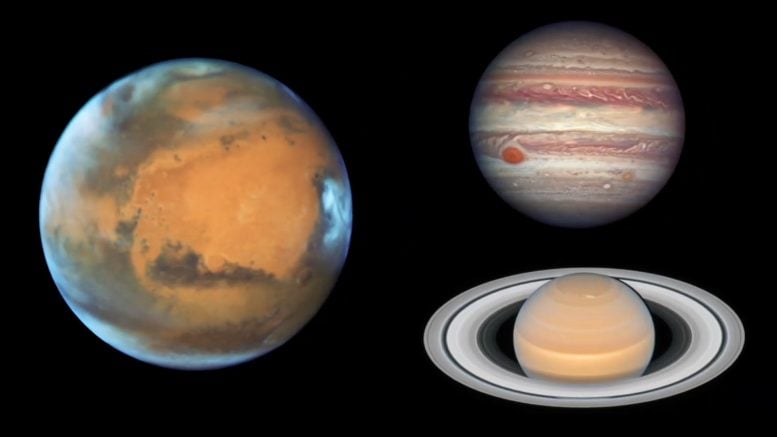
Skywatching Highlights for March 2021
What’s Up for March? Mars and friends in the evening, and a brilliant pair of planets returns…
In the first week or so of March, you’ll find Mars near the Pleiades star cluster high in the west in the few hours after sunset.
NASA’s Perseverance rover successfully landed on Mars on February 18th! And in addition to this latest surface explorer, orbiters from two other nations arrived in orbit around the Red Planet last month, making 2021 a truly international year of Mars exploration.
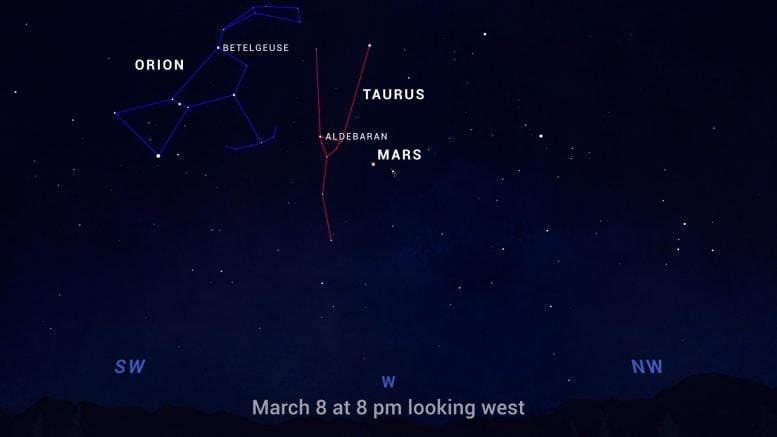
Sky chart showing Mars with the Pleiades, along with bright red stars Aldebaran, in Taurus, and Betelgeuse, in Orion. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
You may also notice a couple of other reddish objects forming a line with Mars – that is, the stars Aldebaran, which forms the angry eye of Taurus the bull, and Betelgeuse, the shoulder of Orion. And speaking of Betelgeuse, astronomers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories have determined the cause of the star’s dimming last year was likely due to a cloud of dust ejected by the aging red giant. And while scientists think the star has moved into burning helium, instead of hydrogen, in its core, they think it’s unlikely to explode in a supernova anytime soon.
Daily Guide
March 5
Friday morning, March 5, 2021, the bright star Antares will appear about 8 degrees below the waning gibbous Moon. Antares will rise after the Moon in the southeast at 1:17 a.m. EST, and it will appear about 6 degrees to the lower left of the Moon as morning twilight begins and the Moon reaches its highest in the sky at 5:37 a.m.
Also on Friday morning, the planets Jupiter and Mercury will appear at their closest to each other as morning twilight begins, appearing about 1.5 degrees above the horizon in the east-southeast.
Friday evening, the waning Moon will appear half-full as it reaches its last quarter at 8:30 p.m. EST. For the Americas, the half-full Moon will not rise until early Saturday morning at 1:44 a.m. EST.
March 6
Saturday morning, March 6, 2021, will be when the planet Mercury reaches its greatest angular separation from the Sun as seen from the Earth for this apparition (called greatest elongation), appearing half-lit through a large enough telescope. Because the angle of the line between the Sun and Mercury and the horizon changes with the seasons, the date when Mercury and the Sun appear farthest apart as seen from the Earth is not the same as when Mercury appears highest above the horizon in the east-southeast as morning twilight begins, which occurred on the morning of February 26, 2021.
March 9
Tuesday morning, March 9, 2021, the waning crescent Moon and the planets Saturn, Jupiter, and Mercury, will appear near the horizon from the southeast to the east-southeast. As morning twilight begins the Moon will appear on the right in the southeast at about 7 degrees above the horizon, with Saturn about 8 degrees to the left of the Moon in the east-southeast at about the same elevation above the horizon. The bright planet Jupiter will appear farther to the lower left at about 3 degrees above the horizon and Mercury will appear to the lower left of Jupiter at only 1 degree above the horizon.
March 10
By Wednesday morning, March 10, 2021, the waning crescent Moon will appear to have shifted to below and about halfway between Jupiter and Saturn in the east-southeast. As morning twilight begins, Saturn will appear on the right at about 8 degrees above the horizon, the Moon will appear to the lower left of Saturn only about a degree above the horizon, Jupiter will appear to the upper left of the Moon at 3 degrees above the horizon, and Mercury will appear farthest to the left at less than a degree above the horizon.
At about 6:45 a.m. EST (2021-Mar-10 11:45 UTC with 36 minutes uncertainty), Near-Earth Object (2021 CF6), between 152 to 339 feet (46 and 103 meters) across, will pass the Earth at between 4.1 and 4.2 lunar distances (nominally 4.2), traveling at 18,700 miles per hour (8.36 kilometers per second).
March 11
Thursday morning, March 11, 2021, will be the last morning Mercury will appear above the east-southeastern horizon at the time morning twilight begins, although Mercury should continue to be visible after it rises until about 30 minutes before sunrise.
March 13
Saturday morning, March 13, 2021, at 5:21 a.m. EST, will be the new Moon, when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun and will not be visible from the Earth.
The day of – or the day after – the new Moon marks the start of the new month for most lunisolar calendars. The second month of the Chinese year of the Ox starts on Sat., March 13, 2021 (at midnight in China’s time zone, which is 13 hours ahead of EST). Sundown on Saturday, March 13, 2021, marks the start of Nisan in the Hebrew calendar. In the Islamic calendar, the months traditionally start with the first sighting of the waxing crescent Moon. Many Muslim communities now follow the Umm al-Qura Calendar of Saudi Arabia, which uses astronomical calculations to start months in a more predictable way. Using this calendar – the eighth month of the year, Sha’ban – will begin at sunset on Saturday, March 13, 2021. Since Sha’ban is the month before Ramadan, it is during Sha’ban that Muslims finalize when to start fasting for Ramadan.
March 14
Sunday, March 14, 2021, is the first day of Daylight Savings Time. Don’t forget to reset your clocks and “Spring Forward.”
The waxing crescent Moon that is visible for a few nights beginning Sunday is called a “Wet Moon” or a “Cheshire Moon.” This is when the thin, waxing crescent Moon appears most like an upward-facing bowl or a smile in the evening sky.
March 18
Thursday, March 18, 2021, at 1:03 a.m. EDT, the Moon will be at apogee, its farthest from the Earth for this orbit.
March 19
On Friday night, March 19, 2021, the waxing crescent Moon, the planet Mars, and the bright star Aldebaran will form a triangle in the evening sky. Mars will appear about 3 degrees to the lower right of the Moon with Aldebaran appearing about 6 degrees to the lower left of the Moon. Aldebaran will set first in the west-northwest early Saturday morning at 12:51 a.m.
March 20
Saturday morning, March 20, 2021, at 5:37 a.m. EDT, will be the spring or vernal equinox, the astronomical end of winter, and the start of spring. From on the equator in eastern Kenya the Sun will appear to pass directly overhead, moving from the Southern Hemisphere to the Northern Hemisphere.
Saturday evening, the planet Mars and the bright star Aldebaran will appear closest to each other, slightly under 7 degrees apart.
March 21
On Sunday morning, March 21, 2021, the Moon will appear half-full as it reaches its first quarter at 10:40 a.m. EDT.
March 22-23
On Monday evening into Tuesday morning, March 22 to 23, 2021, the bright star Pollux, the brighter of the twin stars in the constellation Gemini, will appear above the waxing gibbous Moon. Pollux will appear about 7 degrees to the upper left of the Moon as evening twilight ends at 8:20 p.m. EDT, close to when the Moon will be highest in the sky for the night. Pollux will appear about 5 degrees to the upper right of the Moon by the time the Moon sets in the west-northwest on Tuesday morning at 4:10 a.m. EDT.
March 25-26
On Thursday evening into Friday morning, March 25 to 26, 2021, the bright star Regulus will appear about 5 degrees below the waxing gibbous Moon. Regulus will appear to the lower right of the Moon as evening twilight ends at 8:23 p.m. EDT. By the time the Moon reaches its highest in the sky for the night at 11:08 p.m. EDT – Regulus will appear nearly below the Moon. Regulus will set first in the west-northwest on Friday morning at 5:43 a.m. EDT.
On Friday morning, the planet Venus will be passing on the far side of the Sun as seen from the Earth, called superior conjunction. Because Venus orbits inside of the orbit of Earth, Venus will be shifting from the morning sky to the evening sky. Venus will begin emerging from the glow of dusk on the western horizon after about April 23, 2021.
March 28
The full Moon after next will be Sunday afternoon, March 28, 2021, at 2:48 p.m. EDT. The Moon will appear full for about 3 days around this time, from early Saturday morning into early Tuesday morning.








Be the first to comment on "Mars, Pleiades, Jupiter, Saturn and Other Skywatching Highlights for March 2021"