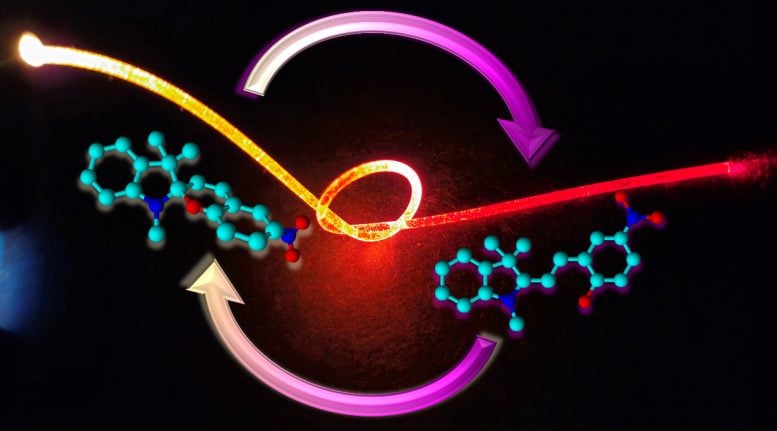
Dye-doped PDMS optical fiber at the center whose flexibility is demonstrated by a knot, and the switching mechanism of the organic dye. Credit: Camila Aparecida Zimmermann, Koffi Novignon Amouzou, Dipankar Sengupta, Aashutosh Kumar, Nicole Raymonde Demarquette, Bora Ung
Scientists have developed a flexible, reusable optical fiber for UV detection, promising enhanced integration with smart devices and advancing UV monitoring technologies.
The old saying “the dose makes the poison” applies equally to ultraviolet (UV) light. While UV light is essential for vitamin D production, shows promising results in phototherapy, and plays a role in various industrial processes and plant growth, it also has harmful effects such as premature skin aging and cancer.
The beneficial or harmful effects of UV light depend, among other variables, on the delivered UV dose. With the rise of point-of-care technology and the Internet of Things, there’s a growing demand for real-time monitoring of environmental variables that impact our health. However, the existing UV optical sensing technologies rely on materials with limited flexibility, or on costly and fragile (scientific grade) apparatus.
Innovative UV Detection Technology
To bridge this gap, researchers led by Prof. Bora Ung at École de Technologie Supérieure (ÉTS), Canada, fabricated a new rubber-like optical fiber for UV detection. For that, poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS), a highly flexible, stretchable, and biocompatible plastic, was doped with an organic dye that acts as a molecular switch to render PDMS responsive to UV light.
The molecular structure of the organic dye, named spiropyran, undergoes a reversible transformation triggered by UV irradiation which results in changes in the optical properties of the PDMS compound. These changes can be measured using commonly available LED/laser sources and photodiodes. Once the UV exposure stops, the material recovers its initial properties, much like a switch, and can be reused many times.
The researchers expect its integrability to smart textiles and wearable devices for continuous UV dose monitoring, leveraging the advantages of optical sensors, such as immunity to electromagnetic interference and corrosion. The findings are an important step toward the research in elastomeric optics, smart optical materials, and polymer optical waveguide sensors.
Reference: “Novel elastomeric spiropyran-doped poly(dimethylsiloxane) optical waveguide for UV sensing” by Camila Aparecida Zimmermann, Koffi Novignon Amouzou, Dipankar Sengupta, Aashutosh Kumar, Nicole Raymonde Demarquette and Bora Ung, 15 July 2024, Frontiers of Optoelectronics.
DOI: 10.1007/s12200-024-00124-4
Funding: Fonds de recherche du Québec – Nature et technologies, ÉTS Research Chair in Engineering Marcelle-Gauvreau









Be the first to comment on "Molecular Marvels: Scientists Revolutionize UV Sensing With Smart Technology"