NASA is seeking applicants to participate in its next simulated one-year Mars surface mission to help inform the agency’s plans for human exploration of the Red Planet. The second of three planned ground-based missions called CHAPEA (Crew Health and Performance Exploration Analog) is scheduled to kick off in spring 2025.
Each CHAPEA mission involves a four-person volunteer crew living and working inside a 1,700-square-foot, 3D-printed habitat based at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. The habitat, called the Mars Dune Alpha, simulates the challenges of a mission on Mars, including resource limitations, equipment failures, communication delays, and other environmental stressors. Crew tasks include simulated spacewalks, robotic operations, habitat maintenance, exercise, and crop growth.
NASA is looking for healthy, motivated U.S. citizens or permanent residents who are non-smokers, 30-55 years old, and proficient in English for effective communication between crewmates and mission control. Applicants should have a strong desire for unique, rewarding adventures and interest in contributing to NASA’s work to prepare for the first human journey to Mars.
The deadline for applicants is Tuesday, April 2.
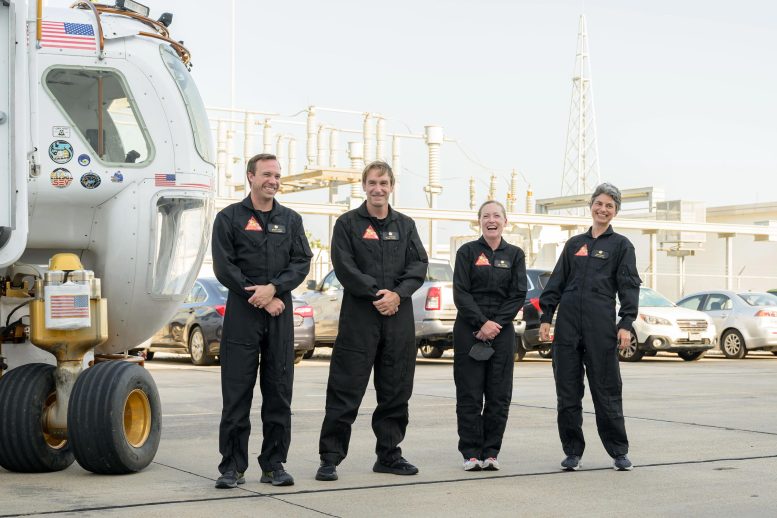

The CHAPEA mission 1 crew (from left: Nathan Jones, Ross Brockwell, Kelly Haston, Anca Selariu) exit a prototype of a pressurized rover and make their way to the CHAPEA facility ahead of their entry into the habitat on June 25, 2023. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
Crew selection will follow additional standard NASA criteria for astronaut candidate applicants. A master’s degree in a STEM field such as engineering, mathematics, or biological, physical or computer science from an accredited institution with at least two years of professional STEM experience or a minimum of one thousand hours piloting an aircraft is required. Candidates who have completed two years of work toward a doctoral program in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, completed a medical degree, or a test pilot program will also be considered. With four years of professional experience, applicants who have completed military officer training or a bachelor of science degree in a STEM field may be considered.
Compensation for participating in the mission is available. More information will be provided during the candidate screening process.
As NASA works to establish a long-term presence for scientific discovery and exploration on the Moon through the Artemis campaign, CHAPEA missions provide important scientific data to validate systems and develop solutions for future missions to the Red Planet. With the first CHAPEA crew more than halfway through their yearlong mission, NASA is using research gained through the simulated missions to help inform crew health and performance support during Mars expeditions.
Under NASA’s Artemis campaign, the agency will establish the foundation for long-term scientific exploration at the Moon, land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the lunar surface, and prepare for human expeditions to Mars for the benefit of all.







A hyperlight speed reactor uses cyclotrons to accelerate charged particles emitted by my injection reactor. As charged particles are fed into the cyclotrons, they repel off of the circulating particles to further accelerate them. The particles behind the ones being fed into the cyclotrons repel off of the ones in front of them and if the particles are placed properly, the repulsive effect should be the hyper acceleration of the particles that are circulated. The cyclotrons use glancing repulsive interactions of particles to increase their velocity. Mixing particles of opposite polarity keep the circulating particles from accelerating beyond control. Feed the hyper-accelerated charged particles into the repulsion-drive field emitters and field discharge unit in front and the field discharge system will push the spaceship well beyond the speed of light as long as the fields are emitted and spaced properly.