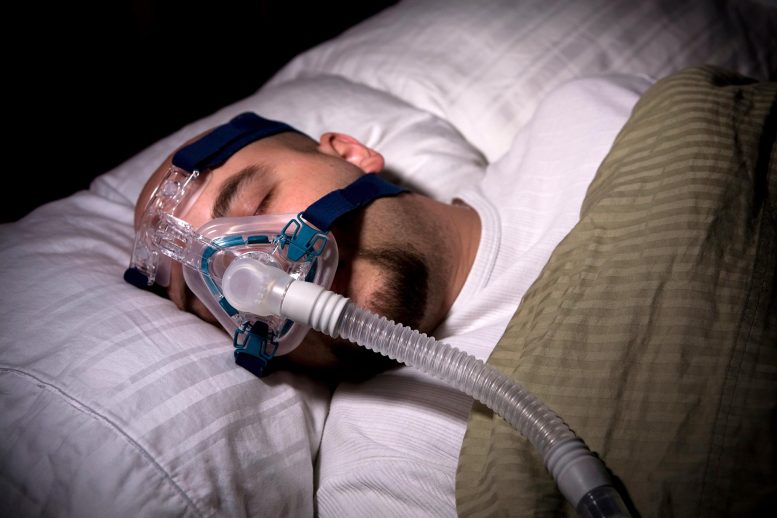
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by repeated cessation of breathing during sleep, which can last from a few seconds to several minutes. These breathing pauses can occur several times throughout the night and can lead to a fragmented sleep pattern, causing feelings of excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and irritability.
Research led by the University at Buffalo suggests a potential link between obstructive sleep apnea and low bone mineral density in adults.
These findings hold significant importance for individuals with sleep apnea, as low bone mineral density is a warning sign for osteoporosis, a condition that weakens and makes bones fragile. Senior author Thikriat Al-Jewair, DDS, Associate Professor of Orthodontics at the UB School of Dental Medicine and Director of the school’s Advanced Education Program in Orthodontics, highlights that in addition to increasing the likelihood of fractures, low bone mineral density also has a negative impact on oral health, causing teeth to become loose and dental implants to fail.
The study was published in The Journal of Craniomandibular and Sleep Practice. The researchers used cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) – a type of X-ray – to measure bone density in the head and neck of 38 adult participants, half of whom had obstructive sleep apnea.
When controlling for age, sex, and weight, the participants with obstructive sleep apnea had significantly lower bone mineral density than the participants without the condition.
Obstructive sleep apnea, which is characterized by difficulty breathing while asleep, can cause hypoxia (low levels of oxygen in the body), inflammation, oxidative stress, and shortened breathing patterns. Each of these symptoms may have a chronic negative effect on bone metabolism and, ultimately, bone density, says Al-Jewair.
“While the link between obstructive sleep apnea and low bone mineral density has yet to be fully explored, this study offers new evidence on their connection that could have several implications for orthodontic treatment,” says Al-Jewair, also assistant dean for equity, diversity, and inclusion in the UB School of Dental Medicine.
“If a patient has been diagnosed with sleep apnea, this can influence treatment planning and management. CBCT imaging has become an integral part of daily orthodontic practice and could be used as a screening tool for low bone mineral density,” she said. “Orthodontists could then inform their patients of their propensity for low bone mineral density and encourage them to seek further consultation with their physician, as well as warn the patient of possible adverse outcomes, increased risks, and effects on treatment time.”
Future research with larger sample sizes is needed, says Al-Jewair.
Reference: “Association between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and bone mineral density in adult orthodontic populations” by Mira Daljeeta, DMD, MS, Stephen Warunek, DDS, MS, David A. Covell, DDS, Ph.D., Alberto Monegro, MD, Terry Giangreco, DDS, MS and Thikriat Al-Jewair, DDS, MSc, MS, FRCD(C), 11 November 2022, The Journal of Craniomandibular & Sleep Practice.
DOI: 10.1080/08869634.2022.2142724







Be the first to comment on "Obstructive Sleep Apnea Tied to Weaker Bones and Teeth in Adults"