
Immunotherapy and anti-inflammatory therapy were more effective when mice consumed omega-3s.
Findings from a new study performed in mice suggest that omega-3 fatty acids could help immunotherapy and other treatments do a better job at fighting cancer. Immunotherapies, which stimulate the body’s own immune system to attack cancer, have revolutionized cancer treatment, but they don’t work for every patient.
“Dietary interventions can be powerful tools because they are relatively simple and inexpensive to implement,” said Abigail Kelly, a research assistant at Harvard Medical School’s Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. “Our findings show that omega-3 supplementation has the potential to broadly improve immunotherapy and other anti-cancer drugs in the clinical setting.”
Kelly will present the new research at the American Society for Investigative Pathology annual meeting during the Experimental Biology (EB) 2022 meeting, to be held on April 2-5, 2022, in Philadelphia.
The Role of Omega-3 and Omega-6 in Cancer
Research from various laboratories has suggested that omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce cancer risk whereas consuming too much omega-6 fatty acids can stimulate cancer. Sources of omega-3s include fish, nuts, and seeds while omegas-6s are found in meats, eggs, and other foods.
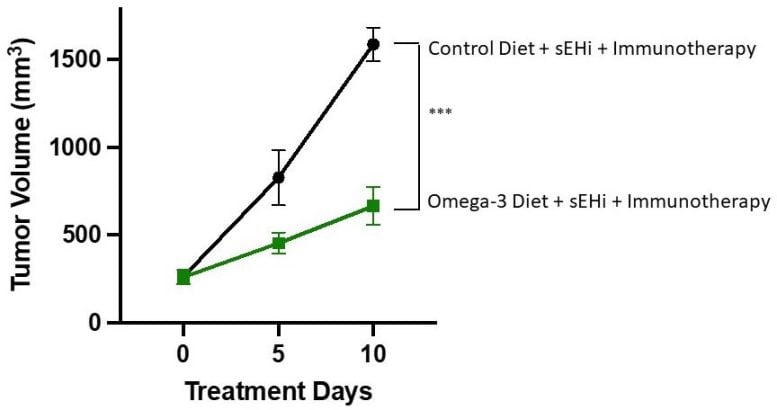
In the new studies, Kelly and senior author Dipak Panigraphy wanted to find out how diets supplemented with these fatty acids affected the anti-tumor activity of immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy and an anti-inflammatory therapy that inhibits the enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). The immunotherapy has regulatory approval and is being used clinically while the anti-inflammatory therapy is undergoing clinical development.
The researchers used state-of-the-art mouse models of primary and metastatic tumors for the new study. They began by feeding the mice either a standard diet or a diet high in omega-3 or 6 for 10 days prior to tumor injection and for the duration of the studies. One week after the tumors were injected, mice in each diet group were started on immunotherapy, anti-inflammatory therapy, both therapies together, or no treatment.
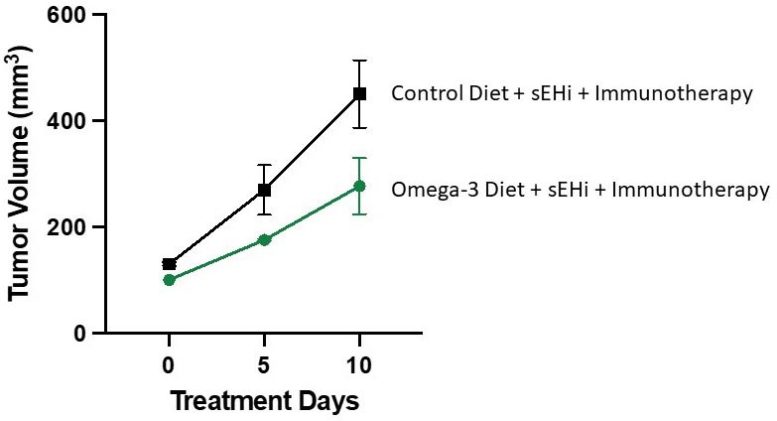
The researchers found that dietary omega-3 fatty acid supplementation blocked tumor growth in mice treated with immunotherapy, sEH inhibitor, or both treatments used together. In contrast, mice on the high-omega-6 diet and given immunotherapy experienced accelerated tumor growth in certain tumor types.
Synergistic Effects of Omega-3 with Cancer Therapies
In mice receiving the high omega-3 diet and both cancer treatments, up to 67 percent of tumor growth was inhibited compared to mice receiving no treatment and a normal diet. This indicates possible synergistic anti-tumor activity, meaning that the combined effect may be greater than the sum of its parts.
“We demonstrated, for the first time, that the combination of immunotherapy and anti-inflammatory treatment (sEHi) was more effective when mice were fed diets enriched with omega-3 fatty acids,” said Kelly. “This is very promising because dietary supplementation is easy to implement for cancer patients and can be added for patients already on immunotherapy.”
The researchers are now performing additional studies to determine the mechanism of action of the potentially synergistic anti-tumor activity imparted by omega-3 supplementation. They are conducting these studies with human cancer tissues and cells, human immune cells, and animal models to aid with translation to cancer patients. These new results from Kelly and colleagues may represent a new treatment approach that remains to be evaluated in humans.
Abigail Kelly will present this research from 11:45 a.m.–12:45 p.m., Monday, April 4, in Exhibit/Poster Hall A-B, Pennsylvania Convention Center (Poster Board Number D32) (abstract). This work will be featured in a virtual press conference from 11–11:45 a.m. EDT on Friday, April 1 (RSVP by Thursday, March 31). Contact the media team for more information or to obtain a free press pass to attend the meeting.
Meeting: Experimental Biology 2022
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.