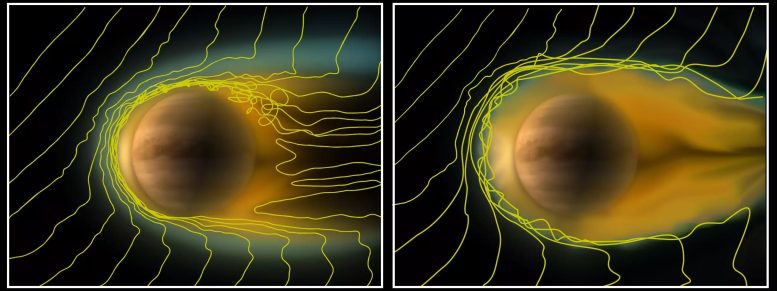
The change in ionosphere of Venus during normal solar wind conditions (left) and reduced solar wind activity (right), as observed by ESA’s Venus Express spacecraft in August 2010. The yellow lines show a projection of the solar magnetic field lines as they interact with the ionosphere. Venus Express follows an elliptical orbit around the planet once every 24 hours, passing within 250 km of the north pole and 66,000 km over the south pole. The observations were made on the night side of the planet, when Venus Express was within 15,000 km of the center of the planet. Although the spacecraft only took measurements within two Venus radii, the findings suggest that the ionosphere likely extends to even greater distances during periods of reduced solar wind intensity. Credit: ESA/Wei et al. (2012)
Scientists were able to study the deformation of the sheath of electrons and ions enveloping Venus for the first time.
In rare events, the sheath of electrons and ions enveloping Venus at a height of 150 to 300 kilometers (93 to 186 miles) can expand into space like a tail. This exceptional deformation occurs on the planet’s night side, when the solar wind, the flow of charged particles from the Sun, nearly comes to a stop. Scientists under the lead of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS) were now for the first time able to study such an event in detail. Their analysis is based on data obtained by instruments on board ESA’s spacecraft Venus Express. The results may help to understand, whether particles in our solar system can travel from one planet to another – for example from Venus to Earth.
On August 3 and 4, 2010 the Sun held its breath: After several heavy coronal mass ejections, the solar wind, the continuous flow of electrons and protons from the Sun, almost completely broke off for approximately 18 hours. In this phase, only 0.2 particles per square centimeter reached Venus. After Mercury, Venus is the second closest planet to the Sun. On normal days, this value is approximately 25 to 50 times higher.
“Phases with such weak solar wind are rare, but occur time and again,” says Markus Fränz from the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research. “However, the event in August 2010 was the first one since the launch of the space probe Venus Express seven years ago,” he adds. Due to the spacecraft’s pronounced elliptical orbit around Venus, the researchers had the chance to study the processes triggered by the weak solar wind in the planet’s atmosphere.
As is Earth, Venus is surrounded by an ionosphere, a sheath consisting of electrons and ions. Scientists refer to this as a plasma. The charged particles are created on the planets’ day sides when ultraviolet light with extremely short wavelengths and X-rays enter the outer layers of the atmospheres. On Earth, the particles are trapped by the strong magnetic field forcing them to rotate together with the Earth (and its magnetic field) around the Earth’s axis. In this way, they reach the planet’s night side thus forming a complete and spherical layer.
“On Venus, this is completely different,” says Yong Wei from the MPS, the new paper’s lead author. “Venus not only lacks a magnetic field of its own. She also rotates much slower,” he adds. For one rotation Venus takes a little more than 224 Earth days.
Nevertheless, one can observe an ionosphere on Venus’ night side. “Measurements performed by older space probes have shown electrons and ions flowing from the day side to the night side,” says Fränz. This flow is driven by the high plasma pressure on the day side. Like a compressed gas escaping from a pressure cylinder, the plasma travels from a region with high pressure to one with lower pressure.
With the help of the magnetometer MAG and the instrument ASPERA-4 (Analyzer of Space Plasmas and Energetic Atoms) on board Venus Express, the researchers were able to take a closer look. They found that in events of weak solar wind Venus’ ionosphere is not magnetized. Under normal conditions, these induced magnetic fields bind the charged particles of the ionosphere close to the planet. When the solar wind breaks off, however, the ionosphere in the region between the day and night side can expand. “The charged particles can therefore reach the night side more easily and in greater numbers,” says Fränz. There, a sort of plasma balloon is created that extends into space like a tail. The whole ionosphere thus takes on a tear-shaped form.
The new measurements prove that the night-side ionosphere protrudes approximately 15,000 kilometers (9,300 miles) into space. “But the tail could be much longer. It might measure up to millions of kilometers,” says Wei. Since Venus Express’ flight route did not lead the spacecraft directly behind the planet, however, this question cannot be answered conclusively.
It is also still unclear, whether the ionosphere of Venus can in principle expand far enough to reach Earth. In 1996 researchers from MPS were able to detect plasma from Venus close to our planet. They analyzed data obtained by the spacecraft SoHO that circles the Sun in line with the Earth. Perhaps the processes now observed by their colleagues from MPS offer an explanation for such events. “Possibly phases with tenuous solar wind allow particles to travel from planets close to the Sun to those further away,” says Wei.
Reference: “A teardrop-shaped ionosphere at Venus in tenuous solar wind” by Y. Wei, M. Fraenz, E. Dubinin, A. J. Coates, T. L. Zhang, W. Wan, L. Feng, A. Angsmann, A. Opitz, J. Woch, S. Barabash and R. Lundin, 1 September 2012, Planetary and Space Science.
DOI:10.1016/j.pss.2012.08.024









Be the first to comment on "Scientists View Changes in Venus’s Ionosphere"