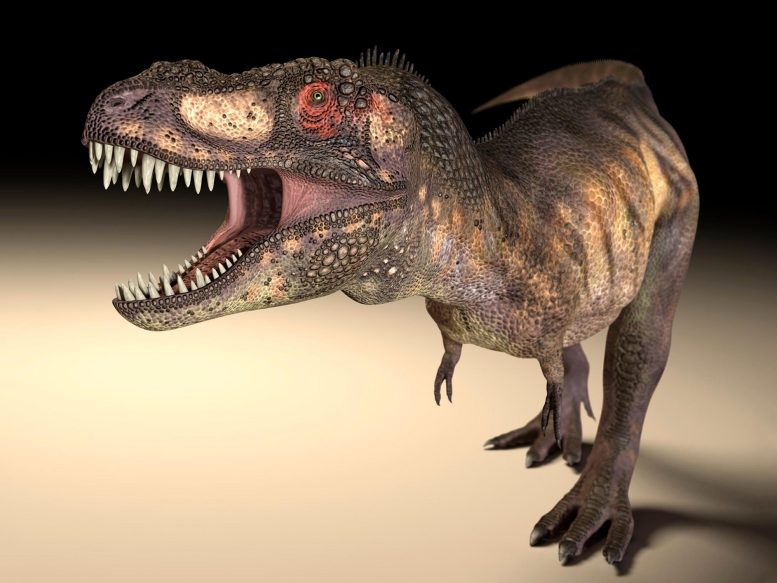

According to new research, large dinosaur predators, such as Tyrannosaurus rex, evolved different shapes of eye sockets to better deal with high bite forces.
While in many animals, including most dinosaurs, the eye socket is just a circular hole in the skull housing the eyeball, this is very different in large carnivores.
A new study reveals how the unusual elliptical, or oval eye sockets found in the skulls of these predators, could have evolved to help the skull absorb impact as they pounced on prey. This research, by scientists at the University of Birmingham, was published today (August 11, 2022) in Communications Biology.
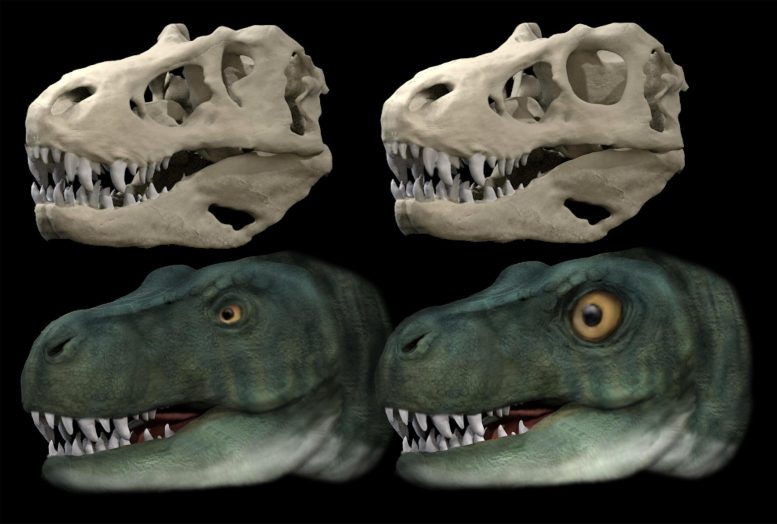

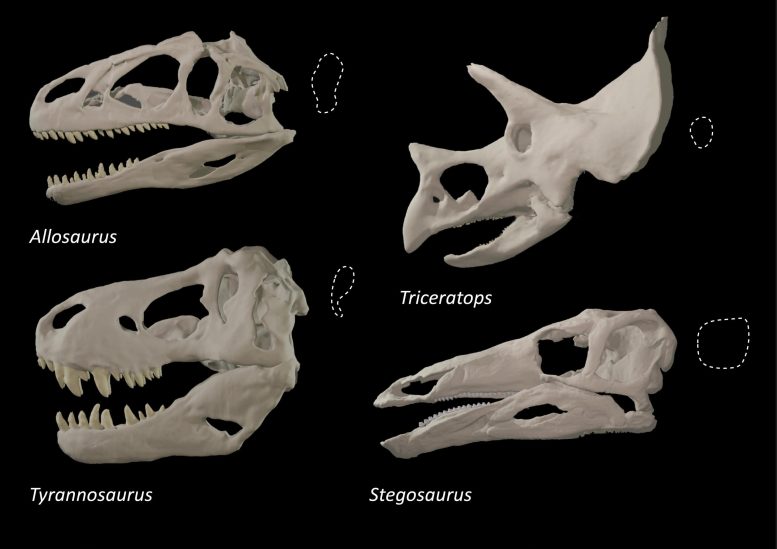
Dr. Stephan Lautenschlager, Senior Lecturer for Palaeobiology at the University of Birmingham and author of the new study, analyzed the shape of the eye sockets of ca. 500 different dinosaurs and related species.
“The results show that only some dinosaurs had eye sockets that were elliptical or keyhole-shaped,” said Dr. Stephan Lautenschlager. “However, all of those were large, carnivorous dinosaurs with skull lengths of 1 m or more.”
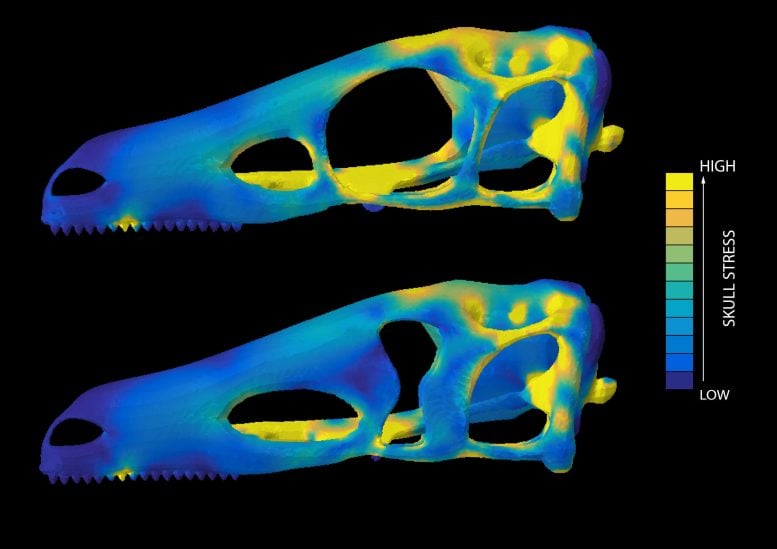
Dr. Lautenschlager tested what purpose these unusual eye socket shapes could have by using computer simulations and stress analysis.
The Benefits of Non-Circular Eye Sockets in Large Predators
The results demonstrated that a skull with a circular eye socket was more prone to high stresses during biting. However, if these were replaced with other eye socket shapes stresses were significantly reduced. This allowed top predators, including Tyrannosaurus rex, to evolve high bite forces without compromising skull stability.
The study also showed that most plant-eating species and juvenile individuals retained a circular eye socket. Only large carnivores adopted other morphologies, such as elliptical, keyhole-shaped, or figure-of-eight-shaped eye sockets.
Dr. Lautenschlager added: “In these species, just the upper part of the eye socket was actually occupied by the eyeball. This also led to a relative reduction of eye size compared with skull size.”
The researchers also investigated what would have happened if eye size had increased at the same rate as skull length. In such a case, the eyes of Tyrannosaurus rex would have been up to 30 cm (12 inches) in diameter and weighed nearly 20 kg (44 pounds). This is instead of an estimated 13 cm (5 inches) and 2 kg (4.4 pounds).
Reference: “Functional and ecomorphological evolution of orbit shape in mesozoic archosaurs is driven by body size and diet” by Stephan Lautenschlager, 11 August 2022, Communications Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03706-0
Never miss a breakthrough: Join the SciTechDaily newsletter.
1 Comment
Old news they allready know that by antorbital fenestra of the gator it’s gone in modern crocodilian that why spinosauridae has to reduce antorbital most of main hole in the skull is reduce the easy hole to see in the skull not the million hole that hard to see.allso gator temporal fenestra is fuse because these dinosaur have the greatest bite force the dwarf caiman it’s not fuse because they have small snout like primitive dinosaur .spinosaurus have to move the nose like a whale a aquatic feature no it’s not a bite force feature they lack back up in there skull not like advance dinosaur the gator with 6 bones fuse to braincase .crocodilian allways have a problem with the snout that why they are so much evolution .spinosaurus and gator round eyes it’s for twisting the skull predator eating feature because of big skull most theropod and protosuchus type of dinosaur eat up and down no death roll so gator spinosaurus skull round eyes is to lighting the big heavy skull.spinosauridae allso reduce the nose it’s behind the kink modern crocodilian is before kink in the snout .spinosaurus gain strength by reduce the nose it’s so reduce it can not smell very well that why it was replace by gator type mesoeucrocodylia modern crocodilian still does reduce the nose like American alligator dwarf crocodile there nose is fuse like primitive theropod but t.rex does not have moveable pubis hip to take in more oxygen .t.rex no back up that why it’s extinct .modern crocodilian can crush metal that a bite force.the champ