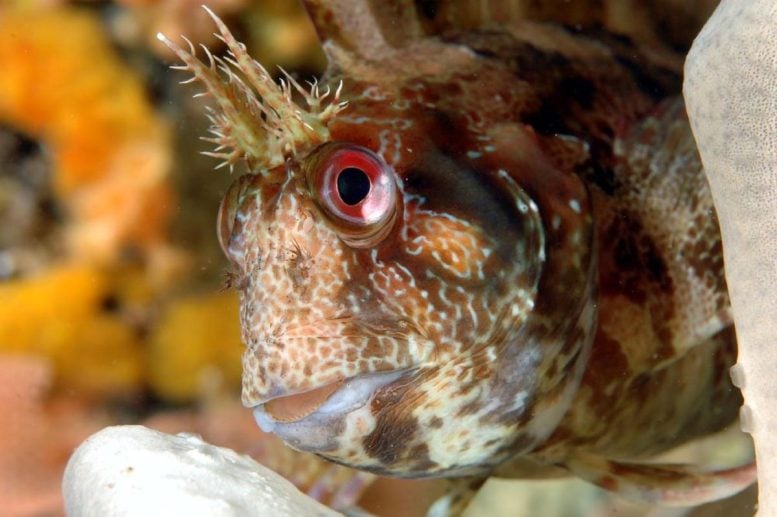

Tompot blenny (Parablennius gattorugine). The Blenniidae and Gobiidae are two families of fish that are rarely studied and receive little public attention. Credit: © Roland GRAILLE/CNRS Images
Research reveals that the most endangered reef fishes are often the least studied and appreciated, with public and scientific interest skewed towards commercially valuable or aesthetically appealing species.
This oversight, highlighted through analysis of big data sources, underscores the need for a conservation strategy that realigns human interest with ecological importance.
Overlooked Reef Fishes: A Surprising Discovery
The most threatened reef fishes are also the most overlooked by scientists and the general public. That is the startling finding of a team of scientists led by a CNRS researcher.[1] In a study to be published in Science Advances on July 17, they measured the level of human interest in 2,408 species of marine reef fish and found that the attention of the scientific community is attracted by the commercial value more than the ecological value of the fishes. The public, on the other hand, is primarily influenced by the aesthetic characteristics of certain species, such as the red lionfish (Pterois volitans) and the mandarinfish (Synchiropus splendidus).
The Role of Blennies and Gobies in Reef Ecosystems
Consider blennies (Blenniidae) and gobies (Gobiidae). These two fish families largely swim under the radar of both researchers and members of the public yet, as cleaners, they play a key role in the functioning of reefs. Small in size, they are essential to transfer of energy and matter from tiny prey to bigger consumers in reefs (trophodynamics).[2]
Big Data Reveals Disparities in Marine Research Attention
To reach their conclusions, the research team relied on big data compiled from scientific databases, social media, and Wikipedia page view statistics for the different fish species. They found that, though the 2,408 species studied accumulated more than 17 million views on Wikipedia, but that over 50% of those views were for only 7% of the species, and that 20% of the views were for only 1%. In addition, nearly 50% of the scientific publications for the fishes studied only concerned a subset of 1% of the species.
Addressing the Conservation Bias
The research team’s work brings to light a bias that directly threatens the conservation of marine reef fish, a bias of such magnitude that it compels them to sound the alarm. They emphasize the importance of aligning human interest in biodiversity with conservation needs and priorities for healthy ecosystems. They suggest launching campaigns to raise public awareness of threatened and neglected species. Finally, they advocate the establishment of research programs that take into account all ecosystem components, for a global conservation strategy that is no longer driven by commercial imperatives.
Notes
- This research was a collaboration between scientists from the Marine Biodiversity, Exploitation and Conservation (CNRS / IFREMER / IRD / University of Montpellier) and Écologie Marine Tropicale des Océans Pacifique et Indien (IFREMER / IRD / University of Réunion / University of New Caledonia) research units and the Foundation for Biodiversity Research.
- The trophodynamic chain is a set of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem.
Reference: “Low human interest for the most at-risk reef fishes worldwide” 17 July 2024, Science Advances.







Be the first to comment on "Biased Waters: The Skewed Science of Marine Conservation"