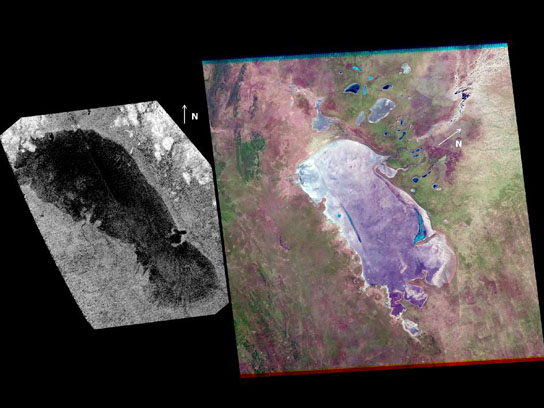
A recent study finds that the lake known as Ontario Lacus on Saturn’s moon Titan (left) bears striking similarity to a salt pan on Earth known as the Etosha Pan (right). A salt pan is a lake bed that fills with a shallow layer of water from groundwater levels that rise during the rainy season. This layer then evaporates and leaves sediments like tide marks showing the previous extent of the water. Ontario Lacus, seen in an image obtained by the radar instrument aboard NASA’s Cassini spacecraft on Jan. 12, 2010, covers an area about 140 by 47 miles (230 by 75 kilometers). The Etosha Pan, seen in an image obtained by a NASA and USGS Landsat satellite on Jan. 21, 2003, covers an area about 75 by 40 miles (120 by 65 kilometers). The north direction is indicated by the arrows. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech and NASA/USGS
Based on data from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, a newly published research paper suggests that Lake Ontario Lacus on Saturn’s moon Titan is very similar to the Etosha salt pan on Earth, although the liquid in Ontario Lacus is methane, ethane, and propane rather than water.
A new study analyzing data from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft suggests that the lake, known as Ontario Lacus, behaves most similarly to what we call a salt pan on Earth.
A group led by Thomas Cornet of the Université de Nantes, France, a Cassini associate, found evidence for long-standing channels etched into the lake bed within the southern boundary of the depression. This suggests that Ontario Lacus, previously thought to be completely filled with liquid hydrocarbons, could actually be a depression that drains and refills from below, exposing liquid areas ringed by materials like saturated sand or mudflats.
“We conclude that the solid floor of Ontario Lacus is most probably exposed in those areas,” said Cornet, whose paper appears in a recent issue of the journal Icarus.
These characteristics make Ontario Lacus very similar to the Etosha salt pan on Earth, which is a lake bed that fills with a shallow layer of water from groundwater levels that rise during the rainy season. This layer then evaporates and leaves sediments like tide marks showing the previous extent of the water.
“Some of the things we see happening in our own backyard are right there on Titan to study and learn from,” said Bonnie Buratti, a co-author and Cassini team member based at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. “On Earth, salt pans tend to form in deserts where liquids can suddenly accumulate, so it appears the same thing is happening on Titan.”
While the liquid on Titan is methane, ethane, and propane rather than water, the cycle appears to work in a very similar fashion to the water cycle on Earth. Beyond Earth, Titan is the only other world known to bear stable liquids on its surface. There, the full hydrocarbon cycle is based on hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen, and takes place between the atmosphere, the surface, and the subsurface. Titan’s lakes are an integral part of this process.
This latest paper is part of an ongoing study of Ontario Lacus, the largest lake in Titan’s south polar region. Cassini has been observing the lake with multiple instruments and employing multiple methods of analysis to see if Titan, like Earth, changes with the seasons. During the time Cassini has been exploring the Saturn system, Titan’s southern hemisphere transitioned from summer to fall.
“These results emphasize the importance of comparative planetology in modern planetary sciences: finding familiar geological features on alien worlds like Titan allows us to test the theories explaining their formation,” said Nicolas Altobelli, ESA’s Cassini–Huygens project scientist.
The Cassini–Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency, and ASI, the Italian Space Agency. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed, and assembled at JPL. The RADAR instrument was built by JPL and the Italian Space Agency, working with team members from the US and several European countries. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.






Be the first to comment on "Cassini Explores Titan’s Lake, Similarities to Etosha Salt Pan"