Note: There is now a newer Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report 11.
WHO Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report 10
- The Emergency Committee on the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) under the International Health Regulations (IHR 2005) is meeting today to discuss whether the outbreak constitutes a public health emergency of international concern.
- First confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease in Finland, India, and Philippines; all had travel history to Wuhan City.
- On January 29, 2020, WHO held its third press briefing to provide update on the situation. The audio can be found here.
- WHO recommends that the interim name of the disease causing the current outbreak should be “2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease” (where ‘n’ is for novel and ‘CoV’ is for coronavirus). This name complies with the WHO Best Practices for Naming of New Human Infectious Diseases, which were developed through a consultative process among partner agencies. Endorsement for the interim name is being sought from WHO’s partner agencies, World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) and Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The final name of the disease will be provided by the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). WHO is also proposing ‘2019-nCoV’ as an interim name of the virus. The final decision on the official name of the virus will be made by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses.
Risk Assessment
China: Very High
Regional Level: High
Global Level: High
Coronavirus Situation in Numbers
Globally
- 7818 confirmed
China
- 7736 confirmed
- 12167 suspected
- 1370 severe
- 170 deaths
Outside of China
- 82 confirmed
- 18 countries
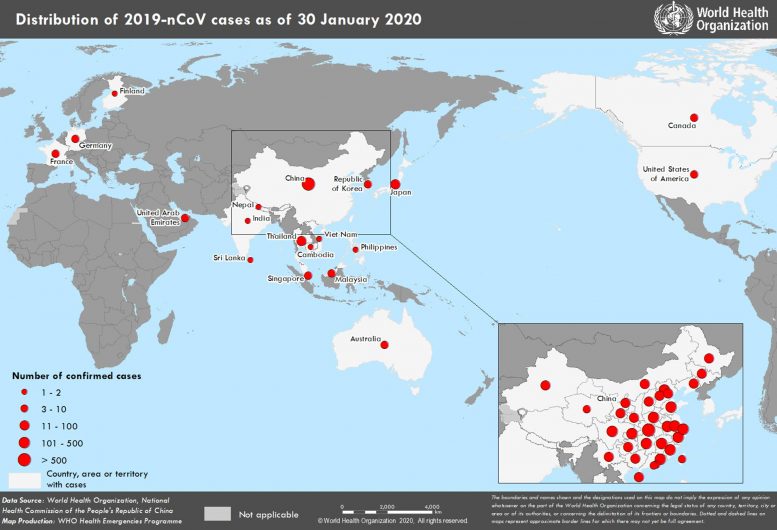
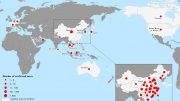
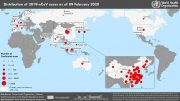
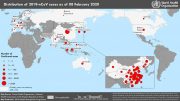
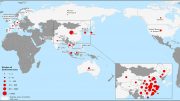
Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV, January 30, 2020
| Country/Territory/Area | Confirmed Cases |
|---|---|
| China | 7736 |
| Thailand | 14 |
| Japan | 11 |
| Singapore | 10 |
| Australia | 7 |
| Malaysia | 7 |
| France | 5 |
| United States of America | 5 |
| Germany | 4 |
| Republic of Korea | 4 |
| United Arab Emirates | 4 |
| Canada | 3 |
| Vietnam | 2 |
| Cambodia | 1 |
| Finland | 1 |
| India | 1 |
| Nepal | 1 |
| Philippines | 1 |
| Sri Lanka | 1 |
| Total | 7818 |
Recommendations and Advice
During previous outbreaks due to other coronaviruses (Middle-East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), human-to-human transmission occurred through droplets, contact, and fomites, suggesting that the transmission mode of the 2019-nCoV can be similar. The basic principles to reduce the general risk of transmission of acute respiratory infections include the following:
- Avoiding close contact with people suffering from acute respiratory infections.
- Frequent hand-washing, especially after direct contact with ill people or their environment.
- Avoiding unprotected contact with farm or wild animals.
- People with symptoms of acute respiratory infection should practice cough etiquette (maintain distance, cover coughs and sneezes with disposable tissues or clothing, and wash hands).
- Within healthcare facilities, enhance standard infection prevention and control practices in hospitals, especially in emergency departments.
WHO does not recommend any specific health measures for travelers. In case of symptoms suggestive of respiratory illness either during or after travel, travelers are encouraged to seek medical attention and share their travel history with their healthcare provider.


Be the first to comment on "Confirmed Coronavirus Cases Climb to 7818 Globally – 170 Deaths in China"