Note: There is now a newer Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report 18.
WHO Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report 17
- No new countries reported cases of 2019-nCoV in the past 24 hours.
- WHO is working with partners to strengthen global diagnostic capacity for 2019-nCoV detection to improve surveillance and track the spread of disease. WHO and partners have activated a network of specialized referral laboratories with demonstrated expertise in the molecular detection of coronaviruses. These international labs can support national labs to confirm new cases and troubleshoot their molecular assays.
- WHO is convening a global research and innovation forum to mobilize international action in response to the new coronavirus, covering a broad spectrum of research areas including epidemiology, clinical care, vaccines, therapeutics, diagnostics, animal health, social sciences, and other topics.
Risk Assessment
China: Very High
Regional Level: High
Global Level: High
Coronavirus Situation in Numbers
Globally
- 28276 confirmed (3722 new)
China
- 28060 confirmed (3697 new)
- 3859 severe (640 new)
- 564 deaths (73 new)
Outside of China
- 216 confirmed (25 new)
- 24 countries (0 new)
- 1 death (0 new)
Technical Focus: Establishing global/regional coordination and technical guidance
WHO is working with partners to strengthen global diagnostic capacity for 2019-nCoV detection to improve surveillance and track the spread of disease. Public health efforts to control the spread of disease in countries with imported cases depend critically on the ability to detect the pathogen quickly. WHO and partners have activated a network of specialized referral laboratories with demonstrated expertise in the molecular detection of coronaviruses. These international labs can support national labs to confirm new cases and troubleshoot their molecular assays.
Currently, there are 15 laboratories have been identified to provide reference testing support for 2019-nCoV. These laboratories include:
- Armed Forces Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Thailand
- Erasmus Medical Center, The Netherlands
- Hong Kong University, Hong Kong SAR, China
- Institute of Tropical Medicine, Nagasaki University, Japan
- Institute of Virology, Charité, Robert Koch Institute, Germany
- National Institute for Communicable Diseases, South Africa
- National Institute of Health, Thailand
- National Institute of Virology, India
- National Public Health Laboratory, Singapore
- Institut Pasteur Dakar, Senegal
- Institut Pasteur, Paris
- Public Health England, UK
- State Research Center for Virology and Biotechnology, VectorInstitute, Russia
- United States Center for Disease Control and Prevention, USA
- Victorian Infectious Diseases Reference Laboratory, Australia
WHO is working to ensure 2019-nCoV test availability, including: a) screening of 2019-nCoV PCR protocols from academic laboratories for validation data,b) evaluation of the potential to use existing commercial coronavirus assays (e.g. SARS-CoV) to detect 2019-nCoV with high sensitivity, and c) working with commercial and non-commercial agencies with capacity to manufacture and distribute newly-developed 2019-nCoV PCR assays. To increase regional testing capacity, efforts to increase national capacity and provide regional reference laboratory support is ongoing. WHO has made 250,000 tests available to WHO Regional Offices and national laboratories. These tests are being shipped to 159 laboratories across all WHO regions.
WHO will also utilize the Shipping Fund Programme established by the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System as a mechanism to send clinical samples from patients meeting the case definition of suspected 2019-nCoV infection to international referral laboratories.
National capacity for detection of 2019-nCoV must be strengthened so that diagnostic testing can be performed rapidly without the need for overseas shipping. One way this will be achieved is by working with existing global networks for detection of respiratory pathogens, such as National Influenza Centres.
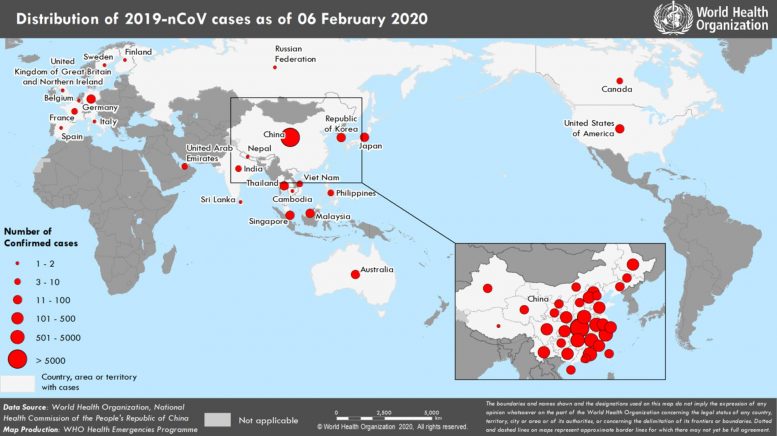
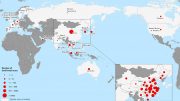
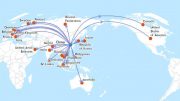
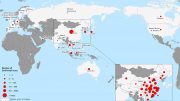
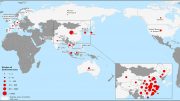
Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV, February 6, 2020
| Country/Territory/Area | Confirmed Cases |
|---|---|
| China | 28060 |
| Singapore | 28 |
| Japan | 25 |
| Thailand | 25 |
| Republic of Korea | 23 |
| International (Cruise Ship in Japan) | 20 |
| Australia | 14 |
| Germany | 12 |
| Malaysia | 12 |
| United States of America | 12 |
| Vietnam | 10 |
| France | 6 |
| Canada | 5 |
| United Arab Emirates | 5 |
| India | 3 |
| Philippines | 3 |
| Italy | 2 |
| Russian Federation | 2 |
| United Kingdom | 2 |
| Belgium | 1 |
| Cambodia | 1 |
| Finland | 1 |
| Nepal | 1 |
| Spain | 1 |
| Sri Lanka | 1 |
| Sweden | 1 |
| Total | 28276 |
Recommendations and Advice for the Public
During previous outbreaks due to other coronaviruses (Middle-East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), human-to-human transmission occurred through droplets, contact, and fomites, suggesting that the transmission mode of the 2019-nCoV can be similar. The basic principles to reduce the general risk of transmission of acute respiratory infections include the following:
- Avoiding close contact with people suffering from acute respiratory infections.
- Frequent hand-washing, especially after direct contact with ill people or their environment.
- Avoiding unprotected contact with farm or wild animals.
- People with symptoms of acute respiratory infection should practice cough etiquette (maintain distance, cover coughs and sneezes with disposable tissues or clothing, and wash hands).
- Within healthcare facilities, enhance standard infection prevention and control practices in hospitals, especially in emergency departments.
WHO does not recommend any specific health measures for travelers. In case of symptoms suggestive of respiratory illness either during or after travel, travelers are encouraged to seek medical attention and share their travel history with their healthcare provider.


Be the first to comment on "Coronavirus Death Toll Reaches 565 As Outbreak Grows to 28,276 Confirmed Cases"