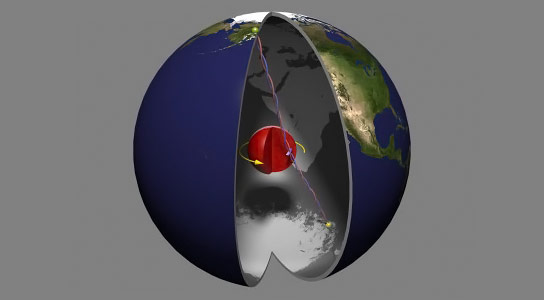
Scientists found that the Earth’s inner core not only spins at a different rate than the mantle (the layer between the core and the crust), but its speed of rotation can vary. Credit: Australian National University
A newly published study provides the first experimental evidence that the Earth’s inner core has rotated at a variety of different speeds and suggests that the Earth’s solid inner core rotates at a different rate than the mantle.
We all know that the Earth rotates beneath our feet, but new research from ANU has revealed that the center of the Earth is out of sync with the rest of the planet, frequently speeding up and slowing down.
Associate Professor Hrvoje Tkalcic from the ANU College of Physical and Mathematical Sciences and his team used earthquake doublets to measure the rotation speed of Earth’s inner core over the last 50 years.
They discovered that not only did the inner core rotate at a different rate to the mantle – the layer between the core and the crust that makes up most of the planet’s interior – but its rotation speed was variable.
“This is the first experimental evidence that the inner core has rotated at a variety of different speeds,” Associate Professor Tkalcic said.
“We found that, compared with the mantle, the inner core was rotating more quickly in the 1970s and 1990s, but slowed down in the 80s. The most dramatic acceleration has possibly occurred in the last few years, although further tests are needed to confirm that observation.
“Interestingly, Edmund Halley, namesake of Halley’s Comet, speculated that the inner shells of the Earth rotate with a different speed back in 1692.”
Scientists have so far assumed the rotation rate of the inner core to be constant because they lacked adequate mathematical methods for interpreting the data, says Associate Professor Tkalcic. A new method applied to earthquake doublets – pairs of almost identical earthquakes that can occur a couple of weeks to 30 or 40 years apart – has provided the solution.
“It’s stunning to see that even 10, 20, or 30 years apart, these earthquakes look so similar. But each pair differs very slightly, and that difference corresponds to the inner core. We have been able to use that small difference to reconstruct a history of how the inner core has rotated over the last 50 years,” he said.
Associate Professor Tkalcic says this new method could help us understand the role of the inner core in creating the magnetic field that allowed life to evolve on Earth by acting as a shield from cosmic radiation.
“What we have developed is a very powerful way to understand the internal structure and dynamics of our planet,” he said.
The research was published in Nature Geoscience.
Reference: “The shuffling rotation of the Earth’s inner core revealed by earthquake doublets” by Hrvoje Tkalčić, Mallory Young, Thomas Bodin, Silvie Ngo and Malcolm Sambridge, 12 May 2013, Nature Geoscience.
DOI: 10.1038/ngeo1813





Be the first to comment on "Earthquake Doublets Reveal Changing Speed of the Earth’s Inner Core"